Korean J Gastroenterol.
2020 Sep;76(3):134-141. 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.3.134.
Endoscopic Prediction for Acid Reflux in Patients without Hiatus Hernia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Biostatistics and Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research Institute for Future Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2506669
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.76.3.134
Abstract
- Background/Aims
A diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease is challenging in patients who have reflux symptoms but do not respond to proton pump inhibitors nor have reflux esophagitis and hiatal hernia (HH) on endoscopy. This study examined the predictive role of the endoscopic findings, including the flap valve grade for pathologic acid exposure (PAE) to establish an endoscopic prediction model in patients with neither reflux esophagitis nor HH.
Methods
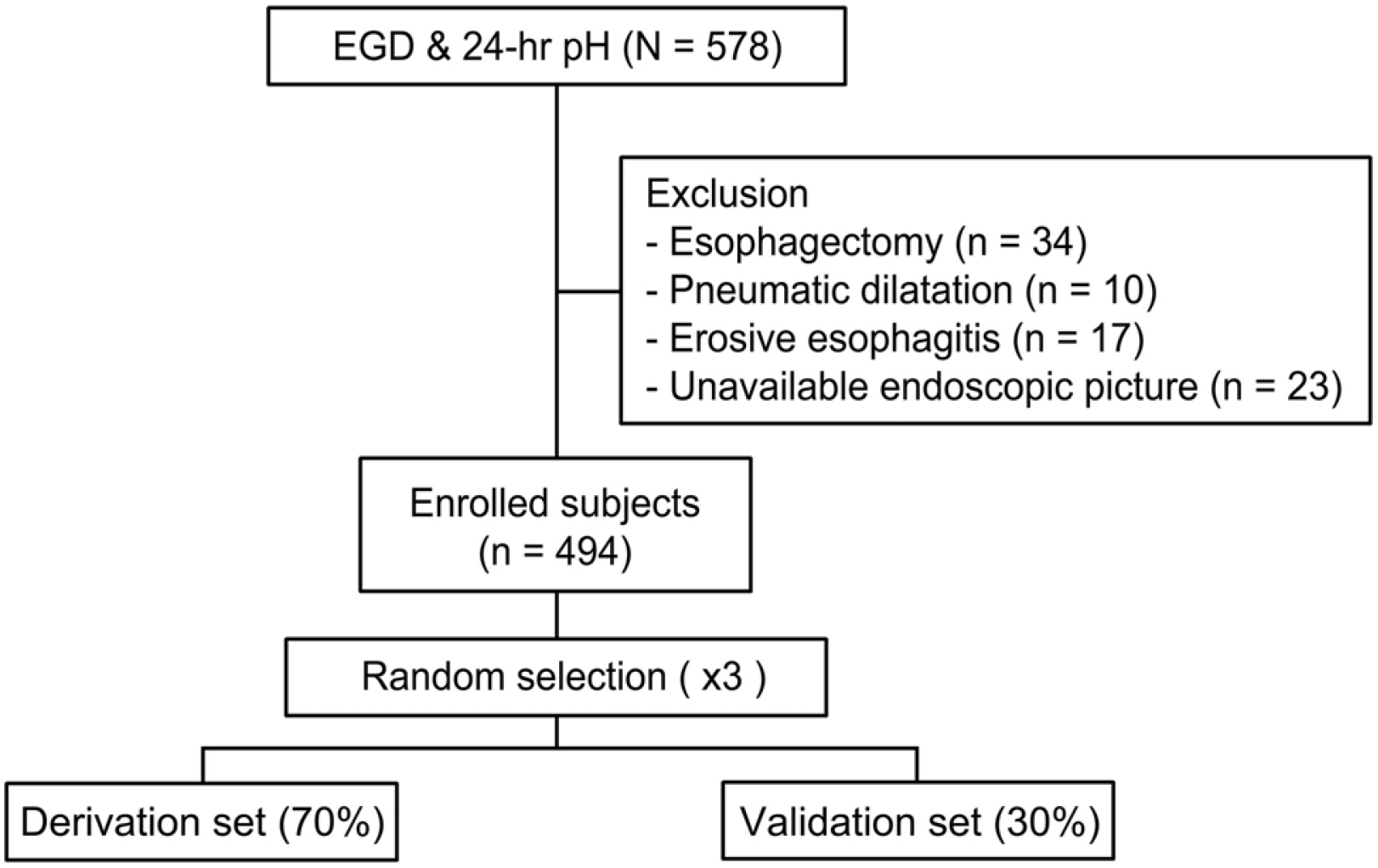
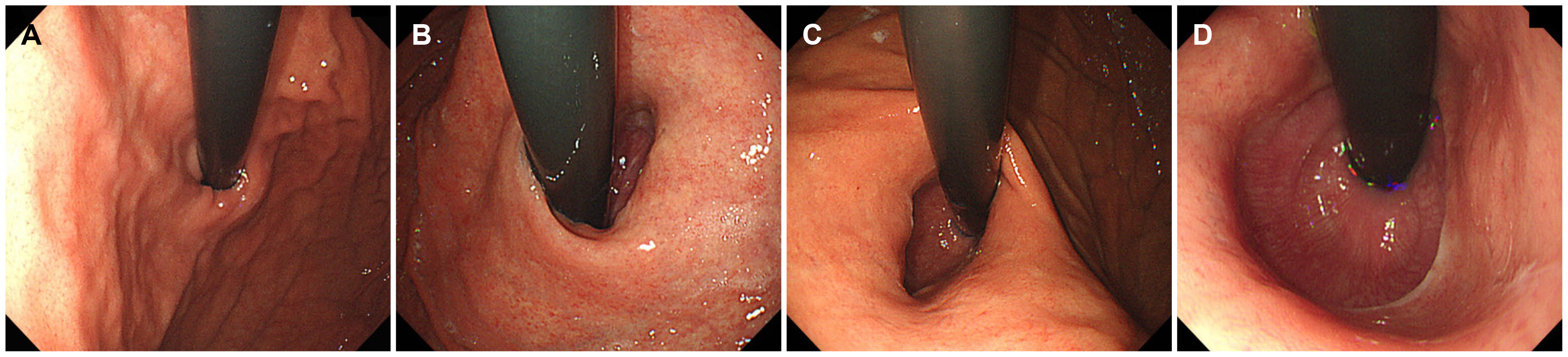
Five hundred seventy-eight patients who underwent upper endoscopy and 24 hours pH monitoring for reflux esophageal symptoms without evidence of reflux esophagitis and HH were analyzed. The gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV), esophageal metaplasia, and chronic atrophic gastritis were assessed. The association between the endoscopic parameters and PAE was evaluated.
Results
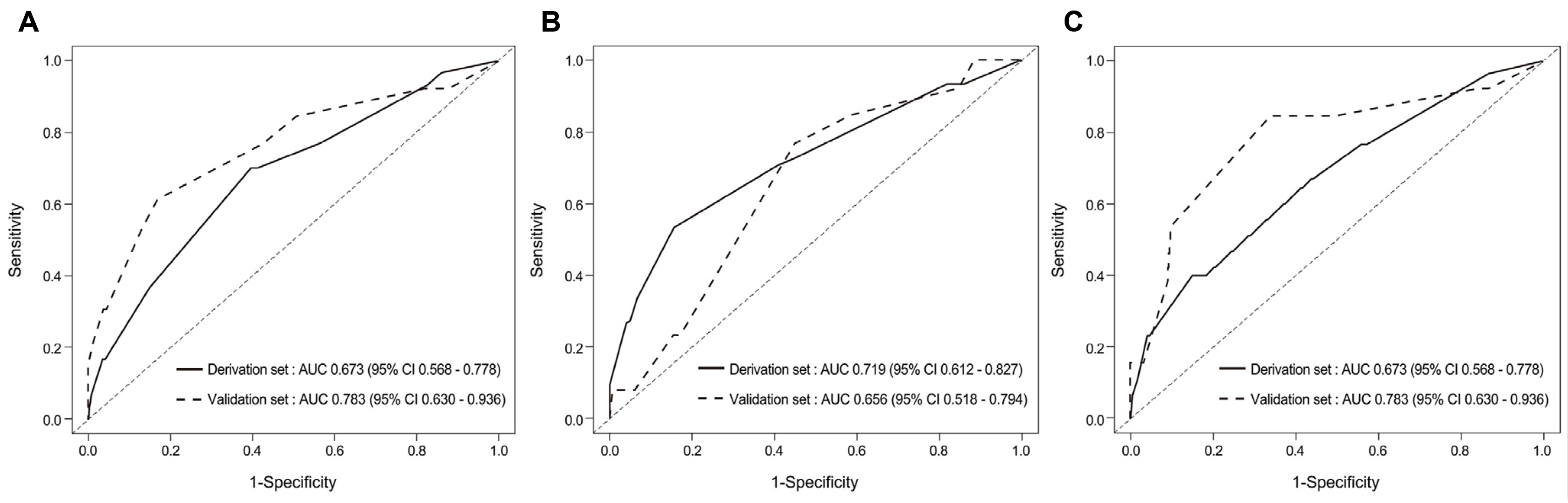
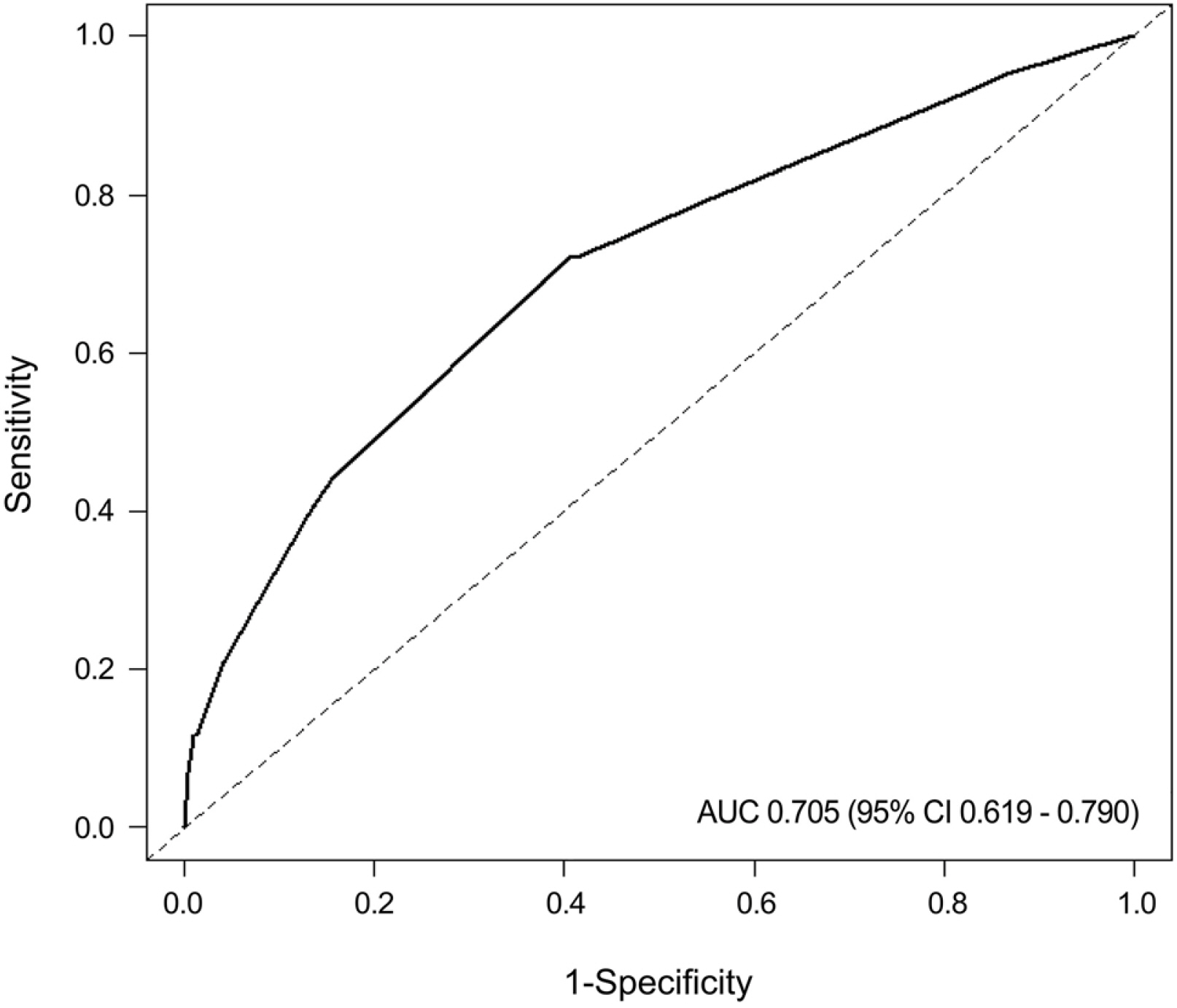
Four hundred ninety-four patients were enrolled. The most common complaint was chest discomfort (42.3%) followed by globus (31.8%), dysphagia (7.9%), and heartburn (7.7%). PAE was present in 43 patients (8.7%). Multivariable analysis revealed PAE to be associated with the GEFV grade (p<0.001) and inversely associated with the chronic atrophic gastritis grade (p=0.005). Using these features, a predictive model was established and showed an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.705 (95% CI 0.619-0.790). The cutoff value of 12.0 had a sensitivity and specificity of 44.0% and 84.0%, respectively.
Conclusions
A loosened GEFV is associated with a risk of PAE in patients with neither reflux esophagitis nor HH, while atrophic gastritis is preventive. On the other hand, the endoscopic predictive model revealed a low sensitivity for detecting PAE. Thus, reflux testing needs to be performed further when gastroesophageal reflux disease is suspected, even without endoscopic evidence.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hershcovici T, Fass R. 2013; Step-by-step management of refractory gastresophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus. 26:27–36. DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01322.x. PMID: 22309405.
Article2. Boeckxstaens G, El-Serag HB, Smout AJ, Kahrilas PJ. 2014; Symptomatic reflux disease: the present, the past and the future. Gut. 63:1185–1193. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306393. PMID: 24607936. PMCID: PMC4078752.
Article3. Kahrilas PJ, Boeckxstaens G, Smout AJ. 2013; Management of the patient with incomplete response to PPI therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 27:401–414. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2013.06.005. PMID: 23998978. PMCID: PMC3761380.
Article4. Herregods TV, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. 2015; Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease: new understanding in a new era. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 27:1202–1213. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12611. PMID: 26053301.
Article5. van Herwaarden MA, Samsom M, Smout AJ. 2000; Excess gastroesophageal reflux in patients with hiatus hernia is caused by mechanisms other than transient LES relaxations. Gastroenterology. 119:1439–1446. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2000.20191. PMID: 11113064.
Article6. Dodds WJ, Dent J, Hogan WJ, et al. 1982; Mechanisms of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with reflux esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 307:1547–1552. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198212163072503. PMID: 7144836.
Article7. Bredenoord AJ, Pandolfino JE, Smout AJ. 2013; Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet. 381:1933–1942. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62171-0. PMID: 23477993.
Article8. Curcic J, Roy S, Schwizer A, et al. 2014; Abnormal structure and function of the esophagogastric junction and proximal stomach in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 109:658–667. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2014.25. PMID: 24589669.
Article9. Park CH, Kim KO, Baek IH, et al. 2014; Differences in the risk factors of reflux esophagitis according to age in Korea. Dis Esophagus. 27:116–121. DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01417.x. PMID: 23009198. PMCID: PMC6543060.
Article10. Kim GH, Song GA, Kim TO, et al. 2008; Endoscopic grading of gastroesophageal flap valve and atrophic gastritis is helpful to predict gastroesophageal reflux. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:208–214. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05038.x. PMID: 18289353.
Article11. Cheong JH, Kim GH, Lee BE, et al. 2011; Endoscopic grading of gastroesophageal flap valve helps predict proton pump inhibitor response in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 46:789–796. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2011.579154. PMID: 21615222.
Article12. Mittal RK, Balaban DH. 1997; The esophagogastric junction. N Engl J Med. 336:924–932. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199703273361306. PMID: 9070474. PMCID: PMC7490797.
Article13. Koch OO, Spaun G, Antoniou SA, et al. 2013; Endoscopic grading of the gastroesophageal flap valve is correlated with reflux activity and can predict the size of the esophageal hiatus in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc. 27:4590–4595. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-013-3071-8. PMID: 23846367.
Article14. Patti MG, Goldberg HI, Arcerito M, Bortolasi L, Tong J, Way LW. 1996; Hiatal hernia size affects lower esophageal sphincter function, esophageal acid exposure, and the degree of mucosal injury. Am J Surg. 171:182–186. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(99)80096-8. PMID: 8554137.
Article15. Kim DH, Kim GH, Kim JY, et al. 2007; Endoscopic grading of atrophic gastritis is inversely associated with gastroesophageal reflux and gastropharyngeal reflux. Korean J Intern Med. 22:231–236. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2007.22.4.231. PMID: 18309680. PMCID: PMC2687671.
Article16. Kimura K, Satoh K, Ido K, Taniguchi Y, Takimoto T, Takemoto T. 1996; Gastritis in the Japanese stomach. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 214:17–23. DOI: 10.3109/00365529609094509. PMID: 8722400.
Article17. Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, et al. 2006; The development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for Barrett's esophagus: the Prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology. 131:1392–1399. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.032. PMID: 17101315.18. Shay S, Tutuian R, Sifrim D, et al. 2004; Twenty-four hour ambulatory simultaneous impedance and pH monitoring: a multicenter report of normal values from 60 healthy volunteers. Am J Gastroenterol. 99:1037–1043. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04172.x. PMID: 15180722.
Article19. Kayaoglu HA. 2013; Correlation of the gastroesophageal flap valve grade with the surgery rate in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc. 27:801–807. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-012-2515-x. PMID: 23052497.
Article20. Lin BR, Wong JM, Chang MC, et al. 2006; Abnormal gastroesophageal flap valve is highly associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease among subjects undergoing routine endoscopy in Taiwan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:556–562. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04003.x. PMID: 16638098.
Article21. Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, et al. 1996; The gastroesophageal flap valve: in vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc. 44:541–547. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(96)70006-8. PMID: 8934159.
Article22. Xia HH, Talley NJ. 1998; Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and atrophic gastritis: an unexplored triangle. Am J Gastroenterol. 93:394–400. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00394.x. PMID: 9517647.
Article23. Koike T, Ohara S, Sekine H, et al. 1999; Helicobacter pylori infection inhibits reflux esophagitis by inducing atrophic gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 94:3468–3472. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01593.x. PMID: 10606305.
Article24. Koike T, Ohara S, Sekine H, et al. 2001; Helicobacter pylori infection prevents erosive reflux oesophagitis by decreasing gastric acid secretion. Gut. 49:330–334. DOI: 10.1136/gut.49.3.330. PMID: 11511552. PMCID: PMC1728422.
Article25. Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K, Shiba M, et al. 2003; Association between gastroesophageal flap valve, reflux esophagitis, Barrett's epithelium, and atrophic gastritis assessed by endoscopy in Japanese patients. J Gastroenterol. 38:533–539. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-002-1100-9. PMID: 12825128.
Article26. Ott DJ, Gelfand DW, Wu WC, Castell DO. 1984; Esophagogastric region and its rings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 142:281–287. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.142.2.281. PMID: 6364745.
Article27. Sloan S, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. 1992; Determinants of gastroesophageal junction incompetence: hiatal hernia, lower esophageal sphincter, or both? Ann Intern Med. 117:977–982. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-12-977. PMID: 1443984.
Article28. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Savarino V. 2013; NERD: an umbrella term including heterogeneous subpopulations. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:371–380. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.50. PMID: 23528345.
Article29. Masiak W, Wallner G, Wallner J, Pedowski T, Solecki M. 2011; Combined esophageal multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring (MII -pH) in the diagnostics and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease and its complications. Pol Przegl Chir. 83:488–496. DOI: 10.2478/v10035-011-0076-7. PMID: 22166737.
Article30. Khan MQ, Alaraj A, Alsohaibani F, Al-Kahtani K, Jbarah S, Al-Ashgar H. 2014; Diagnostic utility of impedance-pH monitoring in refractory non-erosive reflux disease. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 20:497–505. DOI: 10.5056/jnm14038. PMID: 25273120. PMCID: PMC4204403.
Article31. Hershcovici T, Fass R. 2010; Nonerosive reflux disease (NERD) - an update. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 16:8–21. DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2010.16.1.8. PMID: 20535321. PMCID: PMC2879816.
Article32. Shi Y, Tan N, Zhang N, et al. 2016; Predictors of proton pump inhibitor failure in non-erosive reflux disease: a study with impedance-pH monitoring and high-resolution manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 28:674–679. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12763. PMID: 26768192.
Article