Korean J Sports Med.
2020 Sep;38(3):129-136. 10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.3.129.
Comparison of Effects of Acute Tabata-Styled and Moderate Intensity Continuous Exercise on Vascular Function in Healthy Young Men
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Sport Science, University of Seoul, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2506069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.3.129
Abstract
- Purpose
Regular moderate-intensity aerobic exercise confers immense vascular benefits, yet the lack of time remains the most common barrier to a regular exercise routine. A Tabata exercise is a type of high-intensity interval training exercise that is time efficient and has recently been demonstrated to improve cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolic profiles, but its benefits on vascular function still remain unclear. We tested the hypothesis that the Tabata-styled exercise would be as effective as moderate-intensity continuous exercise (MICE) in improving vascular function in young healthy adults.
Methods
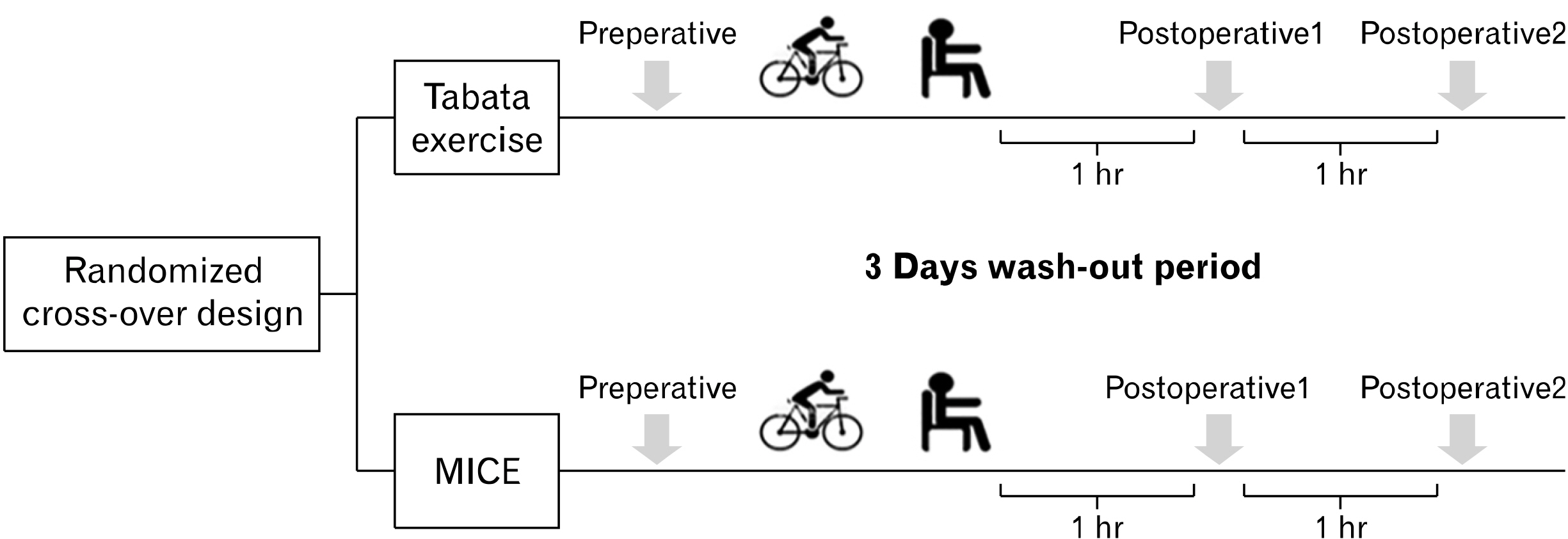
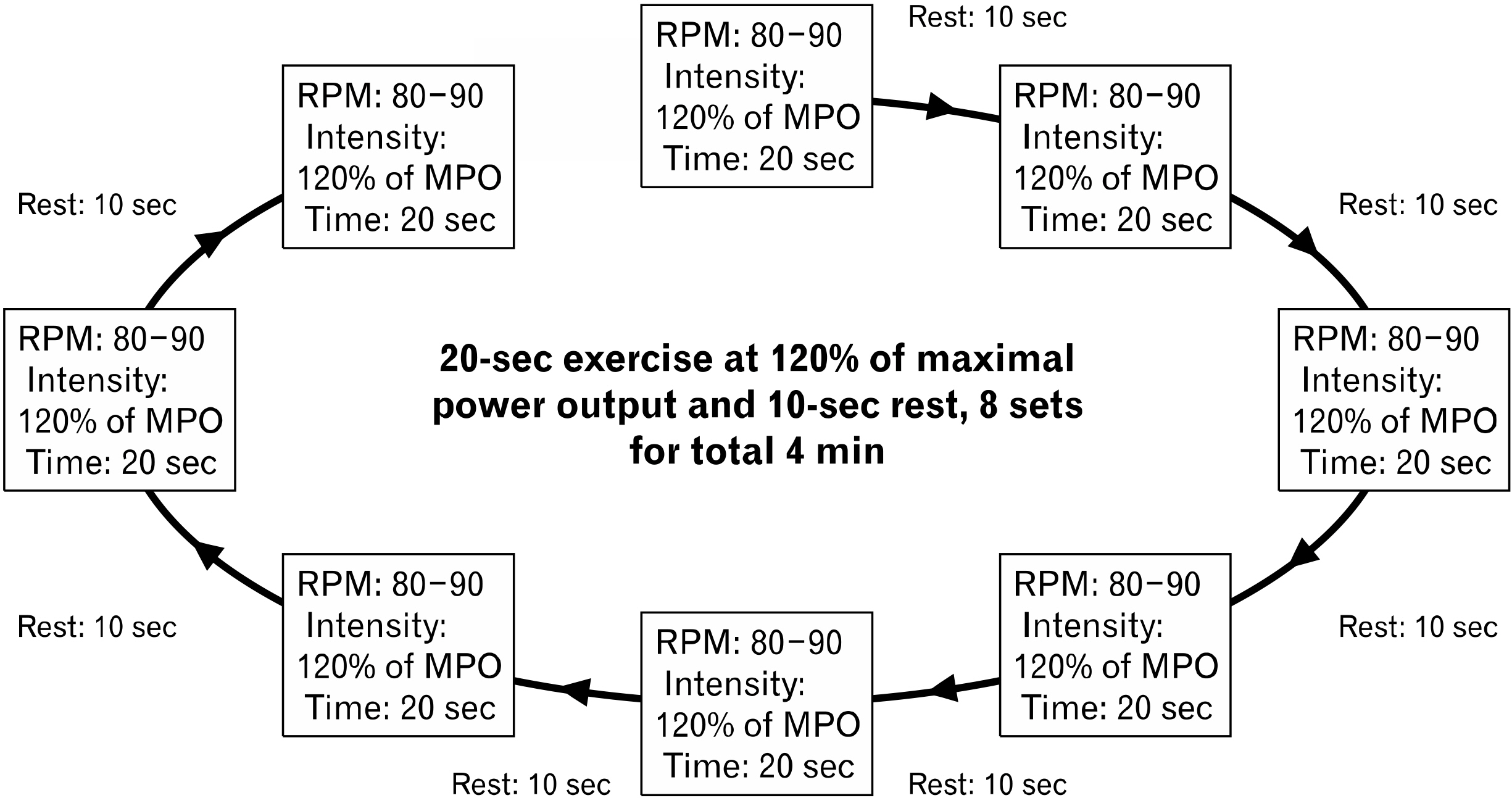
Using a randomized, cross-over design, fourteen healthy men (age, 23.8±2.3 years; body mass index, 23.7±2.2 kg/m2 ) performed two acute exercise trials, separated at least by 72 hours: a modified Tabata-styled exercise (eight sets of 20-second exercise at 120% of maximal power output using a bike and 10-second rest, total 4 minutes) or a MICE for 30 minutes at a heart rate reserve of 40%–60%. Vascular function was assessed via brachial artery flow-mediated dilation and arterial stiffness (pulse wave velocity and augmentation index) at baseline and again at 60 minutes and 120 minutes after exercise.
Results
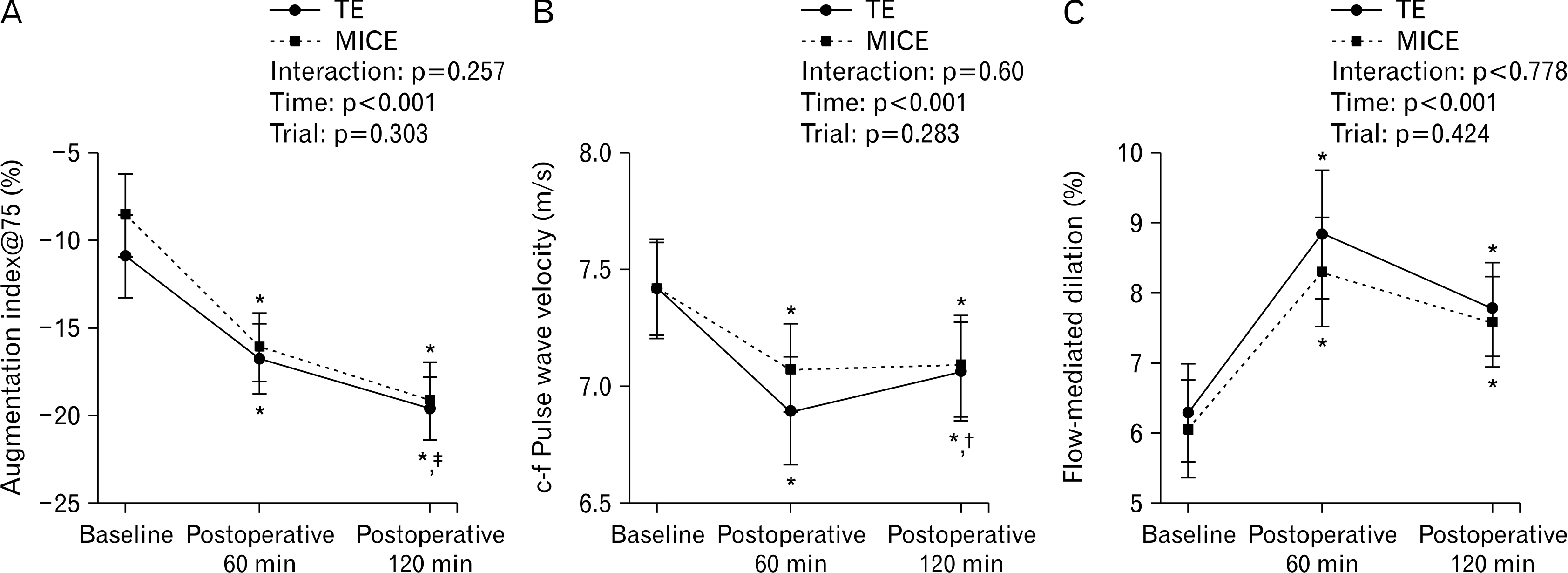
Compared with MICE, a Tabata-styled exercise increased heart rate at 60 minutes (p< 0.05). Both exercises improved vascular function to a similar extent, as evidenced by an increase in flow-mediated dilation and a reduction in arterial stiffness at 60 minutes and 120 minutes (p< 0.05).
Conclusion
These findings demonstrate that the Tabata-styled exercise is a time-efficient exercise strategy that is as effective as MICE in enhancing vascular function in healthy young men.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Piercy KL, Troiano RP, Ballard RM, et al. 2018; The physical activity guidelines for Americans. JAMA. 320:2020–8. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.14854. PMID: 30418471.
Article2. Kim YS. 2012. Development of physical activity guidelines and self-prescription guides for Korean. Korea Health Promotion Institute;Seoul:3. Ministry of Health and Welfare; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018. Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey. Korea Centers for Disease Control;Cheongju:4. Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism. 2017. Survey on the participation in national sports for all. Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism;Sejong:5. Weston KS, Wisloff U, Coombes JS. 2014; High-intensity interval training in patients with lifestyle-induced cardiometabolic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 48:1227–34. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092576. PMID: 24144531.
Article6. Tabata I, Nishimura K, Kouzaki M, et al. 1996; Effects of moderate-intensity endurance and high-intensity intermittent training on anaerobic capacity and VO2max. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 28:1327–30. DOI: 10.1097/00005768-199610000-00018. PMID: 8897392.
Article7. Chuensiri N, Suksom D, Tanaka H. 2018; Effects of high-intensity intermittent training on vascular function in obese preadolescent boys. Child Obes. 14:41–9. DOI: 10.1089/chi.2017.0024. PMID: 29099231.
Article8. Chuensiri N, Tanaka H, Suksom D. 2015; The acute effects of supramaximal high-intensity intermittent exercise on vascular function in lean vs. obese prepubescent boys. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 27:503–9. DOI: 10.1123/pes.2015-0100. PMID: 26252080.
Article9. Olson M. 2014; TABATA: It's a HIIT! ACSMs Health Fit J. 18:17–24. DOI: 10.1249/FIT.0000000000000065.10. Myers J, Bellin D. 2000; Ramp exercise protocols for clinical and cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Sports Med. 30:23–9. DOI: 10.2165/00007256-200030010-00003. PMID: 10907755.
Article11. Roditis P, Dimopoulos S, Sakellariou D, et al. 2007; The effects of exercise training on the kinetics of oxygen uptake in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 14:304–11. DOI: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e32808621a3. PMID: 17446812.
Article12. Mitchell GF. 2014; Arterial stiffness and hypertension: chicken or egg? Hypertension. 64:210–4. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03449. PMID: 24799614. PMCID: PMC4185002.13. Van Bortel LM, Duprez D, Starmans-Kool MJ, et al. 2002; Clinical applications of arterial stiffness, Task Force III: recommendations for user procedures. Am J Hypertens. 15:445–52. DOI: 10.1016/S0895-7061(01)02326-3. PMID: 12022247.
Article14. Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Bull C, Robinson J, Deanfield JE. 1994; Endothelium-dependent dilation in the systemic arteries of asymptomatic subjects relates to coronary risk factors and their interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 24:1468–74. DOI: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90141-4. PMID: 7930277.
Article15. Rakobowchuk M, Stuckey MI, Millar PJ, Gurr L, Macdonald MJ. 2009; Effect of acute sprint interval exercise on central and peripheral artery distensibility in young healthy males. Eur J Appl Physiol. 105:787–95. DOI: 10.1007/s00421-008-0964-7. PMID: 19125283.
Article16. Lauer MS. 2003; Is heart rate recovery a modifiable risk factor? J Cardiopulm Rehabil. 23:88–9. DOI: 10.1097/00008483-200303000-00003. PMID: 12668928.
Article17. Segan R, Gupta V, Walia L, Mittal N. 2013; Rate pressure product predicts cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetics with cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol. 3:43–7. DOI: 10.5455/njppp.2013.3.43-47.
Article18. Hinderliter A, Miller P, Bragdon E, Ballenger M, Sheps D. 1991; Myocardial ischemia during daily activities: the importance of increased myocardial oxygen demand. J Am Coll Cardiol. 18:405–12. DOI: 10.1016/0735-1097(91)90593-X. PMID: 1856408.
Article19. Rakobowchuk M, Tanguay S, Burgomaster KA, Howarth KR, Gibala MJ, MacDonald MJ. 2008; Sprint interval and traditional endurance training induce similar improvements in peripheral arterial stiffness and flow-mediated dilation in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 295:R236–42. DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00069.2008. PMID: 18434437. PMCID: PMC2494806.
Article20. Zhong Q, Hu MJ, Cui YJ, et al. 2018; Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity in the prediction of cardiovascular events and mortality: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Angiology. 69:617–29. DOI: 10.1177/0003319717742544. PMID: 29172654.
Article21. Inaba Y, Chen JA, Bergmann SR. 2010; Prediction of future cardiovascular outcomes by flow-mediated vasodilatation of brachial artery: a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 26:631–40. DOI: 10.1007/s10554-010-9616-1. PMID: 20339920.
Article22. Adams V. 2018; CrossTalk proposal: acute exercise elicits damage to the endothelial layer of systemic blood vessels in healthy individuals. J Physiol. 596:537–9. DOI: 10.1113/JP274750. PMID: 29355949. PMCID: PMC5813617.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Concepts Change of Exercise Intensity for Obesity
- Effects of Short-term Repeated Sprint Exercise Training and Moderate Intensity Continuous Exercise Training on Vascular Function in Healthy Young Adults
- Changes in Functional Connectivity Between Default Mode Network and Attention Network in Response to Changes in Aerobic Exercise Intensity
- Effects of Acute Resistance Exercise on Arterial Stiffness in Young Men
- Differences in Body Weight, Dietary Efficiency, Brain Obesity Control Factor (AMPK), Reactive Oxygen Species (MDA), and Antioxidant Enzymes (SOD) in Young Mice According to the Intensity of Aerobic Exercise for 8 Weeks