Korean J Gastroenterol.
2020 Jul;76(1):49-51. 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.1.49.
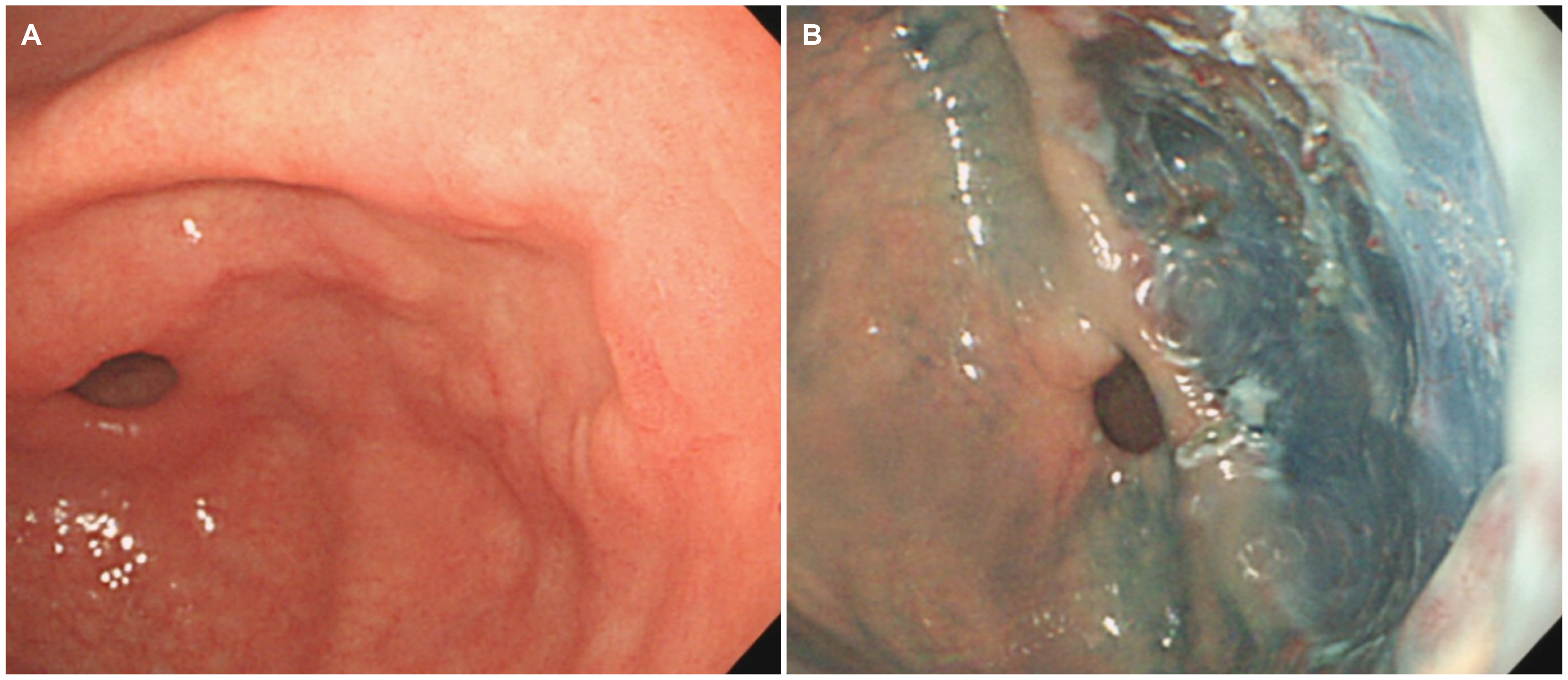
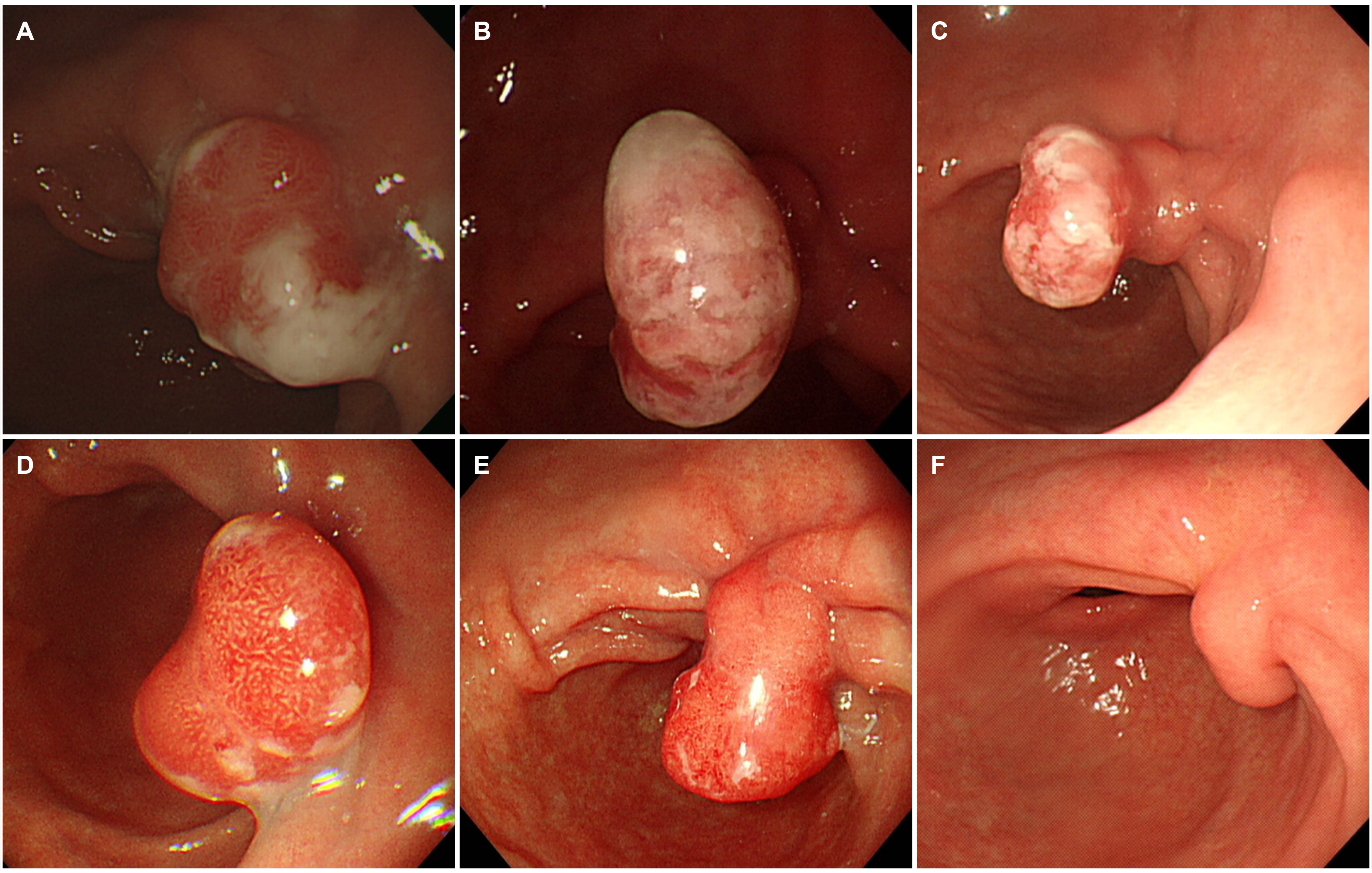
Regression of a Large Hyperplastic Polyp after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoungnam, Korea
- KMID: 2504595
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.76.1.49
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stolte M, Sticht T, Eidt S, Ebert D, Finkenzeller G. 1994; Frequency, location, and age and sex distribution of various types of gastric polyp. Endoscopy. 26:659–665. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1009061. PMID: 7859674.
Article2. Shaib YH, Rugge M, Graham DY, Genta RM. 2013; Management of gastric polyps: an endoscopy-based approach. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:1374–1384. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.03.019. PMID: 23583466. PMCID: PMC3962745.
Article3. Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard DM, Walker MM, Warren B. British Society of Gastroenterology. 2010; The management of gastric polyps. Gut. 59:1270–1276. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2009.182089. PMID: 20675692.
Article4. Ji F, Wang ZW, Ning JW, Wang QY, Chen JY, Li Y. 2006; Effect of drug treatment on hyperplastic gastric polyps infected with Helicobacter pylori: a randomized, controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. 12:1770–1773. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1770. PMID: 16586550. PMCID: PMC4124356.
Article5. Nam SY, Park BJ, Ryu KH, Nam JH. 2016; Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on the fate of gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:449–454. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000553. PMID: 26735158.
Article6. Asaka M, Kato M, Takahashi S, et al. 2010; Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: 2009 revised edition. Helicobacter. 15:1–20. DOI: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2009.00738.x. PMID: 20302585.7. Nam SY, Park BJ, Ryu KH, Nam JH. 2018; Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the regression of gastric polyps in National Cancer Screening Program. Korean J Intern Med. 33:506–511. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.286. PMID: 29232943. PMCID: PMC5943657.
Article8. Lim SA, Yun JW, Yoon D, et al. 2011; Regression of hyperplastic gastric polyp after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 42:74–82.9. Kang KH, Hwang SH, Kim D, et al. 2018; The effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on recurrence of gastric hyperplastic polyp after endoscopic removal. Korean J Gastroenterol. 71:213–218. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2018.71.4.213. PMID: 29684970.10. Nam SY, Lee SW, Jeon SW, Kwon YH, Lee HS. Helicobacter pylori eradication regressed gastric hyperplastic polyp: a randomized controlled trial. Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Jan 23. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06065-0.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the regression of gastric polyps in National Cancer Screening Program
- Helicobacter pylori Eradication and Gastric Cancer Prevention
- Regression of Hyperplastic Gastric Polyp after Helicobacter pylori Eradication
- The Effect of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Recurrence of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyp after Endoscopic Removal
- Change in Size of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps after Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Prospective Study