Intest Res.
2020 Jul;18(3):289-296. 10.5217/ir.2019.00073.
Presentation and outcomes among inflammatory bowel disease patients with concurrent pneumatosis intestinalis: a case series and systematic review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, North Shore University Hospital and Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Manhasset, NY, USA
- 2Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, NY, USA
- 3Department of Medicine, North Shore University Hospital and Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Manhasset, NY, USA
- 4Department of Radiology, North Shore University Hospital and Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Manhasset, NY, USA
- 5Division of Gastroenterology, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY, USA
- KMID: 2504584
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2019.00073
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) involves chronic inflammation of the colon with ulcerative colitis (UC), and the colon and/or small intestine with Crohn’s disease (CD). Pneumatosis intestinalis (PI), characterized by compromise of the intestinal wall with gas-filled cysts, has rarely been reported with IBD. The presentation, best management and outcomes of PI with IBD are poorly defined.
Methods
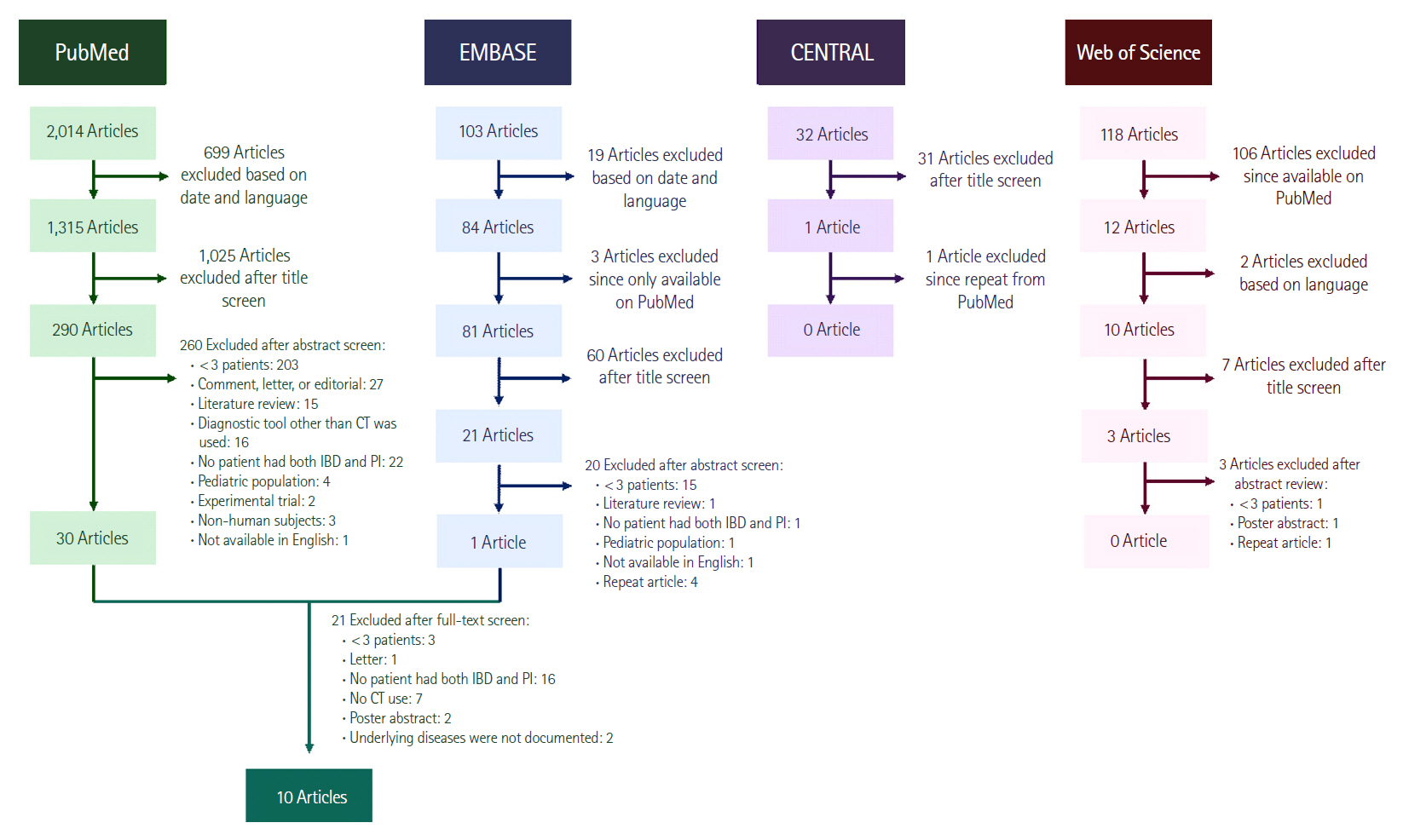
We conducted a search for PI in all abdominal computed tomography (CT) reports at 2 large tertiary care hospitals from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2017, cross referenced to ICD codes for IBD. CT and chart review was performed to confirm PI and IBD respectively. A systematic review excluding case reports was performed for PI with IBD for comparison.
Results
Of 5,990 patients with a CT abdomen report mentioning PI, we identified 11 cases of PI with IBD, 4 UC, 6 CD, and 1 indeterminate colitis. PI was limited to the small bowel in 5 patients, the right colon in 5, and small bowel and colonic in 1. All 3 mortalities had CD, small intestinal PI and portal/mesenteric venous gas. The systematic literature search identified 9 articles describing 58 patients with IBD and PI. These cases were mostly included in larger cohorts of PI patients without extractable data on presentation or outcomes in the IBD subpopulation.
Conclusions
Ours appears to be the first reporting of presentations and outcomes, outside of case reports, for those with PI and IBD. The high mortality for those with CD and PI of the small bowel appears to define a group requiring more than supportive medical care.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Loftus EV Jr. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1504–1517.
Article2. Malik TA. Inflammatory bowel disease: historical perspective, epidemiology, and risk factors. Surg Clin North Am. 2015; 95:1105–1122.3. Abraham C, Cho JH. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2066–2078.
Article4. Friedman S, Blumberg RS. Inflammatory bowel disease. In : Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. New York: McGraw-Hill;2014. p. 351–353.5. Wedlake L, Slack N, Andreyev HJ, Whelan K. Fiber in the treatment and maintenance of inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014; 20:576–586.6. Wald A. Pneumatosis coli (pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis). In : Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, editors. Sleisenger and Fordtran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;2016. p. 2306–2308.7. Galandiuk S, Fazio VW, Petras RE. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in Crohn’s disease: report of two cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985; 28:951–956.8. Ho LM, Paulson EK, Thompson WM. Pneumatosis intestinalis in the adult: benign to life-threatening causes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:1604–1613.
Article9. Yale CE, Balish E, Wu JP. The bacterial etiology of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Arch Surg. 1974; 109:89–94.
Article10. Maizlin ZV, Vos PM. Do we really need to thank the Beatles for the financing of the development of the computed tomography scanner? J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2012; 36:161–164.
Article11. John A, Dickey K, Fenwick J, Sussman B, Beeken W. Pneumatosis intestinalis in patients with Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1992; 37:813–817.
Article12. Wayne E, Ough M, Wu A, et al. Management algorithm for pneumatosis intestinalis and portal venous gas: treatment and outcome of 88 consecutive cases. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010; 14:437–448.
Article13. Greenstein AJ, Nguyen SQ, Berlin A, et al. Pneumatosis intestinalis in adults: management, surgical indications, and risk factors for mortality. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:1268–1274.
Article14. Ferrada P, Callcut R, Bauza G, et al. Pneumatosis Intestinalis Predictive Evaluation Study: a multicenter epidemiologic study of the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017; 82:451–460.15. Treyaud MO, Duran R, Zins M, Knebel JF, Meuli RA, Schmidt S. Clinical significance of pneumatosis intestinalis: correlation of MDCT-findings with treatment and outcome. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:70–79.
Article16. Umapathi BA, Friel CM, Stukenborg GJ, Hedrick TL. Estimating the risk of bowel ischemia requiring surgery in patients with tomographic evidence of pneumatosis intestinalis. Am J Surg. 2016; 212:762–768.
Article17. Lee HS, Cho YW, Kim KJ, Lee JS, Lee SS, Yang SK. A simple score for predicting mortality in patients with pneumatosis intestinalis. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:639–645.
Article18. DuBose JJ, Lissauer M, Maung AA, et al. Pneumatosis Intestinalis Predictive Evaluation Study (PIPES): a multicenter epidemiologic study of the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013; 75:15–23.19. Lassandro F, Mangoni de Santo Stefano ML, Porto AM, Grassi R, Scaglione M, Rotondo A. Intestinal pneumatosis in adults: diagnostic and prognostic value. Emerg Radiol. 2010; 17:361–365.
Article20. Knechtle SJ, Davidoff AM, Rice RP. Pneumatosis intestinalis: surgical management and clinical outcome. Ann Surg. 1990; 212:160–165.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Chronic Diarrhea and Abdominal Pain
- A Case of Primary Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Chronic Abdominal Pain
- A Case of Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A case of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis complicated by pneumoperitoneum in a post-tuberculosis destroyed lung
- A Case of Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Dermatomyositis