Int J Stem Cells.
2020 Jul;13(2):182-191. 10.15283/ijsc20035.
The Role of Lysophosphatidic Acid in Adult Stem Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Convergence Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- 2Department of Anatomy, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- 3Department of Biomedical Informatics, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- 4Department of Physiology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2504331
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc20035
Abstract
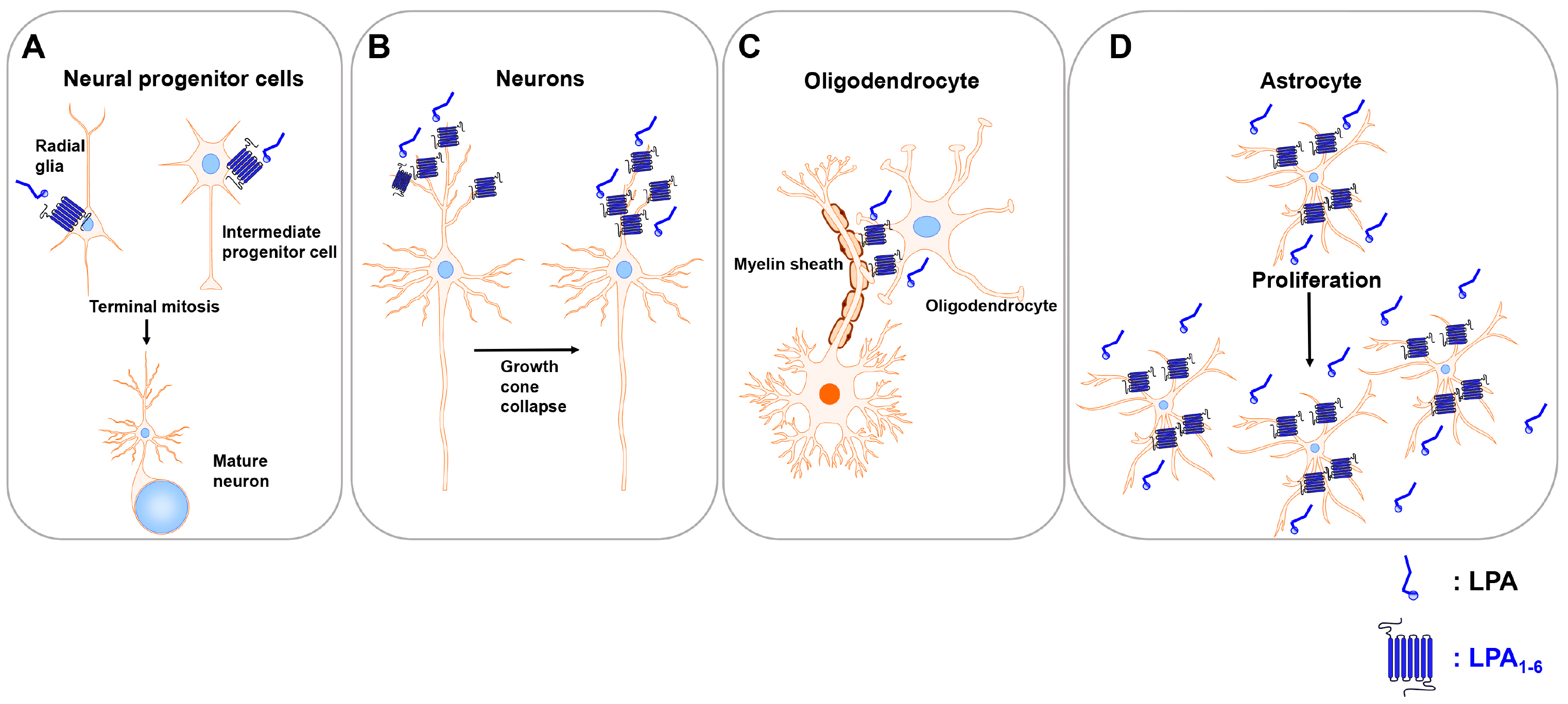
- Stem cells are undifferentiated multipotent precursor cells that are capable both of perpetuating themselves as stem cells (self-renewal) and of undergoing differentiation into one or more specialized types of cells. And these stem cells have been reported to reside within distinct anatomic locations termed “niches”. The long-term goals of stem cell biology range from an understanding of cell-lineage determination and tissue organization to cellular therapeutics for degenerative diseases. Stem cells maintain tissue function throughout an organism’s lifespan by replacing differentiated cells. To perform this function, stem cells provide a unique combination of multilineage developmental potential and the capacity to undergo self-renewing divisions. The loss of self-renewal capacity in stem cells underlies certain degenerative diseases and the aging process. This self-renewal regulation must balance the regenerative needs of tissues that persist throughout life. Recent evidence suggests lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling pathway plays an important role in the regulation of a variety of stem cells. In this review, we summarize the evidence linking between LPA and stem cell regulation. The LPA-induced signaling pathway regulates the proliferation and survival of stem cells and progenitors, and thus are likely to play a role in the maintenance of stem cell population in the body. This lipid mediator regulatory system can be a novel potential therapeutics for stem cell maintenance.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Valdés-Rives SA, González-Arenas A. 2017; Autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid: from inflammation to cancer development. Mediators Inflamm. 2017:9173090. DOI: 10.1155/2017/9173090. PMID: 29430083. PMCID: PMC5753009.
Article2. Chun J. 1999; Lysophospholipid receptors: implications for neural signaling. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 13:151–168. DOI: 10.1615/CritRevNeurobiol.v13.i2.20. PMID: 10512488.
Article3. Fukushima N, Ishii I, Contos JJ, Weiner JA, Chun J. 2001; Lysophospholipid receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 41:507–534. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.507. PMID: 11264467.
Article4. Moolenaar WH, Kranenburg O, Postma FR, Zondag GC. 1997; Lysophosphatidic acid: G-protein signalling and cellular responses. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:168–173. DOI: 10.1016/S0955-0674(97)80059-2. PMID: 9069262.
Article5. Yung YC, Stoddard NC, Chun J. 2014; LPA receptor signaling: pharmacology, physiology, and pathophysiology. J Lipid Res. 55:1192–1214. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R046458. PMID: 24643338. PMCID: PMC4076099.
Article6. Leblanc R, Peyruchaud O. 2015; New insights into the autotaxin/LPA axis in cancer development and metastasis. Exp Cell Res. 333:183–189. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.11.010. PMID: 25460336.
Article7. van Meeteren LA, Moolenaar WH. 2007; Regulation and biological activities of the autotaxin-LPA axis. Prog Lipid Res. 46:145–160. DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2007.02.001. PMID: 17459484.
Article8. Lynch KR. 2002; Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1582:70–71. DOI: 10.1016/S1388-1981(02)00138-5. PMID: 12069811.
Article9. Contos JJ, Ishii I, Chun J. 2000; Lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 58:1188–1196. DOI: 10.1124/mol.58.6.1188. PMID: 11093753.
Article10. An S, Bleu T, Hallmark OG, Goetzl EJ. 1998; Characterization of a novel subtype of human G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 273:7906–7910. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.273.14.7906. PMID: 9525886.
Article11. An S, Bleu T, Zheng Y, Goetzl EJ. 1998; Recombinant human G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors mediate intracellular calcium mobilization. Mol Pharmacol. 54:881–888. DOI: 10.1124/mol.54.5.881. PMID: 9804623.
Article12. Bandoh K, Aoki J, Hosono H, Kobayashi S, Kobayashi T, Murakami-Murofushi K, Tsujimoto M, Arai H, Inoue K. 1999; Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human G-protein-coupled receptor, EDG7, for lysophosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 274:27776–27785. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.39.27776. PMID: 10488122.
Article13. Fukushima N, Kimura Y, Chun J. 1998; A single receptor encoded by vzg-1/lpA1/edg-2 couples to G proteins and mediates multiple cellular responses to lysophosphatidic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95:6151–6156. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6151. PMID: 9600933. PMCID: PMC27607.
Article14. Im DS, Heise CE, Harding MA, George SR, O'Dowd BF, Theodorescu D, Lynch KR. 2000; Molecular cloning and characterization of a lysophosphatidic acid receptor, Edg-7, expressed in prostate. Mol Pharmacol. 57:753–759. DOI: 10.1124/mol.57.4.753. PMID: 10727522.
Article15. Ishii I, Contos JJ, Fukushima N, Chun J. 2000; Functional comparisons of the lysophosphatidic acid receptors, LP(A1)/VZG-1/EDG-2, LP(A2)/EDG-4, and LP(A3)/EDG-7 in neuronal cell lines using a retrovirus expression system. Mol Pharmacol. 58:895–902. DOI: 10.1124/mol.58.5.895. PMID: 11040035.
Article16. Nakamura K, Kishimoto T, Ohkawa R, Okubo S, Tozuka M, Yokota H, Ikeda H, Ohshima N, Mizuno K, Yatomi Y. 2007; Suppression of lysophosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidylcholine formation in the plasma in vitro: proposal of a plasma sample preparation method for laboratory testing of these lipids. Anal Biochem. 367:20–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.05.004. PMID: 17568554.
Article17. Contos JJ, Ishii I, Fukushima N, Kingsbury MA, Ye X, Kawamura S, Brown JH, Chun J. 2002; Characterization of lpa2 (Edg4) and lpa1/lpa2 (Edg2/Edg4) lysophosphatidic acid receptor knockout mice: signaling deficits without obvious phenotypic abnormality attributable to lpa2. Mol Cell Biol. 22:6921–6929. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.19.6921-6929.2002. PMID: 12215548. PMCID: PMC134025.
Article18. Yung YC, Stoddard NC, Mirendil H, Chun J. 2015; Lysophosphatidic acid signaling in the nervous system. Neuron. 85:669–682. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.01.009. PMID: 25695267. PMCID: PMC4400838.
Article19. Sheng X, Yung YC, Chen A, Chun J. 2015; Lysophosphatidic acid signalling in development. Development. 142:1390–1395. DOI: 10.1242/dev.121723. PMID: 25852197. PMCID: PMC4392601.
Article20. Fukushima N, Weiner JA, Kaushal D, Contos JJ, Rehen SK, Kingsbury MA, Kim KY, Chun J. 2002; Lysophosphatidic acid influences the morphology and motility of young, postmitotic cortical neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 20:271–282. DOI: 10.1006/mcne.2002.1123. PMID: 12093159.
Article21. Hecht JH, Weiner JA, Post SR, Chun J. 1996; Ventricular zone gene-1 (vzg-1) encodes a lysophosphatidic acid receptor expressed in neurogenic regions of the developing cerebral cortex. J Cell Biol. 135:1071–1083. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.135.4.1071. PMID: 8922387. PMCID: PMC2133395.
Article22. Weiner JA, Chun J. 1999; Schwann cell survival mediated by the signaling phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96:5233–5238. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.9.5233. PMID: 10220449. PMCID: PMC21847.
Article23. Contos JJ, Fukushima N, Weiner JA, Kaushal D, Chun J. 2000; Requirement for the lpA1 lysophosphatidic acid receptor gene in normal suckling behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 97:13384–13389. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.24.13384. PMID: 11087877. PMCID: PMC27233.
Article24. Ye X, Hama K, Contos JJ, Anliker B, Inoue A, Skinner MK, Suzuki H, Amano T, Kennedy G, Arai H, Aoki J, Chun J. 2005; LPA3-mediated lysophosphatidic acid signalling in embryo implantation and spacing. Nature. 435:104–108. DOI: 10.1038/nature03505. PMID: 15875025. PMCID: PMC1369590.
Article25. Lee Z, Cheng CT, Zhang H, Subler MA, Wu J, Mukherjee A, Windle JJ, Chen CK, Fang X. 2008; Role of LPA4/p2y9/GPR23 in negative regulation of cell motility. Mol Biol Cell. 19:5435–5445. DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-03-0316. PMID: 18843048. PMCID: PMC2592656.26. Sumida H, Noguchi K, Kihara Y, Abe M, Yanagida K, Hamano F, Sato S, Tamaki K, Morishita Y, Kano MR, Iwata C, Miyazono K, Sakimura K, Shimizu T, Ishii S. 2010; LPA4 regulates blood and lymphatic vessel formation during mouse embryogenesis. Blood. 116:5060–5070. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-272443. PMID: 20713964.
Article27. Teo ST, Yung YC, Herr DR, Chun J. 2009; Lysophosphatidic acid in vascular development and disease. IUBMB Life. 61:791–799. DOI: 10.1002/iub.220. PMID: 19621353. PMCID: PMC4307796.
Article28. Verfaillie CM, Pera MF, Lansdorp PM. 2002; Stem cells: hype and reality. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 369–391. DOI: 10.1182/asheducation-2002.1.369. PMID: 12446433.
Article29. Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM. 1998; Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 282:1145–1147. DOI: 10.1126/science.282.5391.1145. PMID: 9804556.
Article30. Lee CW, Rivera R, Gardell S, Dubin AE, Chun J. 2006; GPR92 as a new G12/13- and Gq-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptor that increases cAMP, LPA5. J Biol Chem. 281:23589–23597. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M603670200. PMID: 16774927.
Article31. Kleger A, Busch T, Liebau S, Prelle K, Paschke S, Beil M, Rolletschek A, Wobus A, Wolf E, Adler G, Seufferlein T. 2007; The bioactive lipid sphingosylphosphorylcholine induces differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells and human promyelocytic leukaemia cells. Cell Signal. 19:367–377. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.07.015. PMID: 16978842.
Article32. Schuck S, Soloaga A, Schratt G, Arthur JS, Nordheim A. 2003; The kinase MSK1 is required for induction of c-fos by lysophosphatidic acid in mouse embryonic stem cells. BMC Mol Biol. 4:6. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-4-6. PMID: 12769834. PMCID: PMC161794.33. Pébay A, Wong RC, Pitson SM, Wolvetang EJ, Peh GS, Filipczyk A, Koh KL, Tellis I, Nguyen LT, Pera MF. 2005; Essential roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate and platelet-derived growth factor in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 23:1541–1548. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2004-0338. PMID: 16081668.
Article34. Inniss K, Moore H. 2006; Mediation of apoptosis and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Stem Cells Dev. 15:789–796. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2006.15.789. PMID: 17253942.
Article35. Wong RC, Dottori M, Koh KL, Nguyen LT, Pera MF, Pébay A. 2006; Gap junctions modulate apoptosis and colony growth of human embryonic stem cells maintained in a serum-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 344:181–188. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.127. PMID: 16616002.
Article36. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. 2006; Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024. PMID: 16904174.
Article37. Hsiao C, Lampe M, Nillasithanukroh S, Han W, Lian X, Palecek SP. 2016; Human pluripotent stem cell culture density modulates YAP signaling. Biotechnol J. 11:662–675. DOI: 10.1002/biot.201500374. PMID: 26766309. PMCID: PMC4850094.
Article38. Qin H, Hejna M, Liu Y, Percharde M, Wossidlo M, Blouin L, Durruthy-Durruthy J, Wong P, Qi Z, Yu J, Qi LS, Sebastiano V, Song JS, Ramalho-Santos M. 2016; YAP Induces Human Naive Pluripotency. Cell Rep. 14:2301–2312. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.036. PMID: 26947063. PMCID: PMC4807727.
Article39. Beattie R, Hippenmeyer S. 2017; Mechanisms of radial glia progenitor cell lineage progression. FEBS Lett. 591:3993–4008. DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.12906. PMID: 29121403. PMCID: PMC5765500.
Article40. Pébay A, Bonder CS, Pitson SM. 2007; Stem cell regulation by lysophospholipids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 84:83–97. DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2007.08.004. PMID: 17991611.
Article41. Picard-Riera N, Nait-Oumesmar B, Baron-Van Evercooren A. 2004; Endogenous adult neural stem cells: limits and potential to repair the injured central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 76:223–231. DOI: 10.1002/jnr.20040. PMID: 15048920.
Article42. Svetlov SI, Ignatova TN, Wang KK, Hayes RL, English D, Kukekov VG. 2004; Lysophosphatidic acid induces clonal generation of mouse neurospheres via proliferation of Sca-1- and AC133-positive neural progenitors. Stem Cells Dev. 13:685–693. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2004.13.685. PMID: 15684836.
Article43. Fukushima N, Weiner JA, Chun J. 2000; Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a novel extracellular regulator of cortical neuroblast morphology. Dev Biol. 228:6–18. DOI: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9930. PMID: 11087622.
Article44. Kingsbury MA, Rehen SK, Contos JJ, Higgins CM, Chun J. 2003; Non-proliferative effects of lysophosphatidic acid enhance cortical growth and folding. Nat Neurosci. 6:1292–1299. DOI: 10.1038/nn1157. PMID: 14625558.
Article45. Reynolds BA, Weiss S. 1992; Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. DOI: 10.1126/science.1553558. PMID: 1553558.
Article46. Reynolds BA, Rietze RL. 2005; Neural stem cells and neurospheres--re-evaluating the relationship. Nat Methods. 2:333–336. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth758. PMID: 15846359.
Article47. Fukushima N, Shano S, Moriyama R, Chun J. 2007; Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates neuronal differentiation of cortical neuroblasts through the LPA1-G(i/o) pathway. Neurochem Int. 50:302–307. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2006.09.008. PMID: 17056154.
Article48. Cui HL, Qiao JT. 2006; Promotive action of lysophosphatidic acid on proliferation of rat embryonic neural stem cells and their differentiation to cholinergic neurons in vitro. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 58:547–555. PMID: 17173189.49. Harada J, Foley M, Moskowitz MA, Waeber C. 2004; Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces proliferation and morphological changes of neural progenitor cells. J Neurochem. 88:1026–1039. DOI: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02219.x. PMID: 14756825.
Article50. Yuan XB, Jin M, Xu X, Song YQ, Wu CP, Poo MM, Duan S. 2003; Signalling and crosstalk of Rho GTPases in mediating axon guidance. Nat Cell Biol. 5:38–45. DOI: 10.1038/ncb895. PMID: 12510192.
Article51. Campbell DS, Holt CE. 2001; Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron. 32:1013–1026. DOI: 10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00551-7. PMID: 11754834.
Article52. Kingsbury MA, Rehen SK, Ye X, Chun J. 2004; Genetics and cell biology of lysophosphatidic acid receptor-mediated signaling during cortical neurogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 92:1004–1012. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.20061. PMID: 15258921.
Article53. Dubin AE, Bahnson T, Weiner JA, Fukushima N, Chun J. 1999; Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates neurotransmitter-like conductance changes that precede GABA and L-glutamate in early, presumptive cortical neuroblasts. J Neurosci. 19:1371–1381. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01371.1999. PMID: 9952414. PMCID: PMC6786022.
Article54. Zhao C, Fancy SP, Magy L, Urwin JE, Franklin RJ. 2005; Stem cells, progenitors and myelin repair. J Anat. 207:251–258. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00456.x. PMID: 16185249. PMCID: PMC1571531.
Article55. Weiner JA, Hecht JH, Chun J. 1998; Lysophosphatidic acid receptor gene vzg-1/lpA1/edg-2 is expressed by mature oligodendrocytes during myelination in the postnatal murine brain. J Comp Neurol. 398:587–598. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19980907)398:4<587::AID-CNE10>3.0.CO;2-5.
Article56. Dawson J, Hotchin N, Lax S, Rumsby M. 2003; Lysophosphatidic acid induces process retraction in CG-4 line oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte precursor cells but not in differentiated oligodendrocytes. J Neurochem. 87:947–957. DOI: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02056.x. PMID: 14622125.
Article57. Jaillard C, Harrison S, Stankoff B, Aigrot MS, Calver AR, Duddy G, Walsh FS, Pangalos MN, Arimura N, Kaibuchi K, Zalc B, Lubetzki C. 2005; Edg8/S1P5: an oligodendroglial receptor with dual function on process retraction and cell survival. J Neurosci. 25:1459–1469. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4645-04.2005. PMID: 15703400. PMCID: PMC6726002.
Article58. Rao TS, Lariosa-Willingham KD, Lin FF, Palfreyman EL, Yu N, Chun J, Webb M. 2003; Pharmacological characterization of lysophospholipid receptor signal transduction pathways in rat cerebrocortical astrocytes. Brain Res. 990:182–194. DOI: 10.1016/S0006-8993(03)03527-3. PMID: 14568343.
Article59. Sorensen SD, Nicole O, Peavy RD, Montoya LM, Lee CJ, Murphy TJ, Traynelis SF, Hepler JR. 2003; Common signaling pathways link activation of murine PAR-1, LPA, and S1P receptors to proliferation of astrocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 64:1199–1209. DOI: 10.1124/mol.64.5.1199. PMID: 14573770.
Article60. Shano S, Moriyama R, Chun J, Fukushima N. 2008; Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates astrocyte proliferation through LPA1. Neurochem Int. 52:216–220. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.07.004. PMID: 17692995. PMCID: PMC3265988.61. Adams GB, Scadden DT. 2006; The hematopoietic stem cell in its place. Nat Immunol. 7:333–337. DOI: 10.1038/ni1331. PMID: 16550195.
Article62. Scadden DT. 2006; The stem-cell niche as an entity of action. Nature. 441:1075–1079. DOI: 10.1038/nature04957. PMID: 16810242.
Article63. Whetton AD, Lu Y, Pierce A, Carney L, Spooncer E. 2003; Lysophospholipids synergistically promote primitive hematopoietic cell chemotaxis via a mechanism involving Vav 1. Blood. 102:2798–2802. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3635. PMID: 12829605.
Article64. Lai JM, Lu CY, Yang-Yen HF, Chang ZF. 2001; Lysophosphatidic acid promotes phorbol-ester-induced apoptosis in TF-1 cells by interfering with adhesion. Biochem J. 359:227–233. DOI: 10.1042/bj3590227. PMID: 11563987. PMCID: PMC1222139.
Article65. Ortlepp C, Steudel C, Heiderich C, Koch S, Jacobi A, Ryser M, Brenner S, Bornhäuser M, Brors B, Hofmann WK, Ehninger G, Thiede C. 2013; Autotaxin is expressed in FLT3-ITD positive acute myeloid leukemia and hematopoietic stem cells and promotes cell migration and proliferation. Exp Hematol. 41:444–461.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2013.01.007. PMID: 23377000.
Article66. Yanai N, Matsui N, Furusawa T, Okubo T, Obinata M. 2000; Sphingosine-1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid trigger invasion of primitive hematopoietic cells into stromal cell layers. Blood. 96:139–144. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V96.1.139. PMID: 10891442.
Article67. Chiang CL, Chen SS, Lee SJ, Tsao KC, Chu PL, Wen CH, Hwang SM, Yao CL, Lee H. 2011; Lysophosphatidic acid induces erythropoiesis through activating lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3. Stem Cells. 29:1763–1773. DOI: 10.1002/stem.733. PMID: 21915944.
Article68. Evseenko D, Latour B, Richardson W, Corselli M, Sahaghian A, Cardinal S, Zhu Y, Chan R, Dunn B, Crooks GM. 2013; Lysophosphatidic acid mediates myeloid differentiation within the human bone marrow microenvironment. PLoS One. 8:e63718. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063718. PMID: 23696850. PMCID: PMC3655943.
Article69. Li H, Yue R, Wei B, Gao G, Du J, Pei G. 2014; Lysophosphatidic acid acts as a nutrient-derived developmental cue to regulate early hematopoiesis. EMBO J. 33:1383–1396. DOI: 10.15252/embj.201387594. PMID: 24829209. PMCID: PMC4194126.
Article70. Lin KH, Ho YH, Chiang JC, Li MW, Lin SH, Chen WM, Chiang CL, Lin YN, Yang YJ, Chen CN, Lu J, Huang CJ, Tigyi G, Yao CL, Lee H. 2016; Pharmacological activation of lysophosphatidic acid receptors regulates erythropoiesis. Sci Rep. 6:27050. DOI: 10.1038/srep27050. PMID: 27244685. PMCID: PMC4886675.
Article71. Ankrum JA, Ong JF, Karp JM. 2014; Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 32:252–260. DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2816. PMID: 24561556. PMCID: PMC4320647.
Article72. Mahla RS. 2016; Stem cells applications in regenerative medicine and disease therapeutics. Int J Cell Biol. 2016:6940283. DOI: 10.1155/2016/6940283. PMID: 27516776. PMCID: PMC4969512.
Article73. Schofield R. 1978; The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 4:7–25.74. Calvi LM, Adams GB, Weibrecht KW, Weber JM, Olson DP, Knight MC, Martin RP, Schipani E, Divieti P, Bringhurst FR, Milner LA, Kronenberg HM, Scadden DT. 2003; Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature. 425:841–846. DOI: 10.1038/nature02040. PMID: 14574413.
Article75. Li L, Xie T. 2005; Stem cell niche: structure and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 21:605–631. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.131525. PMID: 16212509.
Article76. Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. 1999; Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 284:143–147. DOI: 10.1126/science.284.5411.143. PMID: 10102814.
Article77. Passier R, Mummery C. 2003; Origin and use of embryonic and adult stem cells in differentiation and tissue repair. Cardiovasc Res. 58:324–335. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6363(02)00770-8. PMID: 12757867.
Article78. Chen J, Baydoun AR, Xu R, Deng L, Liu X, Zhu W, Shi L, Cong X, Hu S, Chen X. 2008; Lysophosphatidic acid protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Stem Cells. 26:135–145. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0098. PMID: 17932426.
Article79. Li Z, Wei H, Liu X, Hu S, Cong X, Chen X. 2010; LPA rescues ER stress-associated apoptosis in hypoxia and serum deprivation-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 111:811–820. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22731. PMID: 20533299.
Article80. Jaganathan BG, Ruester B, Dressel L, Stein S, Grez M, Seifried E, Henschler R. 2007; Rho inhibition induces migration of mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. 25:1966–1974. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0167. PMID: 17510214.
Article81. Annabi B, Thibeault S, Lee YT, Bousquet-Gagnon N, Eliopoulos N, Barrette S, Galipeau J, Béliveau R. 2003; Matrix metalloproteinase regulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced angiogenic properties of bone marrow stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 31:640–649. DOI: 10.1016/S0301-472X(03)00090-0. PMID: 12842709.
Article82. Wei H, Wang F, Wang X, Yang J, Li Z, Cong X, Chen X. 2013; Lysophosphatidic acid promotes secretion of VEGF by increasing expression of 150-kD Oxygen-regulated protein (ORP150) in mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1426–1434. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.05.003. PMID: 23707263.
Article83. Liu YB, Kharode Y, Bodine PV, Yaworsky PJ, Robinson JA, Billiard J. 2010; LPA induces osteoblast differentiation through interplay of two receptors: LPA1 and LPA4. J Cell Biochem. 109:794–800. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22471. PMID: 20069565.
Article84. Lee KP, Lee JH, Kim TS, Kim TH, Park HD, Byun JS, Kim MC, Jeong WI, Calvisi DF, Kim JM, Lim DS. 2010; The Hippo-Salvador pathway restrains hepatic oval cell proliferation, liver size, and liver tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107:8248–8253. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912203107. PMID: 20404163. PMCID: PMC2889558.
Article85. Sautin YY, Jorgensen M, Petersen BE, Saulnier-Blache JS, Crawford JM, Svetlov SI. 2002; Hepatic oval (stem) cell expression of endothelial differentiation gene receptors for lysophosphatidic acid in mouse chronic liver injury. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 11:643–649. DOI: 10.1089/15258160260194785. PMID: 12201952.
Article86. Bonnet D, Dick JE. 1997; Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. DOI: 10.1038/nm0797-730. PMID: 9212098.
Article87. Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. 2008; Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. DOI: 10.1038/nrc2499. PMID: 18784658.
Article88. Lee D, Suh DS, Lee SC, Tigyi GJ, Kim JH. 2018; Role of autotaxin in cancer stem cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 37:509–518. DOI: 10.1007/s10555-018-9745-x. PMID: 29926310. PMCID: PMC6309296.
Article89. Sreepadmanabh M, Toley BJ. 2018; Investigations into the cancer stem cell niche using in-vitro 3-D tumor models and microfluidics. Biotechnol Adv. 36:1094–1110. DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.03.009. PMID: 29559382.
Article90. Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. 2001; Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 414:105–111. DOI: 10.1038/35102167. PMID: 11689955.
Article91. Seo EJ, Kwon YW, Jang IH, Kim DK, Lee SI, Choi EJ, Kim KH, Suh DS, Lee JH, Choi KU, Lee JW, Mok HJ, Kim KP, Matsumoto H, Aoki J, Kim JH. 2016; Autotaxin regulates maintenance of ovarian cancer stem cells through lysophosphatidic acid-mediated autocrine mechanism. Stem Cells. 34:551–564. DOI: 10.1002/stem.2279. PMID: 26800320.
Article92. Kim KS, Sengupta S, Berk M, Kwak YG, Escobar PF, Belinson J, Mok SC, Xu Y. 2006; Hypoxia enhances lysophosphatidic acid responsiveness in ovarian cancer cells and lysophosphatidic acid induces ovarian tumor metastasis in vivo. Cancer Res. 66:7983–7990. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4381. PMID: 16912173.
Article93. Yu S, Murph MM, Lu Y, Liu S, Hall HS, Liu J, Stephens C, Fang X, Mills GB. 2008; Lysophosphatidic acid receptors determine tumorigenicity and aggressiveness of ovarian cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:1630–1642. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djn378. PMID: 19001604. PMCID: PMC2720766.
Article94. van Meeteren LA, Ruurs P, Stortelers C, Bouwman P, van Rooijen MA, Pradère JP, Pettit TR, Wakelam MJ, Saulnier-Blache JS, Mummery CL, Moolenaar WH, Jonkers J. 2006; Autotaxin, a secreted lysophospholipase D, is essential for blood vessel formation during development. Mol Cell Biol. 26:5015–5022. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02419-05. PMID: 16782887. PMCID: PMC1489177.
Article95. Stracke ML, Krutzsch HC, Unsworth EJ, Arestad A, Cioce V, Schiffmann E, Liotta LA. 1992; Identification, purification, and partial sequence analysis of autotaxin, a novel motility-stimulating protein. J Biol Chem. 267:2524–2529. PMID: 1733949.
Article96. Lee H, Goetzl EJ, An S. 2000; Lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulate endothelial cell wound healing. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 278:C612–C618. DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.2000.278.3.C612. PMID: 10712250.97. Gustin C, Van Steenbrugge M, Raes M. 2008; LPA modulates monocyte migration directly and via LPA-stimulated endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C905–C914. DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00544.2007. PMID: 18632732.
Article98. Kim J, Keys JR, Eckhart AD. 2006; Vascular smooth muscle migration and proliferation in response to lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is mediated by LPA receptors coupling to Gq. Cell Signal. 18:1695–1701. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.01.009. PMID: 16504475.
Article99. Panchatcharam M, Miriyala S, Yang F, Rojas M, End C, Vallant C, Dong A, Lynch K, Chun J, Morris AJ, Smyth SS. 2008; Lysophosphatidic acid receptors 1 and 2 play roles in regulation of vascular injury responses but not blood pressure. Circ Res. 103:662–670. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.180778. PMID: 18703779. PMCID: PMC2637300.
Article100. Rother E, Brandl R, Baker DL, Goyal P, Gebhard H, Tigyi G, Siess W. 2003; Subtype-selective antagonists of lysophosphatidic acid receptors inhibit platelet activation triggered by the lipid core of atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation. 108:741–747. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000083715.37658.C4. PMID: 12885756.
Article101. Neidlinger NA, Larkin SK, Bhagat A, Victorino GP, Kuypers FA. 2006; Hydrolysis of phosphatidylserine-exposing red blood cells by secretory phospholipase A2 generates lysophosphatidic acid and results in vascular dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 281:775–781. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M505790200. PMID: 16278219.
Article102. Wu WT, Chen CN, Lin CI, Chen JH, Lee H. 2005; Lysophospholipids enhance matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in human endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 146:3387–3400. DOI: 10.1210/en.2004-1654. PMID: 15878967.
Article103. Braet F, Wisse E. 2002; Structural and functional aspects of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae: a review. Comp Hepatol. 1:1. DOI: 10.1186/1476-5926-1-1. PMID: 12437787. PMCID: PMC131011.104. DeLeve LD. 2013; Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and liver regeneration. J Clin Invest. 123:1861–1866. DOI: 10.1172/JCI66025. PMID: 23635783. PMCID: PMC3635729.
Article105. Chiu JJ, Chien S. 2011; Effects of disturbed flow on vascular endothelium: pathophysiological basis and clinical perspectives. Physiol Rev. 91:327–387. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00047.2009. PMID: 21248169. PMCID: PMC3844671.
Article106. Robinson MW, Harmon C, O'Farrelly C. 2016; Liver immunology and its role in inflammation and homeostasis. Cell Mol Immunol. 13:267–276. DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2016.3. PMID: 27063467. PMCID: PMC4856809.
Article107. Chou CH, Lai SL, Ho CM, Lin WH, Chen CN, Lee PH, Peng FC, Kuo SH, Wu SY, Lai HS. 2015; Lysophosphatidic acid alters the expression profiles of angiogenic factors, cytokines, and chemokines in mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e0122060. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122060. PMID: 25822713. PMCID: PMC4379007.
Article108. Schulze C, Smales C, Rubin LL, Staddon JM. 1997; Lysophosphatidic acid increases tight junction permeability in cultured brain endothelial cells. J Neurochem. 68:991–1000. DOI: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.68030991.x. PMID: 9048744.
Article109. Zheng Y, Kong Y, Goetzl EJ. 2001; Lysophosphatidic acid receptor-selective effects on Jurkat T cell migration through a Matrigel model basement membrane. J Immunol. 166:2317–2322. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2317. PMID: 11160288.
Article110. Stam JC, Michiels F, van der Kammen RA, Moolenaar WH, Collard JG. 1998; Invasion of T-lymphoma cells: cooperation between Rho family GTPases and lysophospholipid receptor signaling. EMBO J. 17:4066–4074. DOI: 10.1093/emboj/17.14.4066. PMID: 9670021. PMCID: PMC1170739.
Article111. Kanda H, Newton R, Klein R, Morita Y, Gunn MD, Rosen SD. 2008; Autotaxin, an ectoenzyme that produces lysophosphatidic acid, promotes the entry of lymphocytes into secondary lymphoid organs. Nat Immunol. 9:415–423. DOI: 10.1038/ni1573. PMID: 18327261. PMCID: PMC2783613.
Article112. Jin Y, Knudsen E, Wang L, Maghazachi AA. 2003; Lysophosphatidic acid induces human natural killer cell chemotaxis and intracellular calcium mobilization. Eur J Immunol. 33:2083–2089. DOI: 10.1002/eji.200323711. PMID: 12884281.
Article113. Bagga S, Price KS, Lin DA, Friend DS, Austen KF, Boyce JA. 2004; Lysophosphatidic acid accelerates the development of human mast cells. Blood. 104:4080–4087. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-1166. PMID: 15319282.
Article114. Lundequist A, Boyce JA. 2011; LPA5 is abundantly expressed by human mast cells and important for lysophosphatidic acid induced MIP-1β release. PLoS One. 6:e18192. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018192. PMID: 21464938. PMCID: PMC3065470.
Article115. Hashimoto T, Yamashita M, Ohata H, Momose K. 2003; Lysophosphatidic acid enhances in vivo infiltration and activation of guinea pig eosinophils and neutrophils via a Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase-mediated pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 91:8–14. DOI: 10.1254/jphs.91.8. PMID: 12686725.
Article116. Rahaman M, Costello RW, Belmonte KE, Gendy SS, Walsh MT. 2006; Neutrophil sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid receptors in pneumonia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 34:233–241. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0126OC. PMID: 16224106.
Article117. Koh JS, Lieberthal W, Heydrick S, Levine JS. 1998; Lysophosphatidic acid is a major serum noncytokine survival factor for murine macrophages which acts via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. J Clin Invest. 102:716–727. DOI: 10.1172/JCI1002. PMID: 9710440. PMCID: PMC508934.
Article118. Rosskopf D, Daelman W, Busch S, Schurks M, Hartung K, Kribben A, Michel MC, Siffert W. 1998; Growth factor-like action of lysophosphatidic acid on human B lymphoblasts. Am J Physiol. 274:C1573–C1582. DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.274.6.C1573. PMID: 9611122.
Article119. Knowlden S, Georas SN. 2014; The autotaxin-LPA axis emerges as a novel regulator of lymphocyte homing and inflammation. J Immunol. 192:851–857. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302831. PMID: 24443508. PMCID: PMC3905607.
Article120. Gardell SE, Dubin AE, Chun J. 2006; Emerging medicinal roles for lysophospholipid signaling. Trends Mol Med. 12:65–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.12.001. PMID: 16406843.
Article121. Ye X, Ishii I, Kingsbury MA, Chun J. 2002; Lysophosphatidic acid as a novel cell survival/apoptotic factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1585:108–113. DOI: 10.1016/S1388-1981(02)00330-X. PMID: 12531543.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of TAZ in Lysophosphatidic Acid-Induced Migration and Proliferation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Inhibition of lyosphosphatidic acid receptor 1 signaling in periodontal ligament stem cells reduces inflammatory paracrine effect in primary astrocyte cells
- The role of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide from Porphyromonas gingivalis in human periodontal ligament stem cells
- Lysophosphatidic acid enhances breast cancer cells-mediated osteoclastogenesis
- Cell Biological Characteristics of Adult Stem Cells