J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Jun;35(24):e231. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e231.
A Case of Breakthrough COVID-19 during Hydroxychloroquine Maintenance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2503019
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e231
Abstract
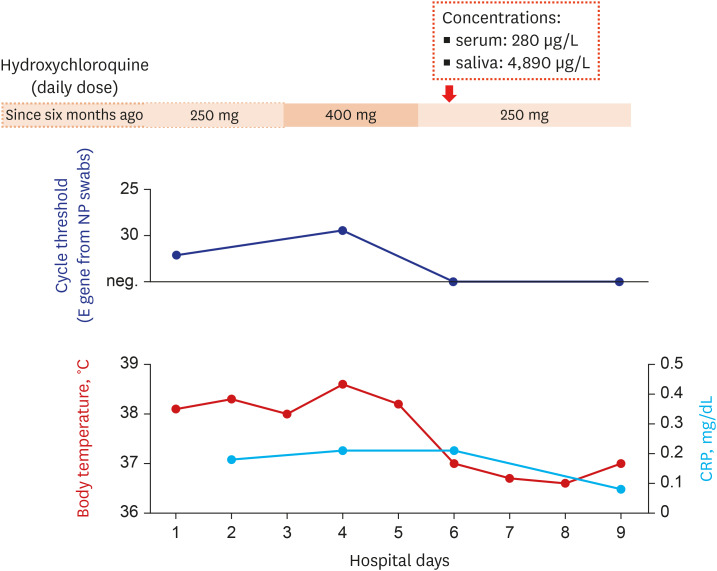
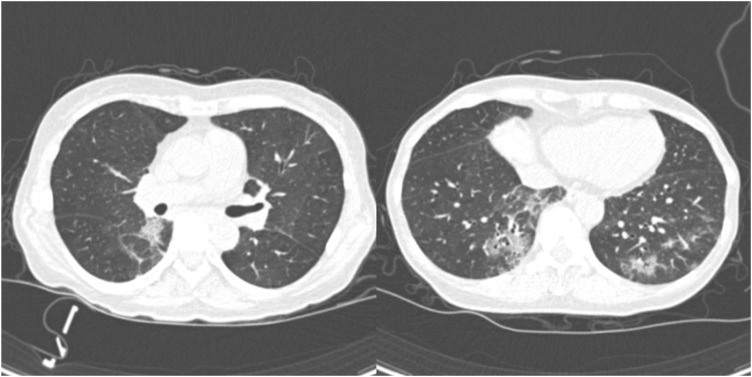
- There have been controversies on the prophylactic effect of hydroxychloroquine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). We describe a patient, 60-year old Korean woman, with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) who had been taking hydroxychloroquine for 6 months. Her serum and saliva concentrations of hydroxychloroquine were 280 μg/L and 4,890 μg/L, respectively. The present case raises concerns on hydroxychloroquine's role as a prophylactic agent for COVID-19.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu M, et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020; 30(3):269–271. PMID: 32020029.
Article2. Yao X, Ye F, Zhang M, Cui C, Huang B, Niu P, et al. In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin Infect Dis. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa237.
Article3. Lee SH, Son H, Peck KR. Can post-exposure prophylaxis for COVID-19 be considered as an outbreak response strategy in long-term care hospitals? Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020; 55(6):105988. PMID: 32305587.
Article4. Lahouati M, Mériglier E, Martin L, Bouchet S, Desclaux A, Bonnet F. COVID-19 infection also occurs in patients taking hydroxychloroquine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020; dkaa193.
Article5. Boulware DR, Pullen MF, Bangdiwala AS, Pastick KA, Lofgren SM, Okafor EC, et al. A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020; NEJMoa2016638.
Article6. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - preliminary report. N Engl J Med. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2016638.
Article7. Efthimiadis A, Spanevello A, Hamid Q, Kelly MM, Linden M, Louis R, et al. Methods of sputum processing for cell counts, immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridisation. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2002; 37:19s–23s. PMID: 12361358.8. Liu J, Cao R, Xu M, Wang X, Zhang H, Hu H, et al. Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020; 6(1):16. PMID: 32194981.
Article9. White MR, Helmerhorst EJ, Ligtenberg A, Karpel M, Tecle T, Siqueira WL, et al. Multiple components contribute to ability of saliva to inhibit influenza viruses. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2009; 24(1):18–24. PMID: 19121065.
Article10. Kang CK, Seong MW, Choi SJ, Kim TS, Choe PG, Song SH, et al. In vitro activity of lopinavir/ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 at concentrations achievable by usual doses. Korean J Intern Med. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2020.157.11. Geleris J, Sun Y, Platt J, Zucker J, Baldwin M, Hripcsak G, et al. Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2012410.
Article12. Chen J, Liu D, Liu L, Liu P, Xu Q, Xia L, et al. A pilot study of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of patients with common coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19). J Zhejiang Univ. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.03.03.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on The Efficacy of Vaccination in Elderly Patients with Breakthrough COVID-19 Infection
- Baseline use of hydroxychloroquine or immunosuppressive drugs and the risk of coronavirus disease 2019
- Involuntary Movements Following Administration of Hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 Pneumonia
- Lopinavir-ritonavir versus hydroxychloroquine for viral clearance and clinical improvement in patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019
- Delayed exacerbation of COVID-19 pneumonia in vaccinated kidney transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressants: a case series