Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2020 May;24(3):267-276. 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.3.267.
Oncogenic Ras downregulates mdr1b expression through generation of reactive oxygen species
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Premedical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 61452, Korea
- 2Departments of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 61452, Korea
- 3Departments of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 61452, Korea
- KMID: 2502509
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.3.267
Abstract
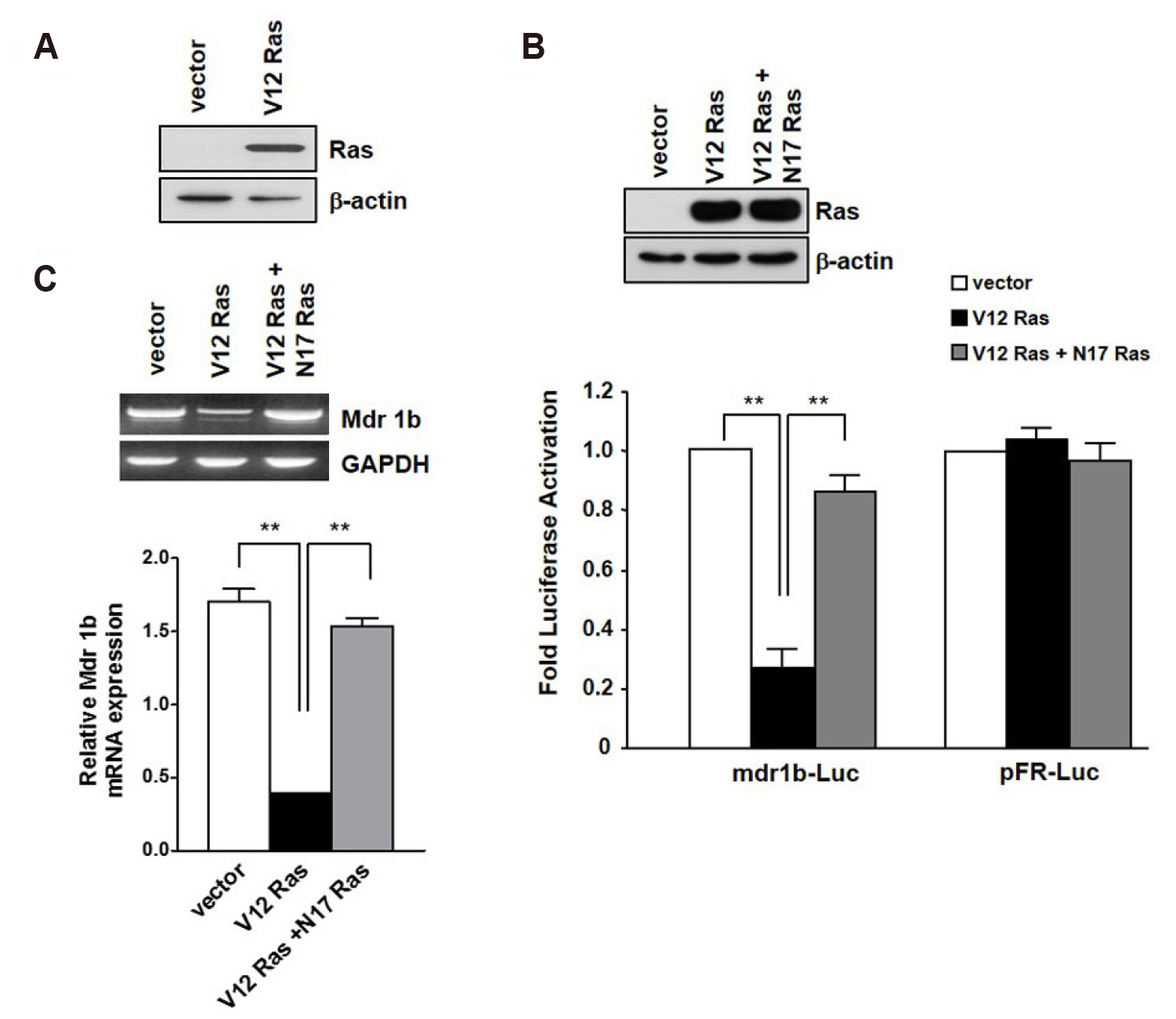
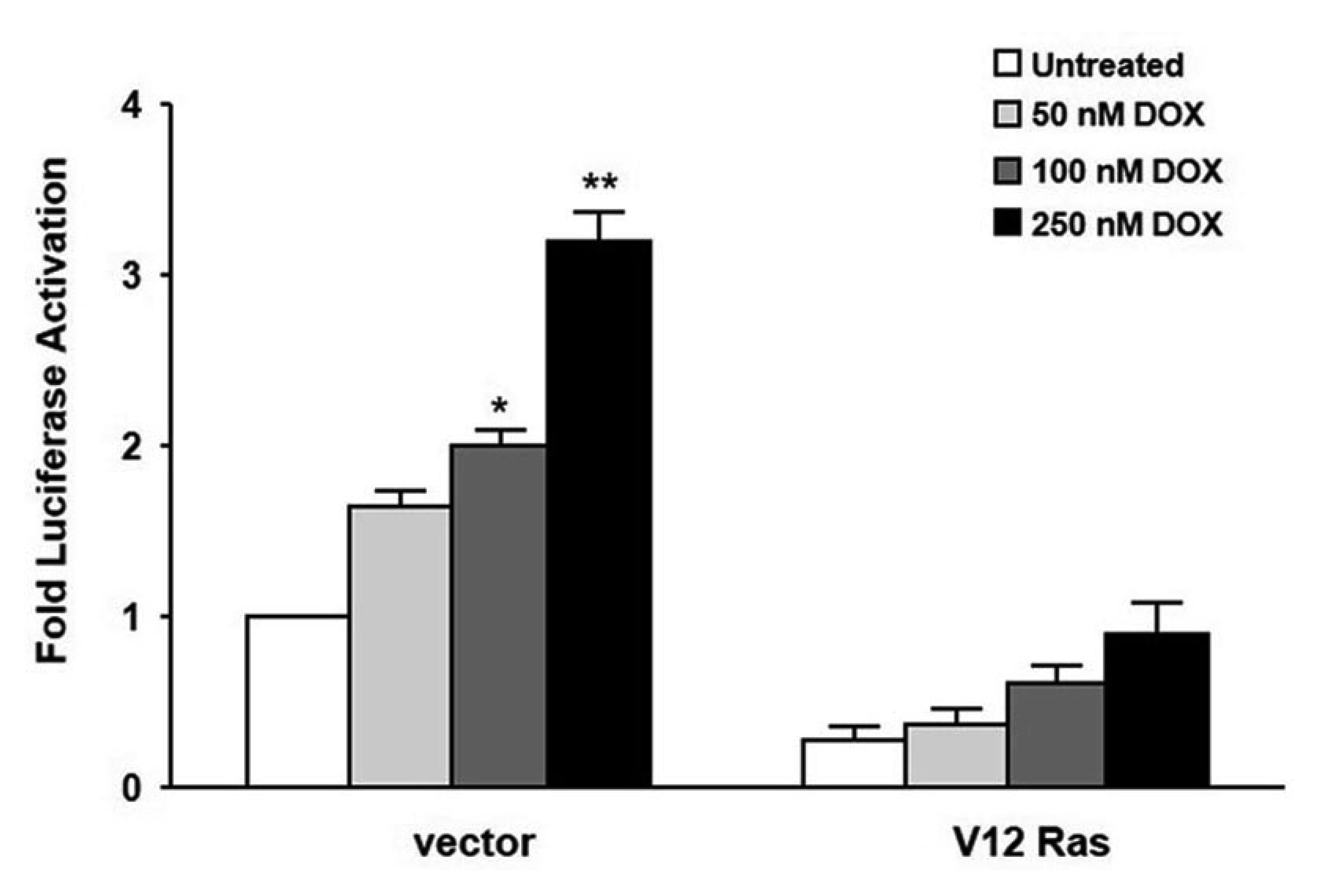
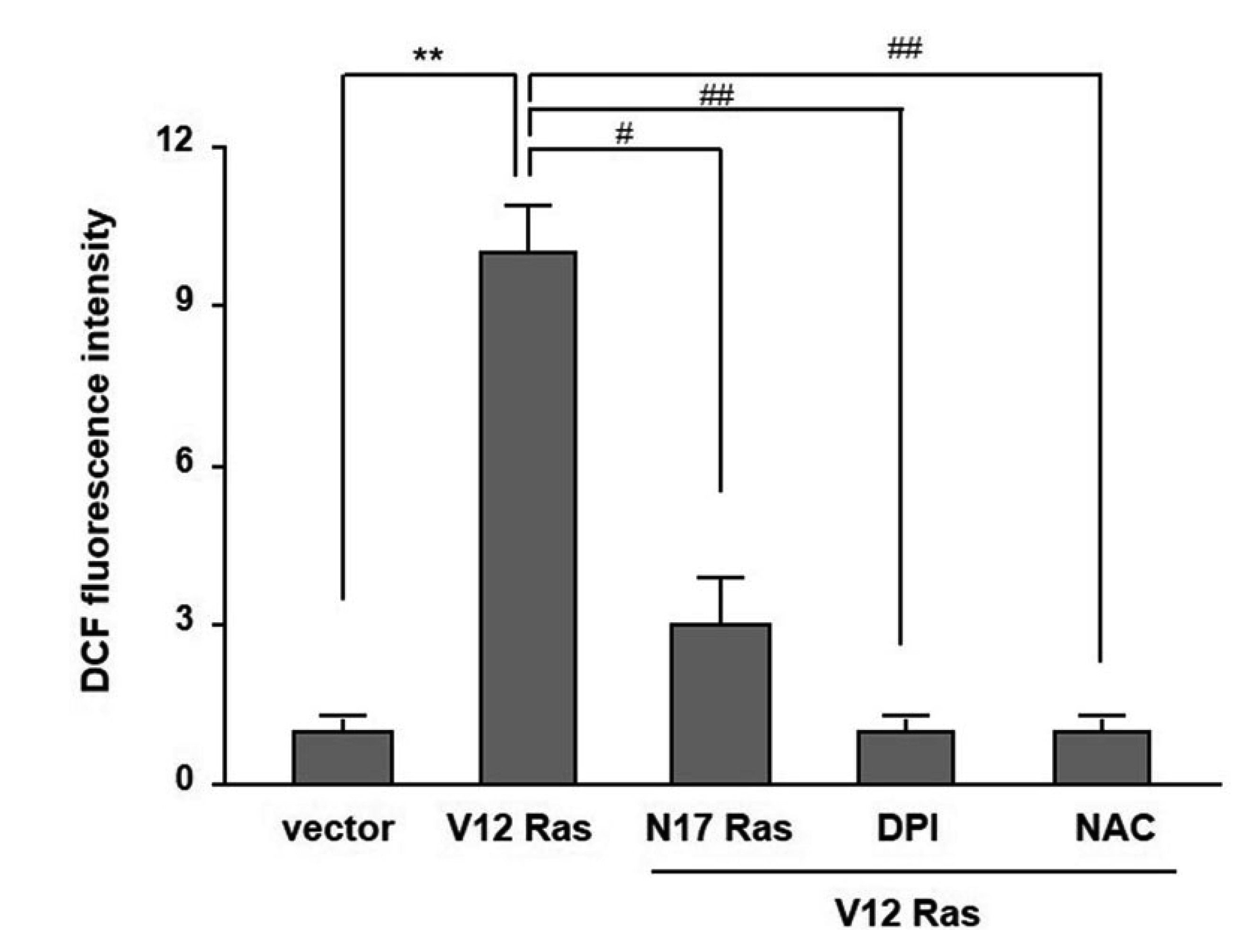
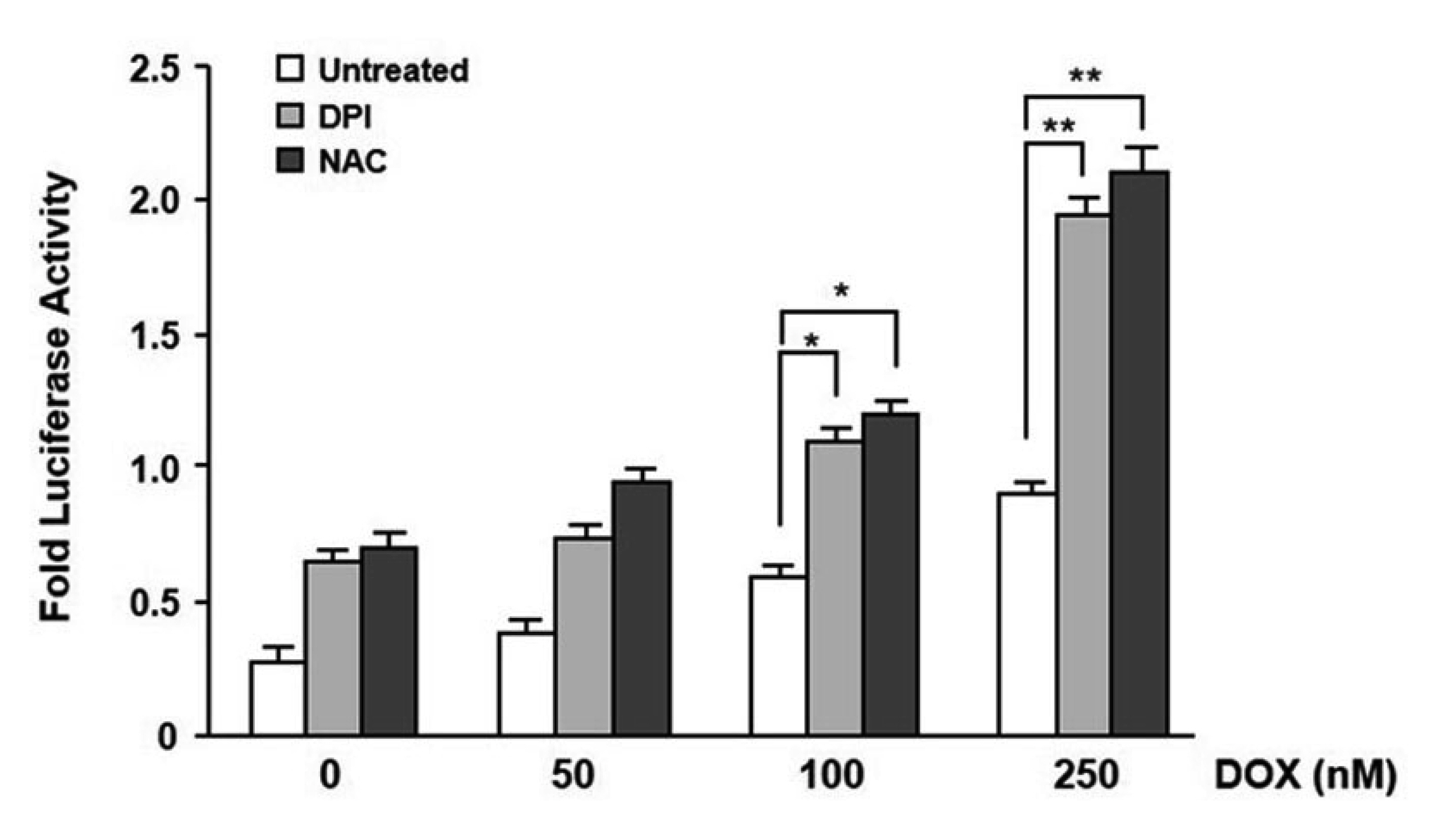
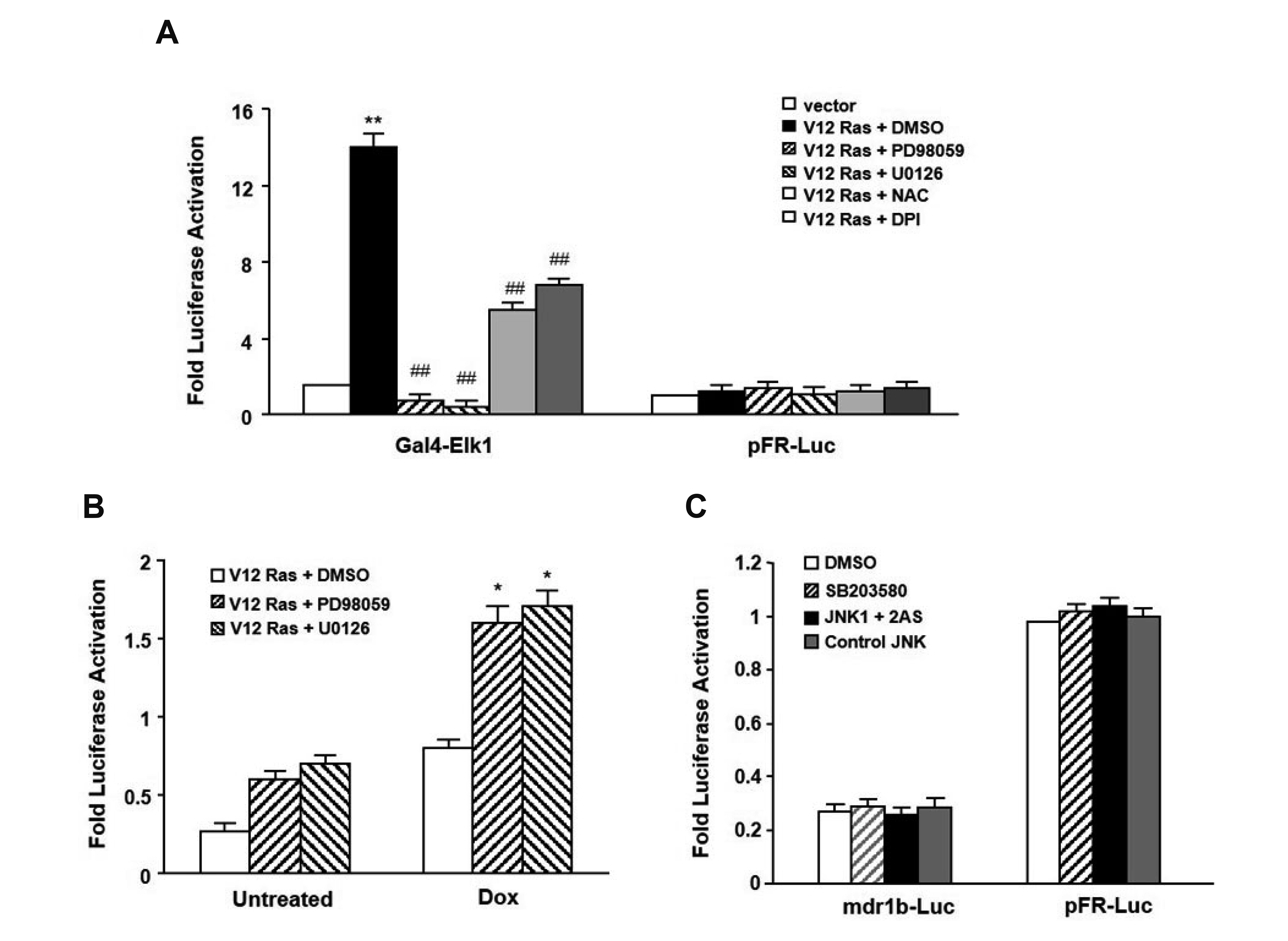
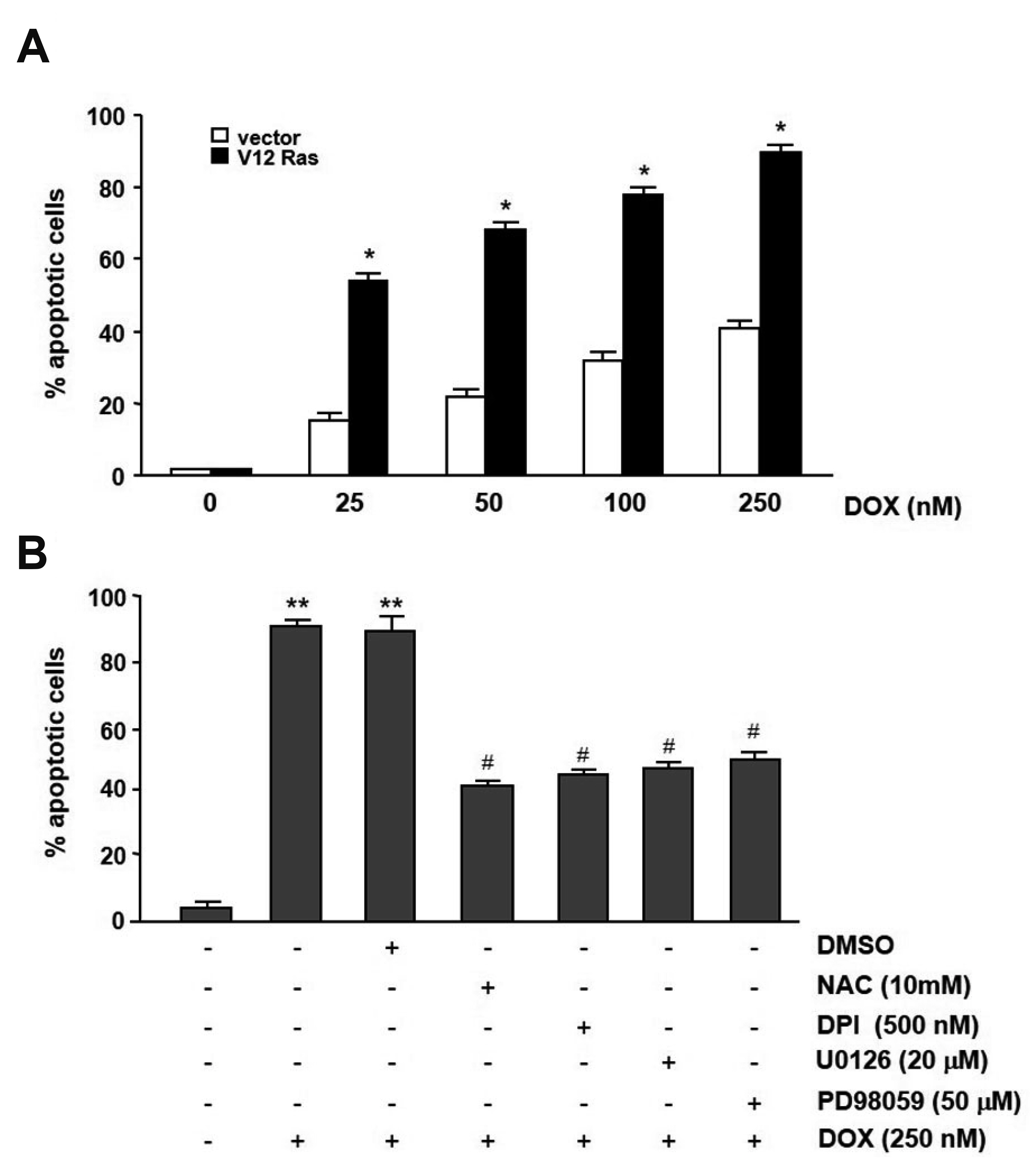
- In the present study, we investigated the effect of oncogenic H-Ras on rat mdr1b expression in NIH3T3 cells. The constitutive expression of H-RasV12 was found to downregulate the mdr1b promoter activity and mdr1b mRNA expression. The doxorubicin-induced mdr1b promoter activity of the H-RasV12 expressing NIH3T3 cells was markedly lower than that of control NIH3T3 cells. Additionally, there is a positive correlation between the level of H-RasV12 expression and a sensitivity to doxorubicin toxicity. To examine the detailed mechanism of H-RasV12-mediated down-regulation of mdr1b expression, antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenylene iodonium (DPI) were used. Pretreating cells with either NAC or DPI significantly enhanced the oncogenic H-Ras-mediated down-regulation of mdr1b expression and markedly prevented doxorubicin-induced cell death. Moreover, NAC and DPI treatment led to a decrease in ERK activity, and the ERK inhibitors PD98059 or U0126 enhanced the mdr1b-Luc activity of H-RasV12-NIH3T3 and reduced doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. These data suggest that RasV12 expression could downregulate mdr1b expression through intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and ERK activation induced by ROS, is at least in part, contributed to the downregulation of mdr1b expression.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakai E, Park K, Yawata T, Chihara T, Kumazawa A, Nakabayashi H, Shimizu K. 2009; Enhanced MDR1 expression and chemoresistance of cancer stem cells derived from glioblastoma. Cancer Invest. 27:901–908. DOI: 10.3109/07357900801946679. PMID: 19832037.
Article2. Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. 2002; Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:48–58. DOI: 10.1038/nrc706. PMID: 11902585.
Article3. Silva R, Vilas-Boas V, Carmo H, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Carvalho F, de Lourdes Bastos M, Remião F. 2015; Modulation of P-glycoprotein efflux pump: induction and activation as a therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol Ther. 149:1–123. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.11.013. PMID: 25435018.
Article4. Malumbres M, Barbacid M. 2003; RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:459–465. DOI: 10.1038/nrc1097. PMID: 12778136.
Article5. Prior IA, Lewis PD, Mattos C. 2012; A comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res. 72:2457–2467. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2612. PMID: 22589270. PMCID: PMC3354961.
Article6. Burt RK, Garfield S, Johnson K, Thorgeirsson SS. 1988; Transformation of rat liver epithelial cells with v-H-ras or v-raf causes expression of MDR-1, glutathione-S-transferase-P and increased resistance to cytotoxic chemicals. Carcinogenesis. 9:2329–2332. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/9.12.2329. PMID: 2903802.
Article7. Wishart GC, Plumb JA, Spandidos DA, Kerr DJ. 1991; H-ras infection in mink lung epithelial cells may induce "atypical" multidrug resistance. Eur J Cancer. 27:673. DOI: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90249-D. PMID: 1828985.8. Sabbatini AR, Basolo F, Valentini P, Mattii L, Calvo S, Fiore L, Ciardiello F, Petrini M. 1994; Induction of multidrug resistance (MDR) by transfection of MCF-10A cell line with c-Ha-ras and c-erbB-2 oncogenes. Int J Cancer. 59:208–211. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.2910590212. PMID: 7927921.9. Di Simone D, Galimberti S, Basolo F, Ciardiello F, Petrini M, Scheper RJ. 1997; c-Ha-ras transfection and expression of MDR-related genes in MCF-10A human breast cell line. Anticancer Res. 17(5A):3587–3592. PMID: 9413207.10. Schaich M, Ritter M, Illmer T, Lisske P, Thiede C, Schäkel U, Mohr B, Ehninger G, Neubauer A. 2001; Mutations in ras proto-oncogenes are associated with lower mdr1 gene expression in adult acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 112:300–307. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02562.x. PMID: 11167822.
Article11. Kramer R, Weber TK, Arceci R, Morse B, Simpson H, Steele GD Jr, Summerhayes IC. 1993; Modulation of mdr-1 expression by a H-ras oncogene in a human colon carcinoma cell line. Int J Cancer. 54:275–281. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.2910540219. PMID: 8098015.
Article12. Ferro E, Goitre L, Retta SF, Trabalzini L. 2012; The interplay between ROS and Ras GTPases: physiological and pathological implications. J Signal Transduct. 2012:365769. DOI: 10.1155/2012/365769. PMID: 22175014. PMCID: PMC3235814.
Article13. Archer H, Bar-Sagi D. 2002; Ras and Rac as activators of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Methods Mol Biol. 189:67–73. DOI: 10.1385/1-59259-281-3:067. PMID: 12094595.
Article14. Xu W, Trepel J, Neckers L. 2011; Ras, ROS and proteotoxic stress: a delicate balance. Cancer Cell. 20:281–282. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.08.020. PMID: 21907917. PMCID: PMC3179373.
Article15. Yu C, Argyropoulos G, Zhang Y, Kastin AJ, Hsuchou H, Pan W. 2008; Neuroinflammation activates Mdr1b efflux transport through NFkappaB: promoter analysis in BBB endothelia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 22:745–756. DOI: 10.1159/000185558. PMID: 19088456. PMCID: PMC2677694.16. Silverman JA, Hill BA. 1995; Characterization of the basal and carcinogen regulatory elements of the rat mdr1b promoter. Mol Carcinog. 13:50–59. DOI: 10.1002/mc.2940130109. PMID: 7766310.17. Hirsch-Ernst KI, Kietzmann T, Ziemann C, Jungermann K, Kahl GF. 2000; Physiological oxygen tensions modulate expression of the mdr1b multidrug-resistance gene in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. Biochem J. 350 Pt 2:434–451. DOI: 10.1042/bj3500443. PMID: 10947958.
Article18. Ziemann C, Bürkle A, Kahl GF, Hirsch-Ernst KI. 1999; Reactive oxygen species participate in mdr1b mRNA and P-glycoprotein overexpression in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. Carcinogenesis. 20:407–414. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/20.3.407. PMID: 10190554.
Article19. Deng L, Lin-Lee YC, Claret FX, Kuo MT. 2001; 2-acetylaminofluorene up-regulates rat mdr1b expression through generating reactive oxygen species that activate NF-kappa B pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:413–420. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M004551200. PMID: 11020383.20. Bost F, McKay R, Dean N, Mercola D. 1997; The JUN kinase/stress-activated protein kinase pathway is required for epidermal growth factor stimulation of growth of human A549 lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 272:33422–33429. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.272.52.33422. PMID: 9407138.
Article21. Lehmann T, Köhler C, Weidauer E, Taege C, Foth H. 2001; Expression of MRP1 and related transporters in human lung cells in culture. Toxicology. 167:59–72. DOI: 10.1016/S0300-483X(01)00458-9. PMID: 11557130.
Article22. Irani K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Sollott SJ, Der CJ, Fearon ER, Sundaresan M, Finkel T, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ. 1997; Mitogenic signaling mediated by oxidants in Ras-transformed fibroblasts. Science. 275:1649–1652. DOI: 10.1126/science.275.5306.1649. PMID: 9054359.
Article23. Yang JQ, Li S, Domann FE, Buettner GR, Oberley LW. 1999; Superoxide generation in v-Ha-ras-transduced human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Mol Carcinog. 26:180–188. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2744(199911)26:3<180::AID-MC7>3.0.CO;2-4. PMID: 10559793.
Article24. Huang WJ, Tung CW, Ho C, Yang JT, Chen ML, Chang PJ, Lee PH, Lin CL, Wang JY. 2007; Ras activation modulates methylglyoxal-induced mesangial cell apoptosis through superoxide production. Ren Fail. 29:911–921. DOI: 10.1080/08860220701573509. PMID: 17994461.
Article25. Liu R, Li B, Qiu M. 2001; Elevated superoxide production by active H-ras enhances human lung WI-38VA-13 cell proliferation, migration and resistance to TNF-alpha. Oncogene. 20:1486–1496. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204214. PMID: 11313892.26. Gupta A, Rosenberger SF, Bowden GT. 1999; Increased ROS levels contribute to elevated transcription factor and MAP kinase activities in malignantly progressed mouse keratinocyte cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 20:2063–2073. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/20.11.2063. PMID: 10545407.
Article27. Chin KV, Ueda K, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. 1992; Modulation of activity of the promoter of the human MDR1 gene by Ras and p53. Science. 255:459–462. DOI: 10.1126/science.1346476. PMID: 1346476.
Article28. Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang DG, Pae HO. 2011; Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal Transduct. 2011:792639. DOI: 10.1155/2011/792639. PMID: 21637379. PMCID: PMC3100083.
Article29. Zhou G, Kuo MT. 1998; Wild-type p53-mediated induction of rat mdr1b expression by the anticancer drug daunorubicin. J Biol Chem. 273:15387–15394. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.273.25.15387. PMID: 9624121.30. Zhou G, Kuo MT. 1997; NF-kappaB-mediated induction of mdr1b expression by insulin in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 272:15174–15183. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.272.24.15174. PMID: 9182539.31. Yu L, Cohen D, Piekarz RL, Horwitz SB. 1993; Three distinct nuclear protein binding sites in the promoter of the murine multidrug resistance mdr1b gene. J Biol Chem. 268:7520–7526. PMID: 8096513.
Article32. Yu L, Wu Q, Yang CP, Horwitz SB. 1995; Coordination of transcription factors, NF-Y and C/EBP beta, in the regulation of the mdr1b promoter. Cell Growth Differ. 6:1505–1512. PMID: 9019155.33. Yin Z, Machius M, Nestler EJ, Rudenko G. 2017; Activator protein-1: redox switch controlling structure and DNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:11425–11436. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx795. PMID: 28981703. PMCID: PMC5737521.
Article34. Novitskiĭ VV, Riazantseva NV, Chasovskikh NIu, Starikova EG, Kaĭgorodova EV, Starikov IuV, Filipenko ML, Boiarskikh UA. 2009; [The role of p53 and NF-kappaB transcription factors in redox-dependent dysregulation of mononuclear leukocyte apoptosis]. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. (4):3–7. Russian. DOI: 10.1134/S1990519X09040014. PMID: 19517606.35. Nakshatri H, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Currie RA. 1996; Subunit association and DNA binding activity of the heterotrimeric transcription factor NF-Y is regulated by cellular redox. J Biol Chem. 271:28784–28791. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.271.46.28784. PMID: 8910521.
Article36. Wartenberg M, Fischer K, Hescheler J, Sauer H. 2000; Redox regulation of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in multicellular prostate tumor spheroids. Int J Cancer. 85:267–274. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000115)85:2<267::AID-IJC19>3.0.CO;2-H. PMID: 10629088.
Article37. Wartenberg M, Ling FC, Schallenberg M, Bäumer AT, Petrat K, Hescheler J, Sauer H. 2001; Down-regulation of intrinsic P-glycoprotein expression in multicellular prostate tumor spheroids by reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem. 276:17420–17428. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M100141200. PMID: 11279018.
Article38. Uchiumi T, Kohno K, Tanimura H, Matsuo K, Sato S, Uchida Y, Kuwano M. 1993; Enhanced expression of the human multidrug resistance 1 gene in response to UV light irradiation. Cell Growth Differ. 4:147–157. PMID: 8466853.39. Miyazaki M, Kohno K, Uchiumi T, Tanimura H, Matsuo K, Nasu M, Kuwano M. 1992; Activation of human multidrug resistance-1 gene promoter in response to heat shock stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 187:677–684. DOI: 10.1016/0006-291X(92)91248-O. PMID: 1356336.
Article40. Hirsch-Ernst KI, Ziemann C, Foth H, Kozian D, Schmitz-Salue C, Kahl GF. 1998; Induction of mdr1b mRNA and P-glycoprotein expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. J Cell Physiol. 176:506–515. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199809)176:3<506::AID-JCP7>3.0.CO;2-S. PMID: 9699503.
Article41. Fardel O, Lecureur V, Corlu A, Guillouzo A. 1996; P-glycoprotein induction in rat liver epithelial cells in response to acute 3-methylcholanthrene treatment. Biochem Pharmacol. 51:1427–1436. DOI: 10.1016/0006-2952(96)00081-0. PMID: 8630083.
Article42. Tainton KM, Smyth MJ, Jackson JT, Tanner JE, Cerruti L, Jane SM, Darcy PK, Johnstone RW. 2004; Mutational analysis of P-glycoprotein: suppression of caspase activation in the absence of ATP-dependent drug efflux. Cell Death Differ. 11:1028–1037. DOI: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401440. PMID: 15131592.
Article43. Johnstone RW, Cretney E, Smyth MJ. 1999; P-glycoprotein protects leukemia cells against caspase-dependent, but not caspase-independent, cell death. Blood. 93:1075–1085. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V93.3.1075. PMID: 9920858.
Article44. Schreck R, Rieber P, Baeuerle PA. 1991; Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 10:2247–2258. DOI: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. PMID: 2065663. PMCID: PMC452914.
Article45. Moloney JN, Cotter TG. 2018; ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 80:50–64. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.023. PMID: 28587975.
Article46. Burdon RH, Gill V, Alliangana D. 1996; Hydrogen peroxide in relation to proliferation and apoptosis in BHK-21 hamster fibroblasts. Free Radic Res. 24:81–93. DOI: 10.3109/10715769609088004. PMID: 8845916.
Article47. Kang CD, Ahn BK, Jeong CS, Kim KW, Lee HJ, Yoo SD, Chung BS, Kim SH. 2000; Downregulation of JNK/SAPK activity is associated with the cross-resistance to P-glycoprotein-unrelated drugs in multidrug-resistant FM3A/M cells overexpressing P-glycoprotein. Exp Cell Res. 256:300–307. DOI: 10.1006/excr.2000.4807. PMID: 10739677.
Article48. Osborn MT, Chambers TC. 1996; Role of the stress-activated/c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase pathway in the cellular response to adriamycin and other chemotherapeutic drugs. J Biol Chem. 271:30950–30955. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.271.48.30950. PMID: 8940082.
Article49. Barancík M, Bohácová V, Kvackajová J, Hudecová S, Krizanová O, Breier A. 2001; SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38-MAPK pathway, is a new reversal agent of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Eur J Pharm Sci. 14:29–36. DOI: 10.1016/S0928-0987(01)00139-7. PMID: 11457647.50. Ding S, Chamberlain M, McLaren A, Goh L, Duncan I, Wolf CR. 2001; Cross-talk between signalling pathways and the multidrug resistant protein MDR-1. Br J Cancer. 85:1175–1184. DOI: 10.1054/bjoc.2001.2044. PMID: 11710832. PMCID: PMC2375166.
Article51. Osborn MT, Berry A, Ruberu MS, Ning B, Bell LM, Chambers TC. 1999; Phorbol ester induced MDR1 expression in K562 cells occurs independently of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Oncogene. 18:5756–5764. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202943. PMID: 10523856.
Article52. McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F, Libra M, Basecke J, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Franklin RA. 2007; Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:1263–1284. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001. PMID: 17126425. PMCID: PMC2696318.
Article53. Abrams SL, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Wong EW, Chappell WH, Bäsecke J, Stivala F, Donia M, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Martelli AM, McCubrey JA. 2010; The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway can govern drug resistance, apoptosis and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Cell Cycle. 9:1781–1791. DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.9.11483. PMID: 20436278. PMCID: PMC3781182.
Article54. Hollmann CA, Owens T, Nalbantoglu J, Hudson TJ, Sladek R. 2006; Constitutive activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase predisposes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines to CD40-mediated cell death. Cancer Res. 66:3550–3557. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2498. PMID: 16585179.
Article55. Kulich SM, Chu CT. 2001; Sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by 6-hydroxydopamine: implications for Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 77:1058–1066. DOI: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00304.x. PMID: 11359871.
Article56. Wang X, Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ. 2000; Requirement for ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 275:39435–39443. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M004583200. PMID: 10993883.
Article57. Joneson T, White MA, Wigler MH, Bar-Sagi D. 1996; Stimulation of membrane ruffling and MAP kinase activation by distinct effectors of RAS. Science. 271:810–812. DOI: 10.1126/science.271.5250.810. PMID: 8628998.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Generation of Free Oxygen Radicals in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Mucosa
- Do Reactive Oxygen Species Cause Aging?
- Effect of Salicylate on the Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Expression and Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Formation in Human Mesangial Cells
- Epilepsy, Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondria
- Mycophenolic Acid Induced Apoptosis in Human Jurkat Cells viathe Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species