J Pathol Transl Med.
2020 May;54(3):237-245. 10.4132/jptm.2020.02.08.
Gene variant profiles and tumor metabolic activity as measured by FOXM1 expression and glucose uptake in lung adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Rush University College of Health Sciences, Chicago, IL, USA
- 2Department of Pathology, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA
- KMID: 2501659
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.02.08
Abstract
- Background
Cancer cells displaying aberrant metabolism switch energy production from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis. Measure of glucose standardized uptake value (SUV) by positron emission tomography (PET), used for staging of adenocarcinoma in high-risk patients, can reflect cellular use of the glycolysis pathway. The transcription factor, FOXM1 plays a role in regulation of glycolytic genes. Cancer cell transformation is driven by mutations in tumor suppressor genes such as TP53 and STK11 and oncogenes such as KRAS and EGFR. In this study, SUV and FOXM1 gene expression were compared in the background of selected cancer gene mutations.
Methods
Archival tumor tissue from cases of lung adenocarcinoma were analyzed. SUV was collected from patient records. FOXM1 gene expression was assessed by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Gene mutations were detected by allele-specific PCR and gene sequencing.
Results
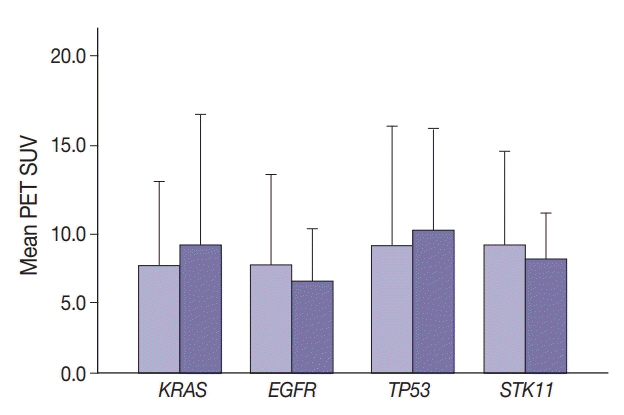
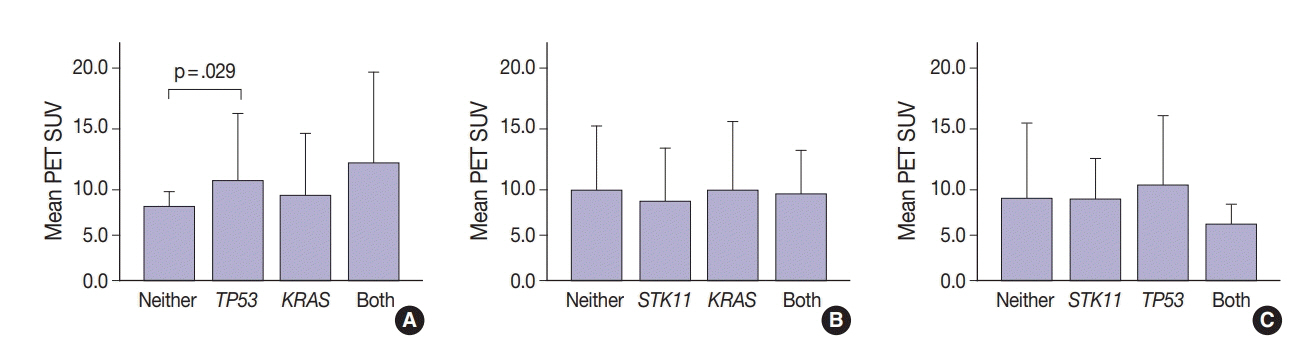
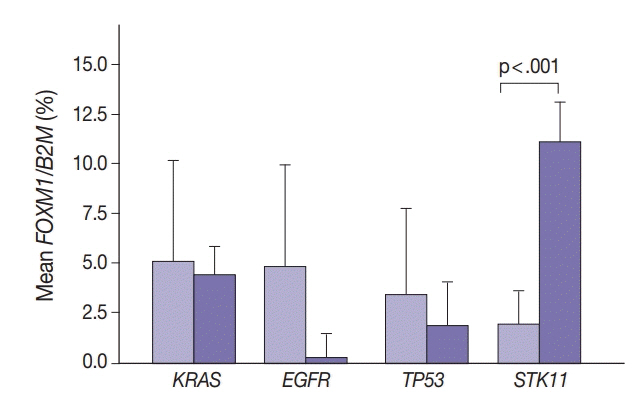
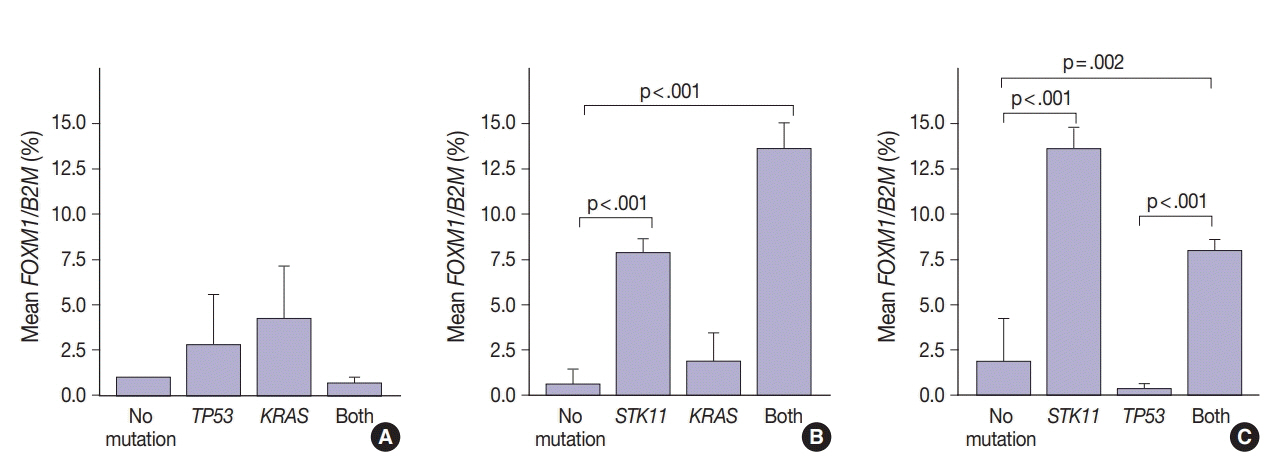
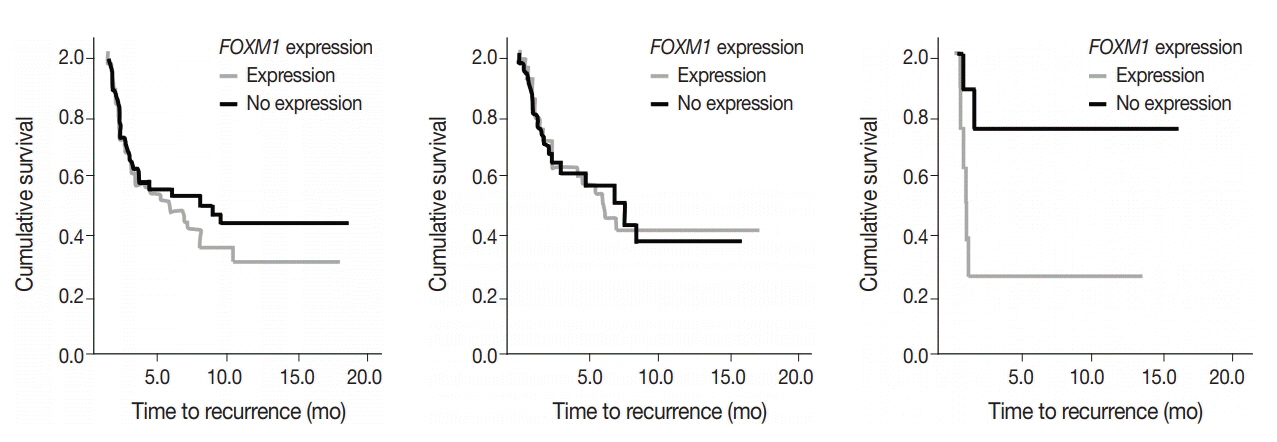
SUV and FOXM1 gene expression patterns differed in the presence of single and coexisting gene mutations. Gene mutations affected SUV and FOXM1 differently. EGFR mutations were found in tumors with lower FOXM1 expression but did not affect SUV. Tumors with TP53 mutations had increased SUV (p = .029). FOXM1 expression was significantly higher in tumors with STK11 mutations alone (p < .001) and in combination with KRAS or TP53 mutations (p < .001 and p = .002, respectively).
Conclusions
Cancer gene mutations may affect tumor metabolic activity. These observations support consideration of tumor cell metabolic state in the presence of gene mutations for optimal prognosis and treatment strategy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tomasini P, Mascaux C, Jao K, et al. Effect of coexisting KRAS and TP53 mutations in patients treated with chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019; 20:e338–45.2. Aggarwal C, Davis CW, Mick R, et al. Influence of TP53 mutation on survival in patients with advanced EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. JCO Precis Oncol. 2018; Aug. 31. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.18.00107.
Article3. Ding M, Li F, Wang B, Chi G, Liu H. A comprehensive analysis of WGCNA and serum metabolomics manifests the lung cancer-associated disordered glucose metabolism. J Cell Biochem. 2019; 120:10855–63.
Article4. Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011; 11:85–95.
Article5. Soga T. Cancer metabolism: key players in metabolic reprogramming. Cancer Sci. 2013; 104:275–81.
Article6. Park HL, Yoo IR, Boo SH, et al. Does FDG PET/CT have a role in determining adjuvant chemotherapy in surgical margin-negative stage IA non-small cell lung cancer patients? J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019; 145:1021–6.
Article7. Brun C, Gay P, Cottier M, et al. Comparison of cytology, chest computed and positron emission tomography findings in malignant pleural effusion from lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10:6903–11.
Article8. Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009; 324:1029–33.
Article9. Cui J, Shi M, Xie D, et al. FOXM1 promotes the warburg effect and pancreatic cancer progression via transactivation of LDHA expression. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20:2595–606.10. Liao GB, Li XZ, Zeng S, et al. Regulation of the master regulator FOXM1 in cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2018; 16:57.11. He Y, Yu D, Zhu L, Zhong S, Zhao J, Tang J. miR-149 in human cancer: a systemic review. J Cancer. 2018; 9:375–88.
Article12. Xu K, Liu X, Mao X, et al. MicroRNA-149 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion by directly targeting forkhead box transcription factor FOXM1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35:499–515.13. Wierstra I, Alves J. FOXM1, a typical proliferation-associated transcription factor. Biol Chem. 2007; 388:1257–74.14. Wang IC, Ustiyan V, Zhang Y, Cai Y, Kalin TV, Kalinichenko VV. FOXM1 transcription factor is required for the initiation of lung tumorigenesis by oncogenic KRAS(G12D.). Oncogene. 2014; 33:5391–6.15. Wang IC, Snyder J, Zhang Y, et al. FOXM1 mediates cross talk between KRAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase and canonical Wnt pathways during development of respiratory epithelium. Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 32:3838–50.16. Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC) [Internet]. Hinxton: Wellcome Sanger Institute;2020. [cited 2020 Feb 2]. Available from: https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic.17. Arbour KC, Jordan E, Kim HR, et al. Effects of co-occurring genomic alterations on outcomes in patients with KRAS-mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018; 24:334–40.18. Zhu L, Yin G, Chen W, et al. Correlation between EGFR mutation status and F(18) -fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography image features in lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac Cancer. 2019; 10:659–64.19. Kim HS, Mendiratta S, Kim J, et al. Systematic identification of molecular subtype-selective vulnerabilities in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell. 2013; 155:552–66.
Article20. Saavedra-Garcia P, Nichols K, Mahmud Z, Fan LY, Lam EW. Unravelling the role of fatty acid metabolism in cancer through the FoxO3-FOXM1 axis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018; 462:82–92.21. Tanaka N, Zhao M, Tang L, et al. Gain-of-function mutant p53 promotes the oncogenic potential of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting the transcription factors FoxO3a and FOXM1. Oncogene. 2018; 37:1279–92.22. Shimamura T, Chen Z, Soucheray M, et al. Efficacy of BET bromodomain inhibition in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:6183–92.23. Kompier LC, Lurkin I, van der Aa MN, van Rhijn BW, van der Kwast TH, Zwarthoff EC. FGFR3, HRAS, KRAS, NRAS and PIK3CA mutations in bladder cancer and their potential as biomarkers for surveillance and therapy. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e13821.24. He SY, Shen HW, Xu L, et al. FOXM1 promotes tumor cell invasion and correlates with poor prognosis in early-stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2012; 127:601–10.25. Wang IC, Meliton L, Ren X, et al. Deletion of Forkhead Box M1 transcription factor from respiratory epithelial cells inhibits pulmonary tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6609.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A gene expression signature of FOXM1 predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Decreased Expression of Surfactant Protein Genes Is Associated with an Increased Expression of Forkhead Box M1 Gene in the Fetal Lung Tissues of Premature Rabbits
- Urushiol V Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Enhances Antitumor Activity of 5-FU in Human Colon Cancer Cells by Downregulating FoxM1
- The Relationship between F-18-FDG Uptake, Hexokinase Activity and Glut-1 Expression in Various Human Cancer Cell Lines
- Glut1 Expression and FDG Uptake in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Its Relationship to Histopathologic Types and Proliferation Rate