Int J Stem Cells.
2020 Mar;13(1):46-54. 10.15283/ijsc19088.
miR-450a-5p Eliminates MGO-Induced Insulin Resistance via Targeting CREB
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology, Jingmen No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jingmen, China
- KMID: 2500565
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc19088
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
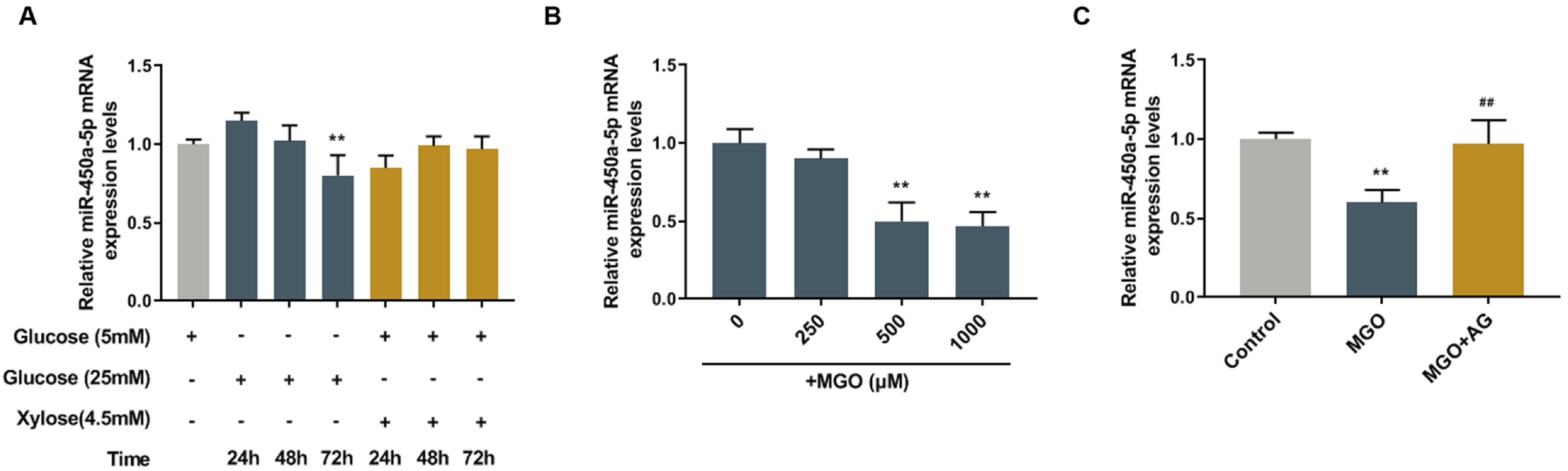
miR-450a-5p was involved in fat formation, however, its role in insulin resistance remains unclear. This study investigated the effects of miR-450a-5p on endothelial cells, with the aim of finding a potential target for diabetes mellitus.
Methods and Results
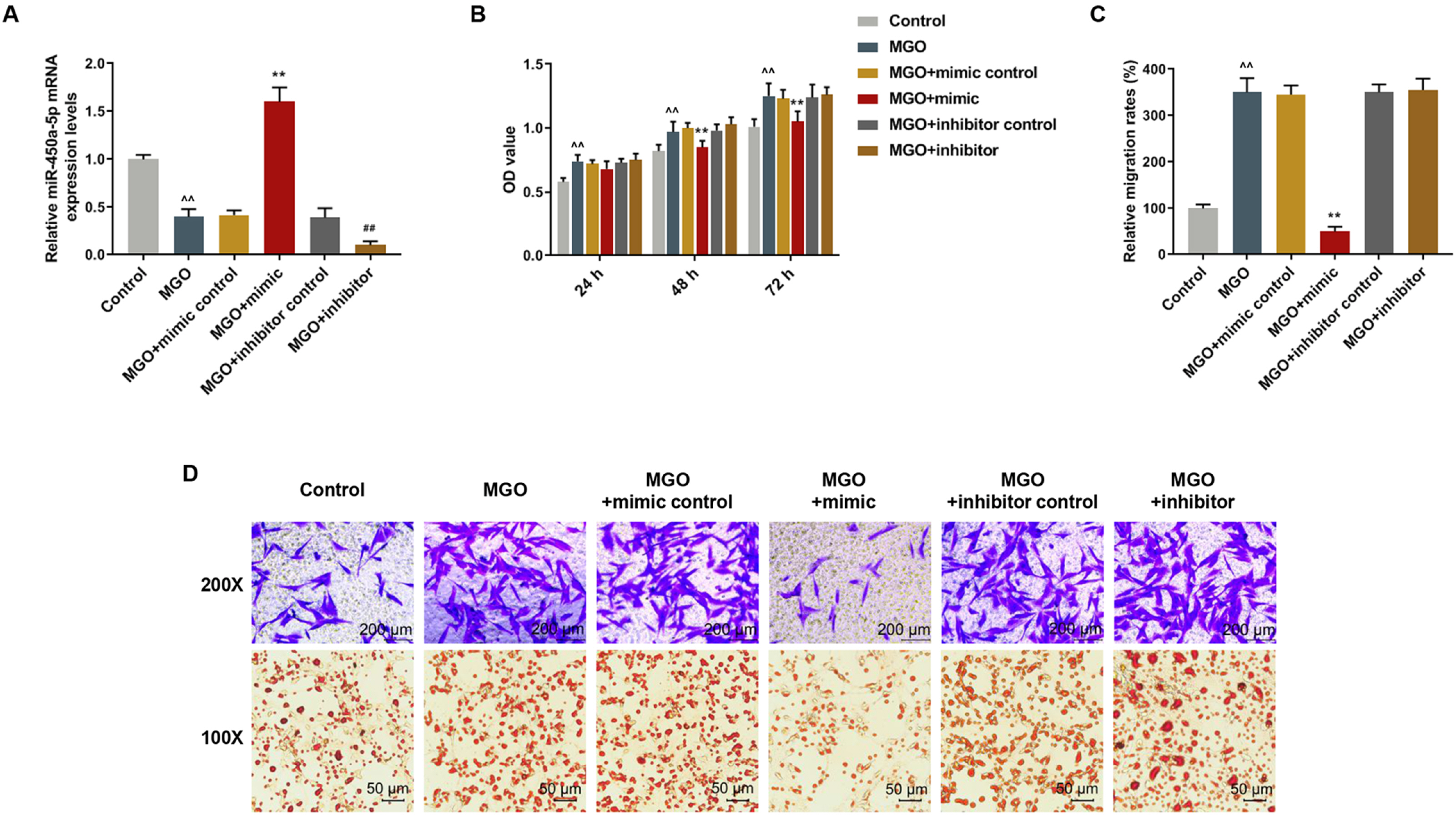
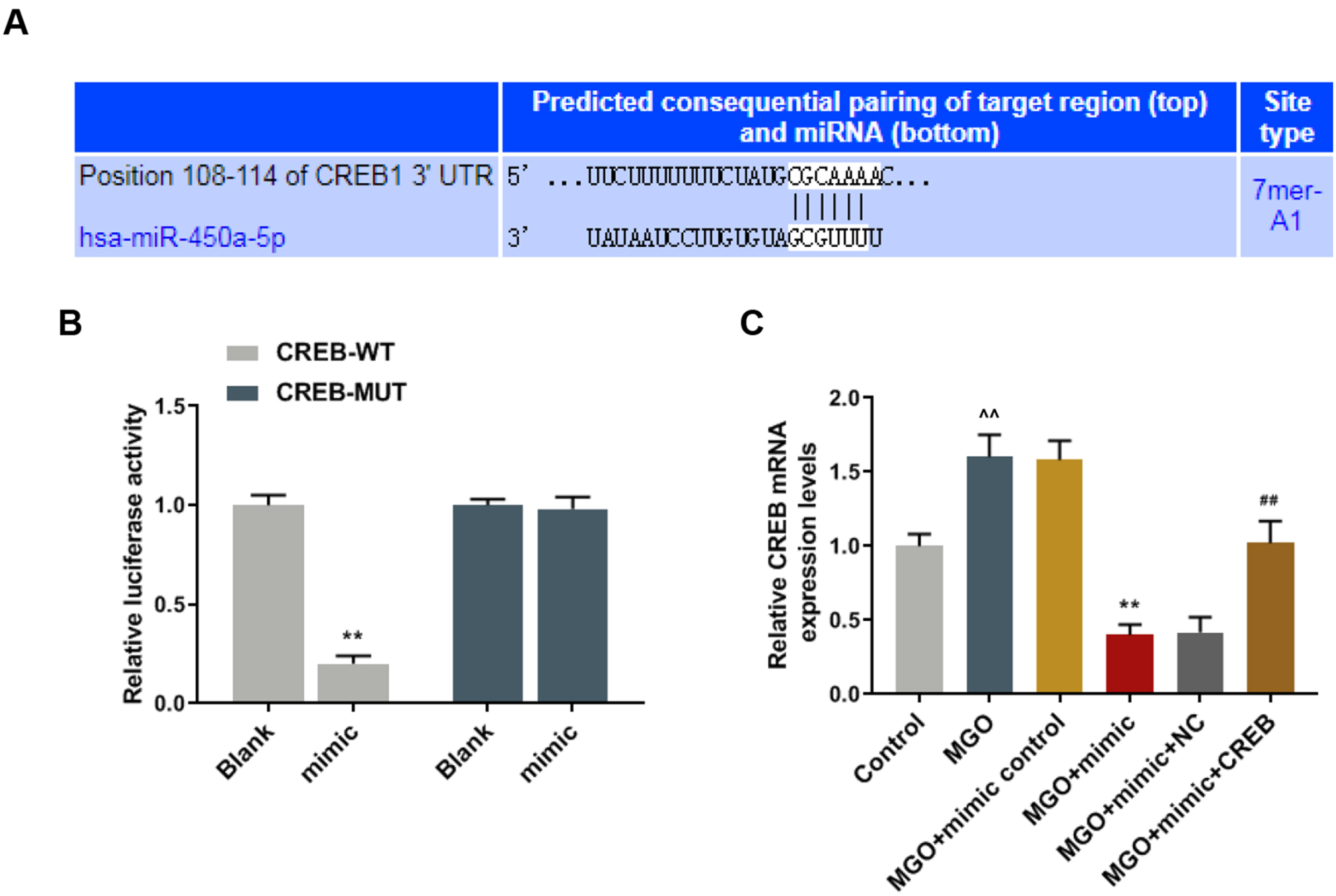
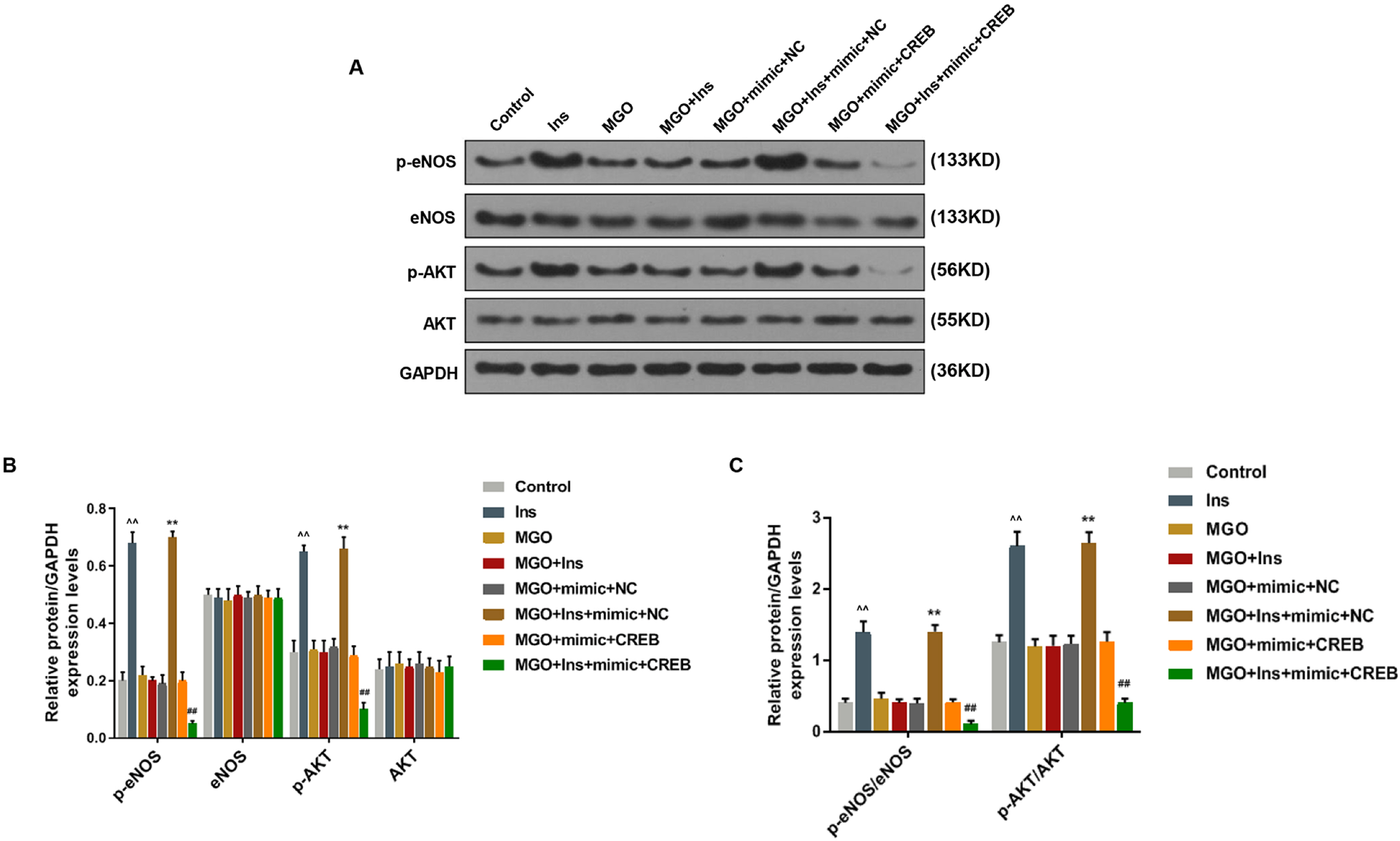
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were treated with low-glucose, high-glucose, methylglyoxal (MGO), and insulin alone or in combination with MGO. The expression of miR-450a-5p in treated cells was measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assays. The cell activity, migration and fat formation were determined by MTT experiments, Transwell assay and oil red O staining. The expressions of eNOS/ AKT pathway-related proteins in cells were assessed by Western blot (WB) analysis. Furthermore, the target gene of miR-450a-5p was analyzed by double-luciferase reporter analysis, and its effects on eNOS/AKT pathway were estimated. We found that the expression of miR-450a-5p was decreased obviously in endothelial cells treated with high-glucose and MGO. In vitro cell experiments showed that MGO could not only promote the activity of endothelial cells, but also accelerate cell migration and fat accumulation, which, however, could be reversed by up-regulation of miR-450a-5p. Moreover, MGO inhibited eNOS/AKT pathway activation and NO release mediated by insulin, and such effects were reversed by up-regulation of miR-450a-5p. Furthermore, CREB was the target gene for miR-450a-5p, had an activation effect on the eNOS/AKT pathway.
Conclusions
Up-regulated miR-450a-5p eliminates MGO-induced insulin resistance via targeting CREB, and therefore could be used as a potential target to improve insulin resistance and treat patients with diabetes-related diseases.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Czech MP. 2017; Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Med. 23:804–814. DOI: 10.1038/nm.4350. PMID: 28697184. PMCID: PMC6048953.
Article2. Shamsaldeen YA, Mackenzie LS, Lione LA, Benham CD. 2016; Methylglyoxal, a metabolite increased in diabetes is associated with insulin resistance, vascular dysfunction and neuropathies. Curr Drug Metab. 17:359–367. DOI: 10.2174/1389200217666151222155216. PMID: 26965039.
Article3. Matafome P, Rodrigues T, Sena C, Seiça R. 2017; Methylglyoxal in metabolic disorders: facts, myths, and promises. Med Res Rev. 37:368–403. DOI: 10.1002/med.21410. PMID: 27636890.
Article4. Nigro C, Raciti GA, Leone A, Fleming TH, Longo M, Prevenzano I, Fiory F, Mirra P, D'Esposito V, Ulianich L, Nawroth PP, Formisano P, Beguinot F, Miele C. 2014; Methylglyoxal impairs endothelial insulin sensitivity both in vitro and in vivo. Diabetologia. 57:1485–1494. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-014-3243-7. PMID: 24759959.
Article5. Hanssen NMJ, Scheijen JLJM, Jorsal A, Parving HH, Tarnow L, Rossing P, Stehouwer CDA, Schalkwijk CG. 2017; Higher plasma methylglyoxal levels are associated with incident cardiovascular disease in individuals with type 1 diabetes: a 12-year follow-up study. Diabetes. 66:2278–2283. DOI: 10.2337/db16-1578. PMID: 28588100.
Article6. Nigro C, Leone A, Raciti GA, Longo M, Mirra P, Formisano P, Beguinot F, Miele C. 2017; Methylglyoxal-Glyoxalase 1 balance: the root of vascular damage. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E188. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18010188. PMID: 28106778. PMCID: PMC5297820.
Article7. Wang XJ, Ma SB, Liu ZF, Li H, Gao WY. 2019; Elevated levels of α-dicarbonyl compounds in the plasma of type II diabetics and their relevance with diabetic nephropathy. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1106(1107):19–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.12.027. PMID: 30639946.8. Kim J, Lee YM, Kim CS, Sohn E, Jo K, Shin SD, Kim JS. 2013; Ethyl pyruvate prevents methyglyoxal-induced retinal vascular injury in rats. J Diabetes Res. 2013:460820. DOI: 10.1155/2013/460820. PMID: 23671872. PMCID: PMC3647584.
Article9. Maessen DE, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk CG. 2015; The role of methylglyoxal and the glyoxalase system in diabetes and other age-related diseases. Clin Sci (Lond). 128:839–861. DOI: 10.1042/CS20140683. PMID: 25818485.
Article10. Zendjabil M, Favard S, Tse C, Abbou O, Hainque B. 2017; [The microRNAs as biomarkers: what prospects?]. C R Biol. 340:114–131. French. DOI: 10.1016/j.crvi.2016.12.001. PMID: 28081967.11. Tiwari J, Gupta G, de Jesus Andreoli Pinto T, Sharma R, Pabreja K, Matta Y, Arora N, Mishra A, Sharma R, Dua K. 2018; Role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus. Panminerva Med. 60:25–28.
Article12. Li X. 2014; MiR-375, a microRNA related to diabetes. Gene. 533:1–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.105. PMID: 24120394.
Article13. Zhang Y, Yu M, Dai M, Chen C, Tang Q, Jing W, Wang H, Tian W. 2017; miR-450a-5p within rat adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles promotes adipogenic differentiation by targeting WISP2. J Cell Sci. 130:1158–1168. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.197764. PMID: 28167681.
Article14. Mirhashemi F, Scherneck S, Kluth O, Kaiser D, Vogel H, Kluge R, Schürmann A, Neschen S, Joost HG. 2011; Diet dependence of diabetes in the New Zealand Obese (NZO) mouse: total fat, but not fat quality or sucrose accelerates and aggravates diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 119:167–171. DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1263127. PMID: 20827663.
Article15. Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z, Lin X. 2013; An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. PMID: 25558171. PMCID: PMC4280562.16. Voziyan P, Brown KL, Chetyrkin S, Hudson B. 2014; Site-specific AGE modifications in the extracellular matrix: a role for glyoxal in protein damage in diabetes. Clin Chem Lab Med. 52:39–45. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0818. PMID: 23492568. PMCID: PMC4104777.
Article17. Schalkwijk CG. 2015; Vascular AGE-ing by methylglyoxal: the past, the present and the future. Diabetologia. 58:1715–1719. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-015-3597-5. PMID: 25962521. PMCID: PMC4499108.18. Liu H, Zhang N, Tian D. 2014; MiR-30b is involved in methylglyoxal-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial cells in rats. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 19:315–329. DOI: 10.2478/s11658-014-0199-z. PMID: 24898602. PMCID: PMC6276001.
Article19. Nigro C, Mirra P, Prevenzano I, Leone A, Fiory F, Longo M, Cabaro S, Oriente F, Beguinot F, Miele C. 2018; miR-214-Dependent increase of PHLPP2 levels mediates the impairment of insulin-stimulated akt activation in mouse aortic endothelial cells exposed to methylglyoxal. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E522. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020522. PMID: 29425121. PMCID: PMC5855744.
Article20. Li SS, Wu Y, Jin X, Jiang C. 2015; The SUR2B subunit of rat vascular KATP channel is targeted by miR-9a-3p induced by prolonged exposure to methylglyoxal. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 308:C139–C145. DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00311.2014. PMID: 25354529. PMCID: PMC4297771.
Article21. Ying C, Sui-Xin L, Kang-Ling X, Wen-Liang Z, Lei D, Yuan L, Fan Z, Chen Z. 2014; MicroRNA-492 reverses high glucose-induced insulin resistance in HUVEC cells through targeting resistin. Mol Cell Biochem. 391:117–125. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-014-1993-7. PMID: 24526524. PMCID: PMC4006129.
Article22. Wang X, Peng B, Xu C, Gao Z, Cao Y, Liu Z, Liu T. 2016; BDNF-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in ketamine-associated lower urinary tract symptoms. Int Urol Nephrol. 48:1387–1393. DOI: 10.1007/s11255-016-1315-y. PMID: 27165402.
Article23. Jia H, Xiaojuan L, Li Y, Jiarui Z, Qiao Z, Xinyi L, Miao L, Yanhong L. 2015; The effect of miR-450a-5p on the biological behavior of serous ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells. Modern Oncol. 7:829–896.24. Memon MA, Khan RN, Riaz S, Ain QU, Ahmed M, Kumar N. 2018; Methylglyoxal and insulin resistance in berberine-treated type 2 diabetic patients. J Res Med Sci. 23:110.25. De Nigris V, Pujadas G, La Sala L, Testa R, Genovese S, Ceriello A. 2015; Short-term high glucose exposure impairs insulin signaling in endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:114. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-015-0278-0. PMID: 26297582. PMCID: PMC4546318.
Article26. Farah C, Kleindienst A, Bolea G, Meyer G, Gayrard S, Geny B, Obert P, Cazorla O, Tanguy S, Reboul C. 2013; Exercise-induced cardioprotection: a role for eNOS uncoupling and NO metabolites. Basic Res Cardiol. 108:389. DOI: 10.1007/s00395-013-0389-2. PMID: 24105420.
Article27. Li JB, Wang HY, Yao Y, Sun QF, Liu ZH, Liu SQ, Zhuang JL, Wang YP, Liu HY. 2017; Overexpression of microRNA-138 alleviates human coronary artery endothelial cell injury and inflammatory response by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 21:1482–1491. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13074. PMID: 28371277. PMCID: PMC5542903.
Article28. Wang L, Hu XH, Huang ZX, Nie Q, Chen ZG, Xiang JW, Qi RL, Yang TH, Xiao Y, Qing WJ, Gigantelli G, Nguyen QD, Li DW. 2017; Regulation of CREB functions by phosphorylation and sumoylation in nervous and visual systems. Curr Mol Med. 16:885–892. DOI: 10.2174/1566524016666161223110106. PMID: 28017136.
Article29. de Jesus DS, DeVallance E, Li Y, Falabella M, Guimaraes D, Shiva S, Kaufman BA, Gladwin MT, Pagano PJ. 2019; Nox1/Ref-1-mediated activation of CREB promotes Gremlin1-driven endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Redox Biol. 22:101138. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101138. PMID: 30802716. PMCID: PMC6395885.
Article30. Hogan MF, Ravnskjaer K, Matsumura S, Huising MO, Hull RL, Kahn SE, Montminy M. 2015; Hepatic insulin resistance following chronic activation of the CREB coactivator CRTC2. J Biol Chem. 290:25997–26006. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.679266. PMID: 26342077. PMCID: PMC4646253.
Article31. Niwano K, Arai M, Koitabashi N, Hara S, Watanabe A, Sekiguchi K, Tanaka T, Iso T, Kurabayashi M. 2006; Competitive binding of CREB and ATF2 to cAMP/ATF responsive element regulates eNOS gene expression in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:1036–1042. DOI: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000215179.76144.39. PMID: 16497991.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MiR-542-5p Inhibits Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipoidemia by Targeting FOXO1 in the Liver
- Exosomal CircPRRX1 Enhances Doxorubicin Resistance in Gastric Cancer by Regulating MiR-3064-5p/PTPN14 Signaling
- Perioperative stress prolong post-surgical pain via miR-339-5p targeting oprm1 in the amygdala
- MSCs-Derived miR-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes Promote Skin Wound Healing by Activating PI3K/AKT Pathway through PTEN
- Down-regulation of microRNA-382-5p reduces neuropathic pain by targeting regulation of dual specificity phosphatase-1