Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2020 Apr;8(1):11-19. 10.14791/btrt.2020.8.e6.
A National Consensus Survey for Current Practicein Brain Tumor Management II:Diffuse Midline Glioma and Meningioma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, International St. Mary’s Hospital, Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea
- 5Department of Neurology, Rare Disease Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Neurosurgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 7Department of Pathology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Neurosurgery, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 9Division of Neurooncology and Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
- 10Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 11Department of Neurosurgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 12Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 13Department of Neurosurgery, Yeungnam University Hospital, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 14Department of Neurosurgery, Dong-A University Hospital, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 15Departments of Radiation Oncology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 16Department of Radiation Oncology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 17Division of Hematology/ Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 18Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 19Department of Radiation Oncology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 20Department of Neurosurgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 21Department of Neurosurgery, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea
- 22Department of Neurosurgery, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 23Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 24Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 25Department of Hospital Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 26Department of Cancer Control, Graduate School of Cancer Science and Policy, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2500117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2020.8.e6
Abstract
- Background
: The Guideline Working Group of the Korean Society for Neuro-Oncology (KSNO) conducted a nationwide questionnaire survey for diverse queries faced in the treatment of brain tumors. As part II of the survey, the aim of this study is to evaluate the national patterns of clinical practice for patients with diffuse midline glioma and meningioma.
Methods
: A web-based survey was sent to all members of the KSNO by email. The survey included 4 questions of diffuse midline glioma and 6 questions of meningioma (including 2 case scenarios). All questions were developed by consensus of the Guideline Working Group.
Results
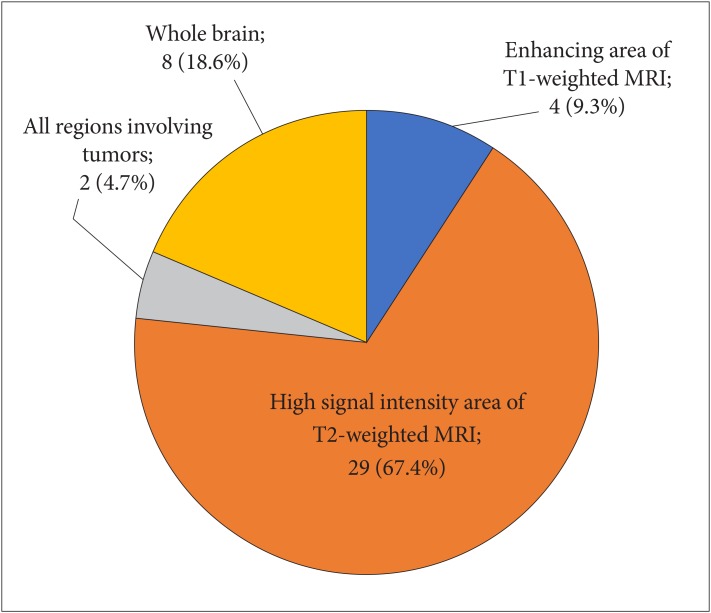
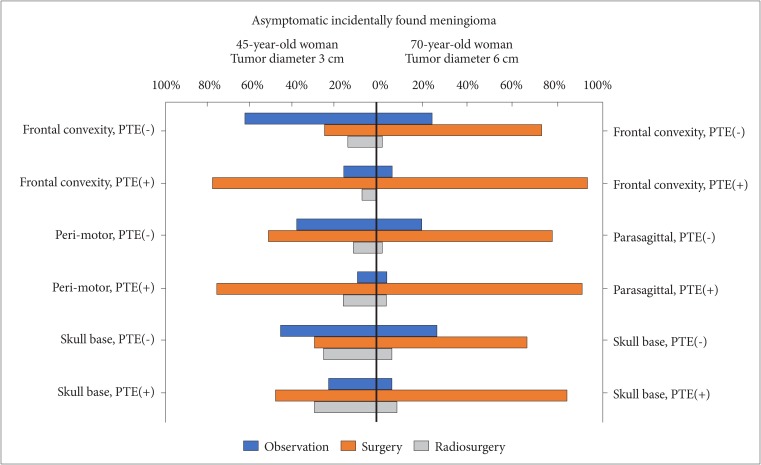
: In the survey about diffuse midline glioma, 76% respondents performed histologic confirmation to identify H3K27M mutation on immunohistochemical staining or sequencing methods. For treatment of diffuse midline glioma, respondents preferred concurrent chemoradiotherapy with temozolomide (TMZ) and adjuvant TMZ (63.8%) than radiotherapy alone (34.0%). In the survey about meningioma, respondents prefer wait-and-see policy for the asymptomatic small meningioma without peritumoral edema. However, a greater number of respondents had chosen surgical resection as the first choice for all large size meningiomas without exception, and small size meningiomas with either peritumoral edema or eloquent location. There was no single opinion with major consensus on long-term follow-up plans for asymptomatic meningioma with observation policy. As many as 68.1% of respondents answered that they would not add any adjuvant therapies for World Health Organization grade II meningiomas if the tumor was totally resected including dura.
Conclusion
: The survey demonstrates the prevailing clinical practice patterns for patients with diffuse midline glioma and meningioma among members of the KSNO. This information provides a point of reference for establishing a practical guideline in the management of diffuse midline glioma and meningioma.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Freeman CR, Krischer JP, Sanford RA, et al. Final results of a study of escalating doses of hyperfractionated radiotherapy in brain stem tumors in children: a Pediatric Oncology Group study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993; 27:197–206. PMID: 8407392.2. Janssens GO, Jansen MH, Lauwers SJ, et al. Hypofractionation vs conventional radiation therapy for newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: a matched-cohort analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 85:315–320. PMID: 22682807.3. Lewis J, Lucraft H, Gholkar A. United Kingdom Childhood Cancer Study Group. UKCCSG study of accelerated radiotherapy for pediatric brain stem gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997; 38:925–929. PMID: 9276356.4. Mandell LR, Kadota R, Freeman C, et al. There is no role for hyperfractionated radiotherapy in the management of children with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic brainstem tumors: results of a Pediatric Oncology Group phase III trial comparing conventional vs. hyperfractionated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:959–964. PMID: 10192340.5. Zaghloul MS, Eldebawy E, Ahmed S, et al. Hypofractionated conformal radiotherapy for pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG): a randomized controlled trial. Radiother Oncol. 2014; 111:35–40. PMID: 24560760.6. Marcus KJ, Dutton SC, Barnes P, et al. A phase I trial of etanidazole and hyperfractionated radiotherapy in children with diffuse brainstem glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 55:1182–1185. PMID: 12654425.7. Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016; 131:803–820. PMID: 27157931.8. Dho YS, Jung KW, Ha J, et al. An updated nationwide epidemiology of primary brain tumors in Republic of Korea, 2013. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2017; 5:16–23. PMID: 28516074.9. Chamoun R, Krisht KM, Couldwell WT. Incidental meningiomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2011; 31:E19.10. Niiro M, Yatsushiro K, Nakamura K, Kawahara Y, Kuratsu J. Natural history of elderly patients with asymptomatic meningiomas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 68:25–28. PMID: 10601396.11. Onizuka M, Suyama K, Shibayama A, Hiura T, Horie N, Miyazaki H. Asymptomatic brain tumor detected at brain check-up. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001; 41:431–434. discussion 435. PMID: 11593969.12. Jo KW, Kim CH, Kong DS, et al. Treatment modalities and outcomes for asymptomatic meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153:62–67. discussion 67. PMID: 20953804.13. Herscovici Z, Rappaport Z, Sulkes J, Danaila L, Rubin G. Natural history of conservatively treated meningiomas. Neurology. 2004; 63:1133–1134. PMID: 15452322.14. Nabika S, Kiya K, Satoh H, Mizoue T, Oshita J, Kondo H. [Strategy for the treatment of incidental meningiomas]. No Shinkei Geka. 2007; 35:27–32. PMID: 17228765.15. Sonoda Y, Sakurada K, Saino M, Kondo R, Sato S, Kayama T. Multimodal strategy for managing meningiomas in the elderly. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147:131–136. discussion 136. PMID: 15570440.16. Yano S, Kuratsu J, Kumamoto Brain. Indications for surgery in patients with asymptomatic meningiomas based on an extensive experience. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:538–543. PMID: 17044555.17. Aghi MK, Carter BS, Cosgrove GR, et al. Long-term recurrence rates of atypical meningiomas after gross total resection with or without postoperative adjuvant radiation. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:56–60. discussion 60. PMID: 19145156.18. Park HJ, Kang HC, Kim IH, et al. The role of adjuvant radiotherapy in atypical meningioma. J Neurooncol. 2013; 115:241–247. PMID: 23949108.19. Graffeo CS, Leeper HE, Perry A, et al. Revisiting adjuvant radiotherapy after gross total resection of World Health Organization grade II meningioma. World Neurosurg. 2017; 103:655–663. PMID: 28450233.20. Champeaux C, Houston D, Dunn L. Atypical meningioma. A study on recurrence and disease-specific survival. Neurochirurgie. 2017; 63:273–281. PMID: 28882609.21. Wu G, Broniscer A, McEachron TA. Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:251–253. PMID: 22286216.22. Khuong-Quang DA, Buczkowicz P, Rakopoulos P, et al. K27M mutation in histone H3.3 defines clinically and biologically distinct subgroups of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012; 124:439–447. PMID: 22661320.23. Weller M, van den Bent M, Tonn JC, et al. European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of adult astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:e315–e329. PMID: 28483413.24. Cohen KJ, Jabado N, Grill J. Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas-current management and new biologic insights. Is there a glimmer of hope? Neuro Oncol. 2017; 19:1025–1034. PMID: 28371920.25. Packer RJ, Krailo M, Mehta M, et al. A phase I study of concurrent RMP-7 and carboplatin with radiation therapy for children with newly diagnosed brainstem gliomas. Cancer. 2005; 104:1968–1974. PMID: 16177987.26. Walter AW, Gajjar A, Ochs JS, et al. Carboplatin and etoposide with hyperfractionated radiotherapy in children with newly diagnosed diffuse pontine gliomas: a phase I/II study. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1998; 30:28–33. PMID: 9371386.27. Korones DN, Fisher PG, Kretschmar C, et al. Treatment of children with diffuse intrinsic brain stem glioma with radiotherapy, vincristine and oral VP-16: a Children's Oncology Group phase II study. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008; 50:227–230. PMID: 17278121.28. Jalali R, Raut N, Arora B, et al. Prospective evaluation of radiotherapy with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in children with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 77:113–118. PMID: 19647954.29. Bailey S, Howman A, Wheatley K, et al. Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma treated with prolonged temozolomide and radiotherapy--results of a United Kingdom phase II trial (CNS 2007 04). Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49:3856–3862. PMID: 24011536.30. Janssens GO, Gidding CE, Van Lindert EJ, et al. The role of hypofractionation radiotherapy for diffuse intrinsic brainstem glioma in children: a pilot study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 73:722–726. PMID: 18990510.31. Kretschmar CS, Tarbell NJ, Barnes PD, Krischer JP, Burger PC, Kun L. Pre-irradiation chemotherapy and hyperfractionated radiation therapy 66 Gy for children with brain stem tumors. A phase II study of the Pediatric Oncology Group, Protocol 8833. Cancer. 1993; 72:1404–1413. PMID: 8339231.32. Behbahani M, Skeie GO, Eide GE, Hausken A, Lund-Johansen M, Skeie BS. A prospective study of the natural history of incidental meningioma– Hold your horses. Neurooncol Pract. 2019; 6:438–450. PMID: 31832214.33. Kim KH, Kang SJ, Choi JW, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of proactive Gamma Knife surgery for asymptomatic meningiomas compared with the natural course without intervention. J Neurosurg. 2019; 130:1740–1749.34. Zeng L, Wang L, Ye F, Chen J, Lei T, Chen J. Clinical characteristics of patients with asymptomatic intracranial meningiomas and results of their surgical management. Neurosurg Rev. 2015; 38:481–488. discussion 488. PMID: 25697143.35. Paldor I, Awad M, Sufaro YZ, Kaye AH, Shoshan Y. Review of controversies in management of non-benign meningioma. J Clin Neurosci. 2016; 31:37–46. PMID: 27338209.36. Sun SQ, Hawasli AH, Huang J, Chicoine MR, Kim AH. An evidence-based treatment algorithm for the management of WHO grade II and III meningiomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2015; 38:E3.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Korean Brain Tumor Society Consensus Review for the Practical Recommendations on Glioma Management in Korea
- The Association of Cerebral Aneurysm and Brain Tumor
- Epigenetic and Metabolic Changes in Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma
- Experience Profiling of Fluorescence-Guided Surgery II: Non-Glioma Pathologies
- Hemorrhagic Recurrence in Diffuse Astrocytoma without Malignant Transformation