J Rheum Dis.
2020 Jan;27(1):37-44. 10.4078/jrd.2020.27.1.37.
Associations Between Circulating Interleukin-17 Levels and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Between Interleukin-17 Gene Polymorphisms and Disease Susceptibility: A Meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lyhcgh@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2471960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2020.27.1.37
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To systematically investigate the relationship between circulating interleukin-17 (IL-17) levels and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and associations between polymorphisms in IL17 genes and SLE susceptibility.
METHODS
We performed a meta-analysis of serum/plasma IL-17 levels in patients with SLE and controls and evaluated the associations between the IL17A rs2275913, IL17F rs763780, and IL17F rs2397084 polymorphisms and IL17F copy number variations (CNVs) and risk of SLE.
RESULTS
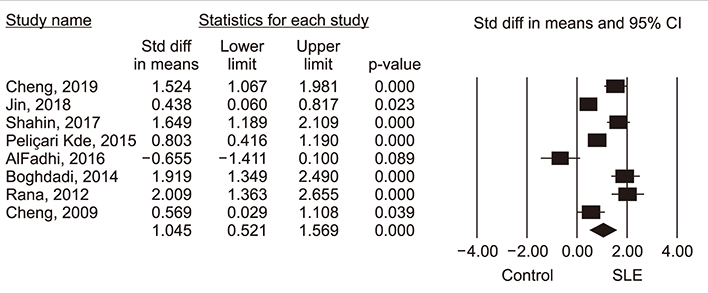
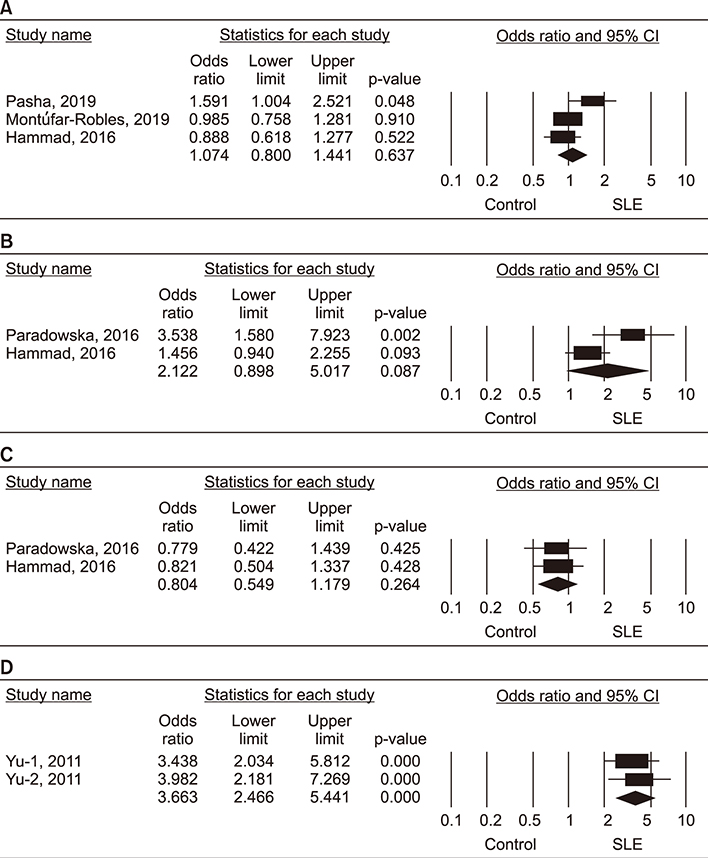
Thirteen studies focusing on 2,096 patients with SLE and 2,587 controls were included. Our meta-analysis revealed that IL-17 levels were significantly higher in the SLE group than the control group (standardized mean difference=1.045, 95% confidence interval [95% CI]=0.521~1.568, p < 0.001). Subgroup analysis using sample size showed increased IL-17 levels in samples from large (n>100) but not small (n < 90) SLE groups. We found no evidence of associations between SLE and the IL17A rs2275913, IL17F rs763780, and IL17F rs2397084 polymorphisms. However, a significant association was found between SLE and IL17F CNVs in a pooled cohort of affected individuals compared to that in pooled controls (odd ratio=3.663, 95% CI=2.466~5.221, p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
This meta-analysis revealed significantly higher circulating IL-17 levels in patients with SLE and showed evidence of associations between IL17F CNVs and SLE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Castellino G, Hughes GR. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2001; 357:1027–1032.
Article2. Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996; 85:303–306.
Article3. Lee YH, Bae SC, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. Genome-wide pathway analysis of genome-wide association studies on systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 2012; 39:10627–10635.
Article4. Kawaguchi M, Adachi M, Oda N, Kokubu F, Huang SK. IL-17 cytokine family. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:1265–1273.
Article5. Pappu R, Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology. 2011; 134:8–16.
Article6. Choi SJ, Rho YH, Ji JD, Song GG, Lee YH. Genome scan meta-analysis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006; 45:166–170.
Article7. Cheng Y, Yang X, Zhang X, An Z. Analysis of expression levels of IL-17 and IL-34 and influencing factors for prognosis in patients with lupus nephritis. Exp Ther Med. 2019; 17:2279–2283.
Article8. Jin L, Bai R, Zhou J, Shi W, Xu L, Sheng J, et al. Association of serum T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin-3 and interleukin-17 with systemic lupus erythematosus. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2018; 24:168–176.
Article9. Shahin D, El-Farahaty RM, Houssen ME, Machaly SA, Sallam M, ElSaid TO, et al. Serum 25-OH vitamin D level in treatment-naïve systemic lupus erythematosus patients: relation to disease activity, IL-23 and IL-17. Lupus. 2017; 26:917–926.
Article10. Peliçari Kde O, Postal M, Sinicato NA, Peres FA, Fernandes PT, Marini R, et al. Serum interleukin-17 levels are associated with nephritis in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015; 70:313–317.11. AlFadhli S, AlFailakawi A, Ghanem AA. Th-17 related regulatory network in the pathogenesis of Arab patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016; 19:512–520.
Article12. Boghdadi G, Elewa EA. Increased serum APRIL differentially correlates with distinct cytokine profiles and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Rheumatol Int. 2014; 34:1217–1223.
Article13. Rana A, Minz RW, Aggarwal R, Anand S, Pasricha N, Singh S. Gene expression of cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ), serum profiles of IL-17 and IL-23 in paediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2012; 21:1105–1112.
Article14. Cheng F, Guo Z, Xu H, Yan D, Li Q. Decreased plasma IL22 levels, but not increased IL17 and IL23 levels, correlate with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:604–606.
Article15. Pasha HF, Tantawy EA, Youssef MA. Osteopontin and interleukin-17A genes polymorphisms in Egyptian systemic lupus erythematosus patients: a relation to disease activity and severity. Gene. 2019; 702:107–113.
Article16. Montúfar-Robles I, Barbosa-Cobos RE, Alemán-Ávila I, Ramírez-Bello J. IL-17A haplotype confers susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus but not to rheumatoid arthritis in Mexican patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019; 22:473–479.17. Paradowska-Gorycka A, Sowinska A, Stypinska B, Grobelna MK, Walczyk M, Olesinska M, et al. Impact of the IL-17F, IL-23 and IL-23R on susceptibility and phenotype of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 2016; 49:373–382.
Article18. Hammad A, Mosaad YM, Hammad EM, Elhanbly S, El-Bassiony SR, Al-Harrass MF, et al. Interleukin-17A rs2275913, Interleukin-17F rs763780 and rs2397084 gene polymorphisms as possible risk factors in Juvenile lupus and lupus related nephritis. Autoimmunity. 2016; 49:31–40.19. Yu B, Guan M, Peng Y, Shao Y, Zhang C, Yue X, et al. Copy number variations of interleukin-17F, interleukin-21, and interleukin-22 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:3487–3492.
Article20. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article21. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005; 5:13.
Article22. Ridout KK, Ridout SJ, Price LH, Sen S, Tyrka AR. Depression and telomere length: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016; 191:237–247.
Article23. Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN. Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ. 1997; 315:1533–1537.
Article24. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–188.
Article25. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1539–1558.
Article26. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article27. Zambrano-Zaragoza JF, Romo-Martínez EJ, Durán-Avelar Mde J, García-Magallanes N, Vibanco-Pérez N. Th17 cells in autoimmune and infectious diseases. Int J Inflam. 2014; 2014:651503.
Article28. Jin Y, Deng Z, Cao C, Li L. IL-17 polymorphisms and asthma risk: a meta-analysis of 11 single nucleotide polymorphisms. J Asthma. 2015; 52:981–988.
Article29. Lee YH, Bae SC. Associations between circulating IL-17 levels and rheumatoid arthritis and between IL-17 gene polymorphisms and disease susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Postgrad Med J. 2017; 93:465–471.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Circulating Interleukin-18 Level in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Circulating Interleukin-37 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Their Correlations With Disease Activity: A Meta-analysis
- Evaluating the association of interleukin-10 gene promoter -592 A/C polymorphism with lupus nephritis susceptibility
- Circulating VEGF levels and genetic polymorphisms in Behçet’s disease: a meta-analysis
- Elevated serum interleukin-15 levels in systemic lupus erythematosus