Yonsei Med J.
2020 Apr;61(4):291-300. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.4.291.
Yonsei Criteria, a Potential Linkage to Intratumoral Foxp3âº/CD8⺠Ratio for the Prediction of Oncologic Outcomes in Resected Left-Sided Pancreatic Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cmkang@yuhs.ac
- 2Pancreatobiliary Cancer Center, Yonsei Cancer Center, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pathology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Pharmacy, Yonsei University College of Pharmacy, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2471914
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.4.291
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study sought to investigate associations among Yonsei criteria (tumor confined to the pancreas, intact fascia layer between the distal pancreas and the left adrenal gland and kidney, and tumor located more than 1-2 cm from the celiac axis) and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in pancreatic cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients who underwent curative distal pancreatectomy due to left-sided pancreatic cancer from January 2000 to December 2011 were enrolled. Follow-up was completed September 30, 2015.
RESULTS
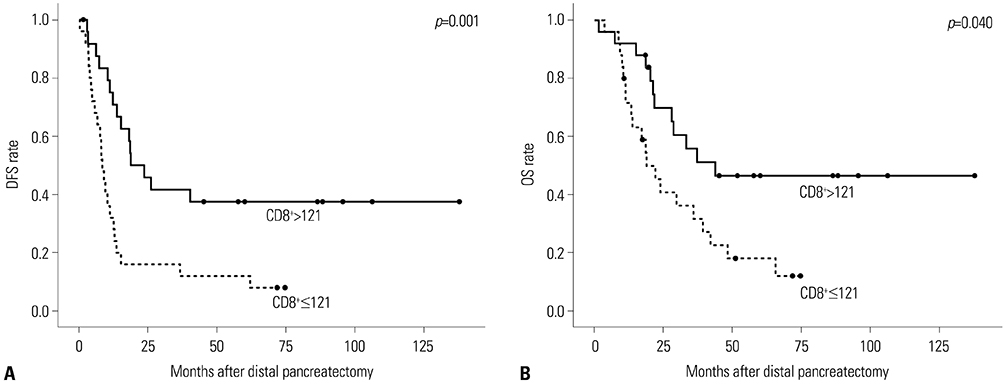
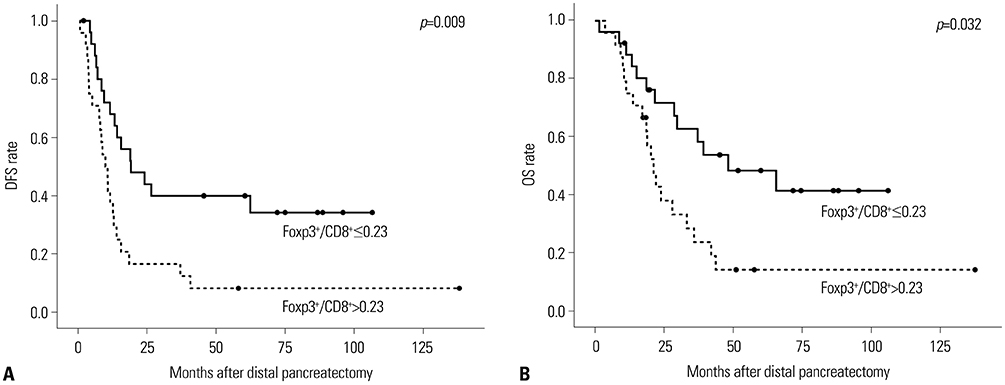
Fifty patients were enrolled. Having ≥ two metastatic lymph nodes (LNs, p=0.002), intraoperative transfusion (p=0.011), low levels of tumor infiltrating CD8⺠T-cells (p=0.001), and a high Foxp3âº/CD8⺠ratio (p=0.009) were independent risk factors for disease-free survival. Not satisfying the Yonsei criteria (p=0.021), having ≥ two metastatic LNs (p=0.032), low levels of tumor infiltrating CD8⺠T-cells (p=0.040) and a high Foxp3âº/CD8⺠ratio (p=0.032) were associated with unfavorable overall survival. High levels of CA19-9 and not satisfying the Yonsei criteria were significantly associated with a high Foxp3âº/CD8⺠ratio [Exp(β)=3.558; 95% confidence inverval: 1.000-12.658; p=0.050].
CONCLUSION
Yonsei criteria may be clinically detectable biologic marker with which to predict immunologic status and survival in pancreatic cancer patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1605–1617.
Article2. Jung YS, Park JH, Park DI, Sohn CI, Lee JM, Kim TI. Physical inactivity and unhealthy metabolic status are associated with decreased natural killer cell activity. Yonsei Med J. 2018; 59:554–562.
Article3. Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, et al. Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:5373–5380.
Article4. Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B, et al. Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:2328–2339.
Article5. Kim HI, Kim H, Cho HW, Kim SY, Song KJ, Hyung WJ, et al. The ratio of intra-tumoral regulatory T cells (Foxp3+)/helper T cells (CD4+) is a prognostic factor and associated with recurrence pattern in gastric cardia cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:728–733.
Article6. Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, et al. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:203–213.
Article7. Balch CM, Riley LB, Bae YJ, Salmeron MA, Platsoucas CD, von Eschenbach A, et al. Patterns of human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in 120 human cancers. Arch Surg. 1990; 125:200–205.
Article8. Clemente CG, Mihm MC Jr, Bufalino R, Zurrida S, Collini P, Cascinelli N. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1996; 77:1303–1310.
Article9. Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY, Xiao YS, et al. Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:2586–2593.
Article10. Petersen RP, Campa MJ, Sperlazza J, Conlon D, Joshi MB, Harpole DH Jr, et al. Tumor infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T-cells are associated with recurrence in pathologic stage I NSCLC patients. Cancer. 2006; 107:2866–2872.
Article11. Cho Y, Miyamoto M, Kato K, Fukunaga A, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, et al. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells cooperate to improve prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:1555–1559.12. Duffour MT, Chaux P, Lurquin C, Cornelis G, Boon T, van der Bruggen P. A MAGE-A4 peptide presented by HLA-A2 is recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29:3329–3337.
Article13. Bleackley RC. A molecular view of cytotoxic T lymphocyte induced killing. Biochem Cell Biol. 2005; 83:747–751.
Article14. Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004; 22:531–562.15. Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003; 299:1057–1061.
Article16. Hwang HK, Kim HI, Kim SH, Choi J, Kang CM, Kim KS, et al. Prognostic impact of the tumor-infiltrating regulatory T-cell (Foxp3+)/activated cytotoxic T lymphocyte (granzyme B+) ratio on resected left-sided pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett. 2016; 12:4477–4484.
Article17. Choi SH, Kang CM, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Multimedia article. Laparoscopic modified anterior RAMPS in well-selected left-sided pancreatic cancer: technical feasibility and interim results. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2360–2361.
Article18. Choi SH, Kang CM, Hwang HK, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Robotic anterior RAMPS in well-selected left-sided pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:868–869.
Article19. Lee SH, Kang CM, Hwang HK, Choi SH, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Minimally invasive RAMPS in well-selected left-sided pancreatic cancer within Yonsei criteria: long-term (>median 3 years) oncologic outcomes. Surg Endosc. 2014; 28:2848–2855.
Article20. Fukunaga A, Miyamoto M, Cho Y, Murakami S, Kawarada Y, Oshikiri T, et al. CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes together with CD4+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and dendritic cells improve the prognosis of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2004; 28:e26–e31.
Article21. Ikemoto T, Yamaguchi T, Morine Y, Imura S, Soejima Y, Fujii M, et al. Clinical roles of increased populations of Foxp3+CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood from advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Pancreas. 2006; 33:386–390.
Article22. Wachsmann MB, Pop LM, Vitetta ES. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a review of immunologic aspects. J Investig Med. 2012; 60:643–663.23. Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S. Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:5423–5434.
Article24. Slidell MB, Chang DC, Cameron JL, Wolfgang C, Herman JM, Schulick RD, et al. Impact of total lymph node count and lymph node ratio on staging and survival after pancreatectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a large, population-based analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15:165–174.
Article25. Hwang HK, Jung MJ, Lee SH, Kang CM, Lee WJ. Adverse oncologic effects of intraoperative transfusion during pancreatectomy for left-sided pancreatic cancer: the need for strict transfusion policy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2016; 23:497–507.
Article26. Burrows L, Tartter P. Effect of blood transfusions on colonic malignancy recurrent rate. Lancet. 1982; 2:662.27. Katz SC, Shia J, Liau KH, Gonen M, Ruo L, Jarnagin WR, et al. Operative blood loss independently predicts recurrence and survival after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:617–623.
Article28. Nagai S, Fujii T, Kodera Y, Kanda M, Sahin TT, Kanzaki A, et al. Impact of operative blood loss on survival in invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Pancreas. 2011; 40:3–9.
Article29. Blajchman MA, Bardossy L, Carmen R, Sastry A, Singal DP. Allogeneic blood transfusion-induced enhancement of tumor growth: two animal models showing amelioration by leukodepletion and passive transfer using spleen cells. Blood. 1993; 81:1880–1882.
Article30. Tempero MA, Malafa MP, Behrman SW, Benson AB 3rd, Casper ES, Chiorean EG, et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2014: featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014; 12:1083–1093.31. Yoshida S, Ito Z, Suka M, Bito T, Kan S, Akasu T, et al. Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating T cells and programed death ligand-1 in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer Invest. 2019; 37:463–477.
Article32. Sideras K, Biermann K, Yap K, Mancham S, Boor PPC, Hansen BE, et al. Tumor cell expression of immune inhibitory molecules and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte count predict cancer-specific survival in pancreatic and ampullary cancer. Int J Cancer. 2017; 141:572–582.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Port-site metastasis after laparoscopic radical pancreatosplenectomy in left-sided pancreatic cancer
- Laparoscopic distal pancreatosplenectomy for left-sided pancreatic cancer in patients with radical subtotal gastrectomy for gastric cancer
- Complete response of locally advanced left-sided pancreatic cancer after modified FOLFIRINOX chemotherapy followed by conversion surgery: A case report
- Extended versus peripancreatic lymph node dissection for the treatment of left-sided pancreatic cancer
- A Five-Year Survivor without Recurrence Following Robotic Anterior Radical Antegrade Modular Pancreatosplenectomy for a Well-Selected Left-Sided Pancreatic Cancer