Yonsei Med J.
2014 Jan;55(1):276-279. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.276.
A Five-Year Survivor without Recurrence Following Robotic Anterior Radical Antegrade Modular Pancreatosplenectomy for a Well-Selected Left-Sided Pancreatic Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cmkang@yuhs.ac
- 2Pancreaticobiliary Cancer Clinic, Institute of Gastroenterology, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.276
Abstract
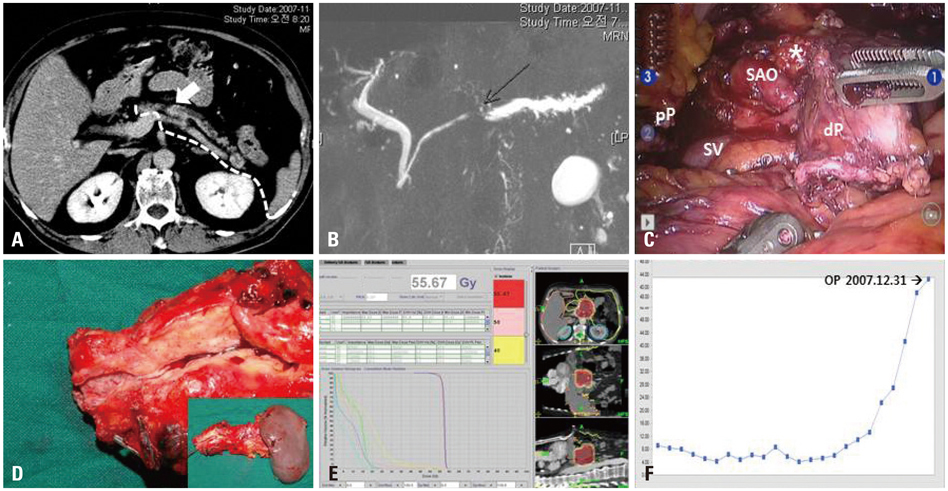
- Radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (RAMPS) is regarded as a reasonable approach for margin-negative and systemic lymph node clearance in left-sided pancreatic cancer. We present a patient with more than 5 years disease-free survival after robotic anterior RAMPS for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in the body of the pancreas. The distal part of pancreas, soft tissue around the celiac trunk, and the origin of splenic vessels was dissected with the underlying fascia between the pancreas and adrenal gland. Resected specimen was removed through small vertical abdominal incision. Robot working time was about 8 hours, and blood loss was about 700 mL without blood transfusion. He returned to an oral diet on the postoperative first day and recovered without any clinically relevant complications. There was no lymph node metastasis, perineural or lymphovascular invasion. Both the pancreatic resection margin and the tangential posterior margin were free of carcinoma. The patient received only postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy around the tumor bed. The patient has survived for more than 5 years without evidence of cancer recurrence. Minimally invasive radical left-sided pancreatectomy with splenectomy may be oncologically feasible in well-selected pancreatic cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colon Cancer Laparoscopic or Open Resection Study Group. Buunen M, Veldkamp R, Hop WC, Kuhry E, Jeekel J, et al. Survival after laparoscopic surgery versus open surgery for colon cancer: long-term outcome of a randomised clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:44–52.
Article2. Huscher CG, Mingoli A, Sgarzini G, Sansonetti A, Di Paola M, Recher A, et al. Laparoscopic versus open subtotal gastrectomy for distal gastric cancer: five-year results of a randomized prospective trial. Ann Surg. 2005; 241:232–237.
Article3. Jacob BP, Gagner M. Robotics and general surgery. Surg Clin North Am. 2003; 83:1405–1419.
Article4. Strasberg SM, Linehan DC, Hawkins WG. Radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy procedure for adenocarcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas: ability to obtain negative tangential margins. J Am Coll Surg. 2007; 204:244–249.
Article5. Mitchem JB, Hamilton N, Gao F, Hawkins WG, Linehan DC, Strasberg SM. Long-term results of resection of adenocarcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas using radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy procedure. J Am Coll Surg. 2012; 214:46–52.
Article6. Kang CM, Kim DH, Lee WJ. Ten years of experience with resection of left-sided pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: evolution and initial experience to a laparoscopic approach. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1533–1541.
Article7. Choi SH, Kang CM, Hwang HK, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Robotic anterior RAMPS in well-selected left-sided pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:868–869.
Article8. Choi SH, Kang CM, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Multimedia article. Laparoscopic modified anterior RAMPS in well-selected left-sided pancreatic cancer: technical feasibility and interim results. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2360–2361.
Article9. Taylor C, O'Rourke N, Nathanson L, Martin I, Hopkins G, Layani L, et al. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: the Brisbane experience of forty-six cases. HPB (Oxford). 2008; 10:38–42.
Article10. Kooby DA, Gillespie T, Bentrem D, Nakeeb A, Schmidt MC, Merchant NB, et al. Left-sided pancreatectomy: a multicenter comparison of laparoscopic and open approaches. Ann Surg. 2008; 248:438–446.11. Jayaraman S, Gonen M, Brennan MF, D'Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, et al. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: evolution of a technique at a single institution. J Am Coll Surg. 2010; 211:503–509.
Article12. Fernández-Cruz L, Cosa R, Blanco L, Levi S, López-Boado MA, Navarro S. Curative laparoscopic resection for pancreatic neoplasms: a critical analysis from a single institution. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:1607–1621.
Article13. Marangos IP, Buanes T, Røsok BI, Kazaryan AM, Rosseland AR, Grzyb K, et al. Laparoscopic resection of exocrine carcinoma in central and distal pancreas results in a high rate of radical resections and long postoperative survival. Surgery. 2012; 151:717–723.
Article14. Song KB, Kim SC, Park JB, Kim YH, Jung YS, Kim MH, et al. Single-center experience of laparoscopic left pancreatic resection in 359 consecutive patients: changing the surgical paradigm of left pancreatic resection. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:3364–3372.
Article15. Daouadi M, Zureikat AH, Zenati MS, Choudry H, Tsung A, Bartlett DL, et al. Robot-assisted minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy is superior to the laparoscopic technique. Ann Surg. 2013; 257:128–132.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally invasive radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy: routine vs. modified
- Port-site metastasis after laparoscopic radical pancreatosplenectomy in left-sided pancreatic cancer
- Initial experience with radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy in a single institution
- Laparoscopic distal pancreatosplenectomy for left-sided pancreatic cancer in patients with radical subtotal gastrectomy for gastric cancer
- Two Cases of Portal Annular Pancreas