Tuberc Respir Dis.
2020 Apr;83(2):122-131. 10.4046/trd.2020.0012.
Current Diagnosis and Management of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, Italy. paolomaria.leone@gmail.com
- 2Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy.
- KMID: 2471888
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2020.0012
Abstract
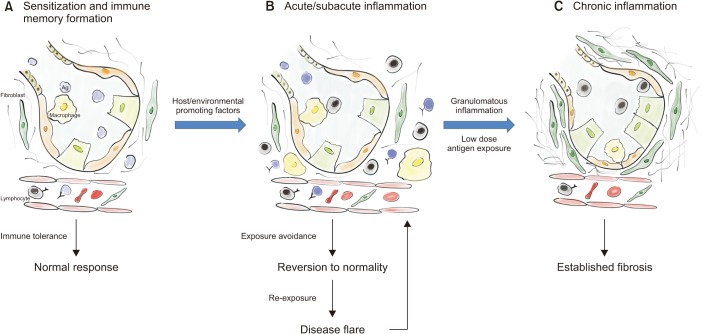
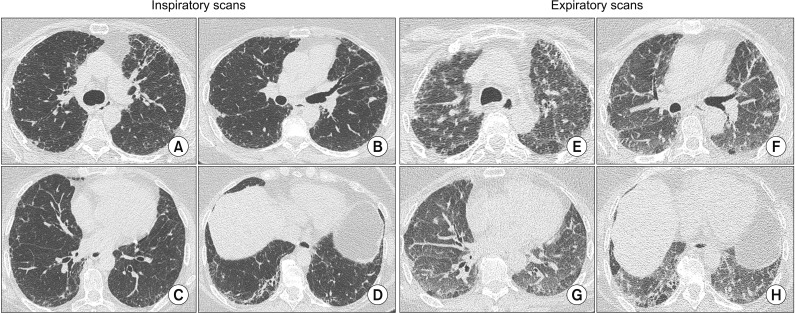
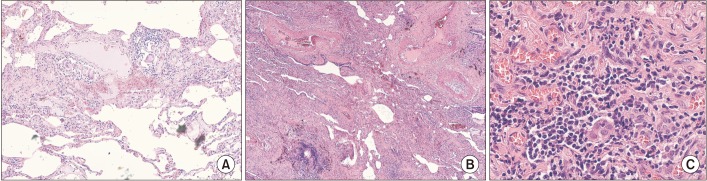
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) one of the most common interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) is characterized by exposure to an inhaled inciting antigen that leads to a host immunologic reaction determining interstitial inflammation and architectural distortion. The underlying pathogenetic mechanisms are unclear. The absence of international shared diagnostic guidelines and the lack of a "gold-standard" test for HP combined with the presence of several clinical and radiologic overlapping features makes it particularly challenging to differentiate HP from other ILDs, also in expert contests. Radiology is playing a more crucial role in this process; recently the headcheese sign was recognized as a more specific for chronic-HP than the extensive mosaic attenuation. Several classification proposals and diagnostic models have been advanced by different groups, with no prospective validation. Therapeutic options for HP have been limited to antigen avoidance and immunosuppressant drugs over the last decades. Several questions about this condition remain unanswered and there is a need for more studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. King TE Jr. Clinical advances in the diagnosis and therapy of the interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 172:268–279. PMID: 15879420.
Article2. Hyldgaard C, Hilberg O, Muller A, Bendstrup E. A cohort study of interstitial lung diseases in central Denmark. Respir Med. 2014; 108:793–799. PMID: 24636811.
Article3. Mohr LC. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004; 10:401–411. PMID: 15316440.
Article4. Johansson E, Boivin GP, Yadav JS. Early immunopathological events in acute model of mycobacterial hypersensitivity pneumonitis in mice. J Immunotoxicol. 2017; 14:77–88. PMID: 28094581.
Article5. Okamoto T, Miyazaki Y, Ogura T, Chida K, Kohno N, Kohno S, et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in Japan. Respir Investig. 2013; 51:191–199.6. Fernandez Perez ER, Kong AM, Raimundo K, Koelsch TL, Kulkarni R, Cole AL. Epidemiology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis among an insured population in the United States: a claims-based cohort analysis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018; 15:460–469. PMID: 29236517.7. Ley B, Collard HR, King TE Jr. Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 183:431–440. PMID: 20935110.
Article8. Martinez FJ, Collard HR, Pardo A, Raghu G, Richeldi L, Selman M, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017; 3:17074. PMID: 29052582.
Article9. Noone A, Howlader N, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, et al. SEER cancer statistics review (CST) 1975-2015 [Internet]. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute;2018. cited 2019 Dec 10. Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/.10. Morell F, Villar A, Montero MA, Munoz X, Colby TV, Pipvath S, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective case-cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2013; 1:685–694. PMID: 24429272.
Article11. Thomeer MJ, Costabe U, Rizzato G, Poletti V, Demedts M. Comparison of registries of interstitial lung diseases in three European countries. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2001; 32:114s–118s. PMID: 11816817.12. Solaymani-Dodaran M, West J, Smith C, Hubbard R. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis: incidence and mortality in the general population. QJM. 2007; 100:233–237. PMID: 17307752.
Article13. Barber CM, Wiggans RE, Carder M, Agius R. Epidemiology of occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis; reports from the SWORD scheme in the UK from 1996 to 2015. Occup Environ Med. 2017; 74:528–530. PMID: 27919062.14. Buchvald F, Petersen BL, Damgaard K, Deterding R, Langston C, Fan LL, et al. Frequency, treatment, and functional outcome in children with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2011; 46:1098–1107. PMID: 21618714.
Article15. Sommerfeld CG, Weiner DJ, Nowalk A, Larkin A. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis and acute respiratory distress syndrome from E-cigarette use. Pediatrics. 2018; 141:e20163927. PMID: 29773665.
Article16. Selman M. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In : Schwarz M, King TE, editors. Interstitial lung disease. 5th ed. Shelton, CT: People's Medical Publishing House-USA;2011. p. 597–625.17. Ohtsuka Y, Munakata M, Tanimura K, Ukita H, Kusaka H, Masaki Y, et al. Smoking promotes insidious and chronic farmer's lung disease, and deteriorates the clinical outcome. Intern Med. 1995; 34:966–971. PMID: 8563097.
Article18. Camarena A, Aquino-Galvez A, Falfan-Valencia R, Sanchez G, Montano M, Ramos C, et al. PSMB8 (LMP7) but not PSMB9 (LMP2) gene polymorphisms are associated to pigeon breeder's hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir Med. 2010; 104:889–894. PMID: 20153157.
Article19. Aquino-Galvez A, Camarena A, Montano M, Juarez A, Zamora AC, Gonzalez-Avila G, et al. Transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) 1 gene polymorphisms in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2008; 84:173–177. PMID: 18342853.
Article20. Fink JN, Ortega HG, Reynolds HY, Cormier YF, Fan LL, Franks TJ, et al. Needs and opportunities for research in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:792–798. PMID: 15657460.
Article21. Agostini C, Trentin L, Facco M, Semenzato G. New aspects of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004; 10:378–382. PMID: 15316436.
Article22. Lopez M, Salvaggio JE. Epidemiology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis/allergic alveolitis. Monogr Allergy. 1987; 21:70–86. PMID: 3317002.23. Selman M, Pardo A, King TE Jr. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: insights in diagnosis and pathobiology. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 186:314–324. PMID: 22679012.24. Salisbury ML, Myers JL, Belloli EA, Kazerooni EA, Martinez FJ, Flaherty KR. Diagnosis and treatment of fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonia: where we stand and where we need to go. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017; 196:690–699. PMID: 28002680.
Article25. Vasakova M, Morell F, Walsh S, Leslie K, Raghu G. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: perspectives in diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017; 196:680–689. PMID: 28598197.
Article26. Cottin V, Hirani NA, Hotchkin DL, Nambiar AM, Ogura T, Otaola M, et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018; 27:180076. PMID: 30578335.
Article27. Fernandez Perez ER, Swigris JJ, Forssen AV, Tourin O, Solomon JJ, Huie TJ, et al. Identifying an inciting antigen is associated with improved survival in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2013; 144:1644–1651. PMID: 23828161.
Article28. Morisset J, Johannson KA, Jones KD, Wolters PJ, Collard HR, Walsh SL, et al. Identification of diagnostic criteria for chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: an international modified Delphi survey. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197:1036–1044. PMID: 29172641.
Article29. Ojanguren I, Morell F, Ramon MA, Villar A, Romero C, Cruz MJ, et al. Long-term outcomes in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Allergy. 2019; 74:944–952. PMID: 30515826.
Article30. Soumagne T, Dalphin JC. Current and emerging techniques for the diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018; 12:493–507. PMID: 29727203.
Article31. Cormier Y, Belanger J, Tardif A, Leblanc P, Laviolette M. Relationships between radiographic change, pulmonary function, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lymphocytes in farmer's lung disease. Thorax. 1986; 41:28–33. PMID: 3704964.
Article32. Kokkarinen JI, Tukiainen HO, Terho EO. Recovery of pulmonary function in farmer's lung: a five-year follow-up study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993; 147:793–796. PMID: 8466111.
Article33. Gimenez A, Storrer K, Kuranishi L, Soares MR, Ferreira RG, Pereira CA. Change in FVC and survival in chronic fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Thorax. 2018; 73:391–392. PMID: 28883091.
Article34. Dias OM, Baldi BG, Pennati F, Aliverti A, Chate RC, Sawamura MV, et al. Computed tomography in hypersensitivity pneumonitis: main findings, differential diagnosis and pitfalls. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018; 12:5–13. PMID: 29048936.
Article35. Schwaiblmair M, Beinert T, Vogelmeier C, Fruhmann G. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing following hay exposure challenge in farmer's lung. Eur Respir J. 1997; 10:2360–2365. PMID: 9387965.
Article36. Dias OM, Baldi BG, Ferreira JG, Cardenas LZ, Pennati F, Salito C, et al. Mechanisms of exercise limitation in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. ERJ Open Res. 2018; 4:00043-2018. PMID: 30151370.
Article37. Lacasse Y, Selman M, Costabel U, Dalphin JC, Ando M, Morell F, et al. Clinical diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 168:952–958. PMID: 12842854.
Article38. Chong BJ, Kanne JP, Chung JH. Headcheese sign. J Thorac Imaging. 2014; 29:W13. PMID: 24361976.
Article39. Kligerman SJ, Henry T, Lin CT, Franks TJ, Galvin JR. Mosaic attenuation: etiology, methods of differentiation, and pitfalls. Radiographics. 2015; 35:1360–1380. PMID: 26274445.
Article40. Lynch DA, Newell JD, Logan PM, King TE Jr, Muller NL. Can CT distinguish hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 165:807–811. PMID: 7676971.
Article41. Silva CI, Muller NL, Lynch DA, Curran-Everett D, Brown KK, Lee KS, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: differentiation from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia by using thin-section CT. Radiology. 2008; 246:288–297. PMID: 18096541.
Article42. Barnett J, Molyneaux PL, Rawal B, Abdullah R, Hare SS, Vancheeswaran R, et al. Variable utility of mosaic attenuation to distinguish fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2019; 54:1900531. PMID: 31164428.43. Soumagne T, Chardon ML, Dournes G, Laurent L, Degano B, Laurent F, et al. Emphysema in active farmer's lung disease. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0178263. PMID: 28614400.
Article44. Franquet T, Hansell DM, Senbanjo T, Remy-Jardin M, Muller NL. Lung cysts in subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003; 27:475–478. PMID: 12886127.
Article45. Salisbury ML, Gross BH, Chughtai A, Sayyouh M, Kazerooni EA, Bartholmai BJ, et al. Development and validation of a radiological diagnosis model for hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur Respir J. 2018; 52:1800443. PMID: 29946001.
Article46. Walsh SL, Richeldi L. Demystifying fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis diagnosis: it's all about shades of grey. Eur Respir J. 2019; 54:1900906. PMID: 31345989.
Article47. Chung JH, Zhan X, Cao M, Koelsch TL, Manjarres DC, Brown KK, et al. Presence of air trapping and mosaic attenuation on chest computed tomography predicts survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017; 14:1533–1538. PMID: 28513215.
Article48. Salisbury ML, Gu T, Murray S, Gross BH, Chughtai A, Sayyouh M, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: radiologic phenotypes are associated with distinct survival time and pulmonary function trajectory. Chest. 2019; 155:699–711. PMID: 30243979.49. Lynch DA. CT phenotypes in hpersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2019; 155:655–656. PMID: 30955565.50. Jacob J, Bartholmai BJ, Egashira R, Brun AL, Rajagopalan S, Karwoski R, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: identification of key prognostic determinants using automated CT analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2017; 17:81. PMID: 28472939.
Article51. Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an oficial ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 198:e44–e68. PMID: 30168753.52. Meyer KC, Raghu G, Baughman RP, Brown KK, Costabel U, du Bois RM, et al. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: the clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage cellular analysis in interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 185:1004–1014. PMID: 22550210.
Article53. Ohtani Y, Saiki S, Kitaichi M, Usui Y, Inase N, Costabel U, et al. Chronic bird fancier's lung: histopathological and clinical correlation: an application of the 2002 ATS/ERS consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Thorax. 2005; 60:665–671. PMID: 16061708.
Article54. Santos V, Martins N, Sousa C, Jacob M, Padrao E, Melo N, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: main features characterization in a Portuguese cohort. Pulmonology. 2019; 10. 29. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.09.004.
Article55. Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Cherniack RM, Curran-Everett D, Cool CD, Tuder RM, et al. The effect of pulmonary fibrosis on survival in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Med. 2004; 116:662–668. PMID: 15121492.
Article56. Fireman E, Vardinon N, Burke M, Spizer S, Levin S, Endler A, et al. Predictive value of response to treatment of T-lymphocyte subpopulations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 1998; 11:706–711. PMID: 9596125.57. Ohshimo S, Bonella F, Cui A, Beume M, Kohno N, Guzman J, et al. Significance of bronchoalveolar lavage for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 179:1043–1047. PMID: 19246718.
Article58. Patel AM, Ryu JH, Reed CE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts and future questions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:661–670. PMID: 11692086.
Article59. Barrera L, Mendoza F, Zuniga J, Estrada A, Zamora AC, Melendro EI, et al. Functional diversity of T-cell subpopulations in subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177:44–55. PMID: 17947613.
Article60. Myers JL. Hypersensitivity pneumonia: the role of lung biopsy in diagnosis and management. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25 Suppl 1:S58–S67. PMID: 22214971.
Article61. Sharp C, McCabe M, Adamali H, Medford AR. Use of transbronchial cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and cost analysis. QJM. 2017; 110:207–214. PMID: 27521581.62. Iftikhar IH, Alghothani L, Sardi A, Berkowitz D, Musani AI. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy and video-assisted thoracoscopic lung biopsy in the diagnosis of diffuse parenchymal lung disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017; 14:1197–1211. PMID: 28399377.
Article63. Grunes D, Beasley MB. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a review and update of histologic findings. J Clin Pathol. 2013; 66:888–895. PMID: 23881224.
Article64. Miller R, Allen TC, Barrios RJ, Beasley MB, Burke L, Cagle PT, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis A perspective from members of the Pulmonary Pathology Society. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018; 142:120–126. PMID: 28613913.
Article65. Castonguay MC, Ryu JH, Yi ES, Tazelaar HD. Granulomas and giant cells in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Hum Pathol. 2015; 46:607–613. PMID: 25694347.
Article66. Wang P, Jones KD, Urisman A, Elicker BM, Urbania T, Johannson KA, et al. Pathologic findings and prognosis in a large prospective cohort of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2017; 152:502–509. PMID: 28223152.67. Johannson KA, Elicker BM, Vittinghoff E, Assayag D, de Boer K, Golden JA, et al. A diagnostic model for chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Thorax. 2016; 71:951–954. PMID: 27245779.
Article68. Molyneaux PL, Maher TM. Time for an international consensus on hypersensitivity pneumonitis. A Call to Arms. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017; 196:665–666. PMID: 28723313.
Article69. Swigris J. DELPHIning diagnostic criteria for chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197:980–981. PMID: 29262259.
Article70. Fernandez Perez ER. Diagnostic decision-making in hypersensitivity pneumonitis: toward a consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197:1646–1647. PMID: 29505271.
Article71. Takei R, Yamano Y, Kataoka K, Yokoyama T, Matsuda T, Kimura T, et al. Usefulness of new diagnostic criteria for chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis established on the basis of a Delphi survey: a Japanese cohort study. Respir Investig. 2020; 58:52–58.
Article72. Walsh SL, Wells AU, Desai SR, Poletti V, Piciucchi S, Dubini A, et al. Multicentre evaluation of multidisciplinary team meeting agreement on diagnosis in diffuse parenchymal lung disease: a case-cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2016; 4:557–565. PMID: 27180021.73. Lynch DA, Sverzellati N, Travis WD, Brown KK, Colby TV, Galvin JR, et al. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a Fleischner Society White Paper. Lancet Respir Med. 2018; 6:138–153. PMID: 29154106.
Article74. Vasakova M, Morell F, Raghu G. Reply to Fernandez Perez: diagnostic decision-making in hypersensitivity pneumonitis: toward a consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197:1648. PMID: 29505280.75. Cormier Y, Desmeule M. Treatment of hypersensitivity pneumonitis: contact avoidance versus corticosteroid treatment. Can Respir J. 1994; 1:223–228.
Article76. De Sadeleer LJ, Hermans F, De Dycker E, Yserbyt J, Verschakelen JA, Verbeken EK, et al. Effects of corticosteroid treatment and antigen avoidance in a large hypersensitivity pneumonitis cohort: a single-centre cohort study. J Clin Med. 2018; 8:E14. PMID: 30577667.
Article77. Kokkarinen JI, Tukiainen HO, Terho EO. Effect of corticosteroid treatment on the recovery of pulmonary function in farmer's lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992; 145:3–5. PMID: 1731594.
Article78. Morisset J, Johannson KA, Vittinghoff E, Aravena C, Elicker BM, Jones KD, et al. Use of mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine for the management of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2017; 151:619–625. PMID: 27816444.
Article79. Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, Fernandez Perez ER, Hamblin M, Patel N, Tener M, et al. Outcomes of immunosuppressive therapy in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. ERJ Open Res. 2017; 3:00016-2017. PMID: 28845429.
Article80. Morell F, Ojanguren I, Villar A, Ramon MA, Munoz X, Cruz MJ. Addition of rituximab to oral corticosteroids in the treatment of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2019; 9. 07. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1016/j.arbres.2019.07.013.
Article81. Carlsen KH, Leegaard J, Lund OD, Skjaervik H. Allergic alveolitis in a 12-year-old boy: treatment with budesonide nebulizing solution. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1992; 12:257–259. PMID: 1614753.
Article82. Wuyts WA, Agostini C, Antoniou KM, Bouros D, Chambers RC, Cottin V, et al. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: a moving target. Eur Respir J. 2013; 41:1207–1218. PMID: 23100500.
Article83. Flaherty KR, Wells AU, Cottin V, Devaraj A, Walsh SL, Inoue Y, et al. Nintedanib in progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:1718–1727. PMID: 31566307.
Article84. Mateos-Toledo H, Mejia-Avila M, Rodriguez-Barreto O, Mejia-Hurtado JG, Rojas-Serrano J, Estrada A, et al. An open-label study with pirfenidone on chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2019; 11. 26. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1016/j.arbres.2019.08.019.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of hypersensitivity pneumonitis with positive precipitin antibody to Trichosporon cutaneum
- A Case of Gold Induced Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Diagnosed by Lymphocyte Stimulation Test with Gold
- Hypersenstivity Pheumonitis
- A Case of Secondary Syphilis with Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction Presenting as Hypersensitivity Pneumonit
- Occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis