J Breast Cancer.
2020 Feb;23(1):20-35. 10.4048/jbc.2020.23.e7.
Protocatechuic Aldehyde Represses Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells through Targeting C-terminal Binding Protein 1
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Medicine, Chengdu University, Chengdu, China.
- 2Institute of Cancer Biology and Drug Discovery, Chengdu University, Chengdu, China.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, affiliated with Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China. drlifulun@163.com
- 4The Seventh People's Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China.
- 5Department of Dermatology, Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital, Tianjin, China.
- 6Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, University of Colorado Denver, Aurora, CO, USA.
- 7Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, College for Public Health and Social Justice, Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO, USA.
- 8Central Lab, Chengdu Univerisity Hospital, Chengdu, China.
- 9CAS Key Laboratory of Receptor Research, Drug Discovery and Design Center, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
- KMID: 2470879
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2020.23.e7
Abstract
- PURPOSE
C-terminal binding protein 1 (CtBP1) is a transcriptional co-repressor that is overexpressed in many cancers. CtBP1 transcriptionally represses a broad array of tumor suppressors, which promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and resistance to apoptosis. Recent studies have demonstrated that CtBP1 is a potential target for cancer therapy. This study was designed to screen for compounds that potentially target CtBP1.
METHODS
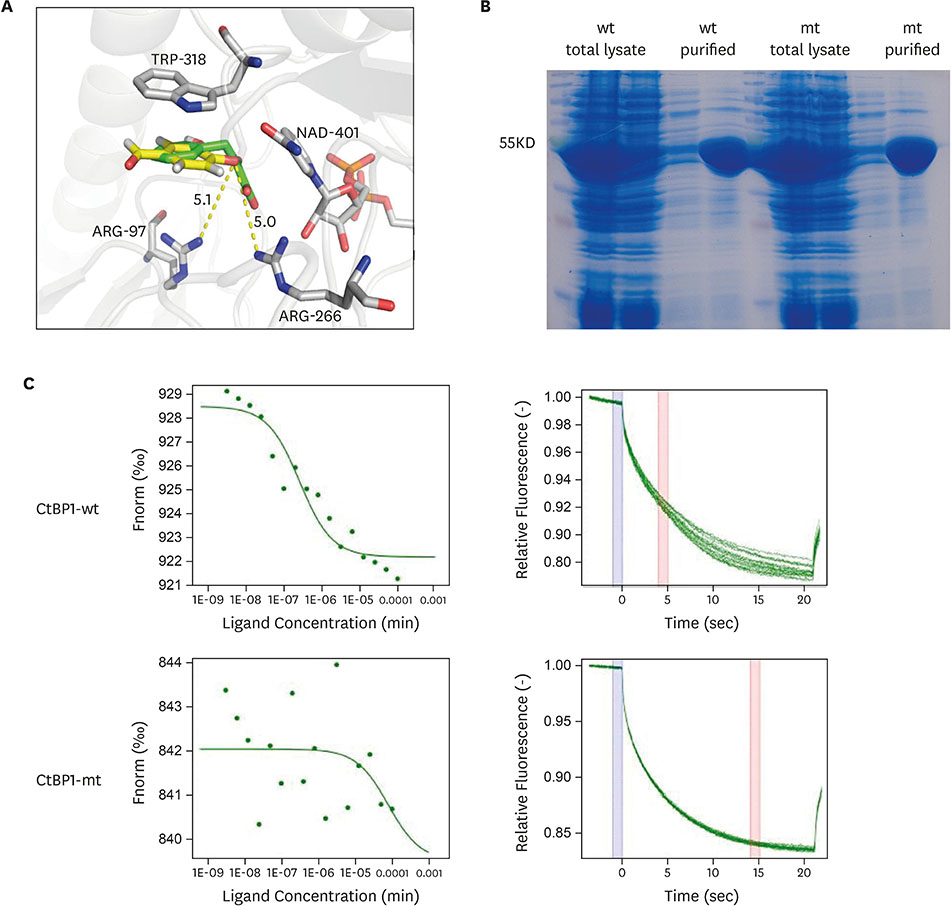
Using a structure-based virtual screening for CtBP1 inhibitors, we found protocatechuic aldehyde (PA), a natural compound found in the root of a traditional Chinese herb, Salvia miltiorrhiza, that directly binds to CtBP1. Microscale thermophoresis assay was performed to determine whether PA and CtBP1 directly bind to each other. Further, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats associated Cas9 nuclease-mediated CtBP1 knockout in breast cancer cells was used to validate the CtBP1 targeting specificity of PA.
RESULTS
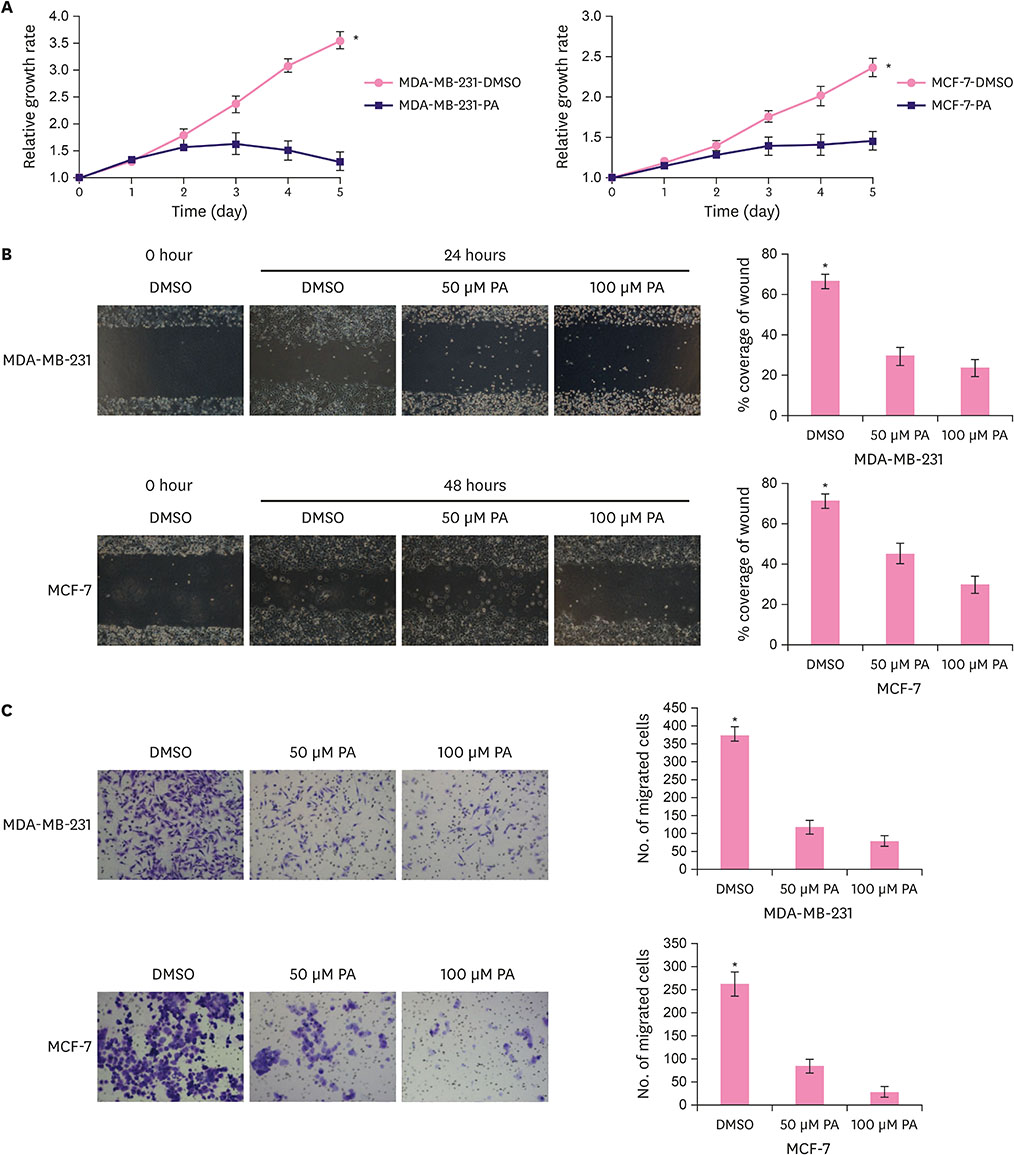
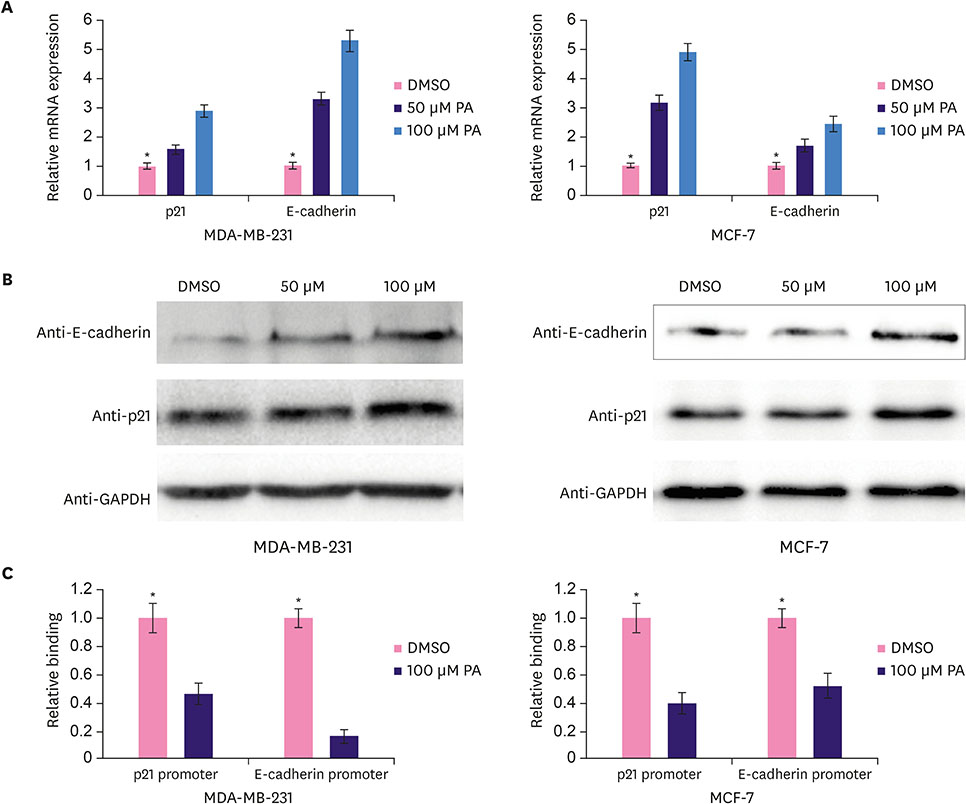
Functional studies showed that PA repressed the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells. Furthermore, PA elevated the expression of the downstream targets of CtBP1, p21 and E-cadherin, and decreased CtBP1 binding affinity for the promoter regions of p21 and E-cadherin in breast cancer cells. However, PA did not affect the expression of p21 and E-cadherin in the CtBP1 knockout breast cancer cells. In addition, the CtBP1 knockout breast cancer cells showed resistance to PA-induced repression of proliferation and migration.
CONCLUSION
Our findings demonstrated that PA directly bound to CtBP1 and inhibited the growth and migration of breast cancer cells through CtBP1 inhibition. Structural modifications of PA are further required to enhance its binding affinity and selectivity for CtBP1.
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Breast Neoplasms*
Breast*
Cadherins
Carrier Proteins*
Cell Proliferation
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats
Humans
Mass Screening
Promoter Regions, Genetic
Repression, Psychology
Salvia miltiorrhiza
Sensitivity and Specificity
Cadherins
Carrier Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schaeper U, Boyd JM, Verma S, Uhlmann E, Subramanian T, Chinnadurai G. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cellular phosphoprotein that interacts with a conserved C-terminal domain of adenovirus E1A involved in negative modulation of oncogenic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92:10467–10471.
Article2. Byun JS, Gardner K. C-terminal binding protein: a molecular link between metabolic imbalance and epigenetic regulation in breast cancer. Int J Cell Biol. 2013; 2013:647975.
Article3. Chinnadurai G. CtBP, an unconventional transcriptional corepressor in development and oncogenesis. Mol Cell. 2002; 9:213–224.
Article4. Postigo AA, Dean DC. ZEB represses transcription through interaction with the corepressor CtBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:6683–6688.
Article5. Guaita S, Puig I, Franci C, Garrido M, Dominguez D, Batlle E, et al. Snail induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells is accompanied by MUC1 repression and ZEB1 expression. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:39209–39216.
Article6. Zhang Q, Wang SY, Nottke AC, Rocheleau JV, Piston DW, Goodman RH. Redox sensor CtBP mediates hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:9029–9033.
Article7. Madison DL, Lundblad JR. C-terminal binding protein and poly(ADP)ribose polymerase 1 contribute to repression of the p21(waf1/cip1) promoter. Oncogene. 2010; 29:6027–6039.
Article8. Liu G, Zheng H, Ai W. C-terminal binding proteins (CtBPs) attenuate KLF4-mediated transcriptional activation. FEBS Lett. 2009; 583:3127–3132.
Article9. Zhang Q, Piston DW, Goodman RH. Regulation of corepressor function by nuclear NADH. Science. 2002; 295:1895–1897.
Article10. Kumar V, Carlson JE, Ohgi KA, Edwards TA, Rose DW, Escalante CR, et al. Transcription corepressor CtBP is an NAD(+)-regulated dehydrogenase. Mol Cell. 2002; 10:857–869.
Article11. Deng Y, Liu J, Han G, Lu SL, Wang SY, Malkoski S, et al. Redox-dependent Brca1 transcriptional regulation by an NADH-sensor CtBP1. Oncogene. 2010; 29:6603–6608.
Article12. Deng H, Liu J, Deng Y, Han G, Shellman YG, Robinson SE, et al. CtBP1 is expressed in melanoma and represses the transcription of p16INK4a and Brca1. J Invest Dermatol. 2013; 133:1294–1301.
Article13. Deng Y, Deng H, Liu J, Han G, Malkoski S, Liu B, et al. Transcriptional down-regulation of Brca1 and E-cadherin by CtBP1 in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2012; 51:500–507.
Article14. Nadauld LD, Phelps R, Moore BC, Eisinger A, Sandoval IT, Chidester S, et al. Adenomatous polyposis coli control of C-terminal binding protein-1 stability regulates expression of intestinal retinol dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:37828–37835.
Article15. Di LJ, Byun JS, Wong MM, Wakano C, Taylor T, Bilke S, et al. Genome-wide profiles of CtBP link metabolism with genome stability and epithelial reprogramming in breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2013; 4:1449.
Article16. Kim KJ, Kim MA, Jung JH. Antitumor and antioxidant activity of protocatechualdehyde produced from Streptomyces lincolnensis M-20. Arch Pharm Res. 2008; 31:1572–1577.
Article17. Jerabek-Willemsen M, Wienken CJ, Braun D, Baaske P, Duhr S. Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011; 9:342–353.
Article18. Deng Y, Li F, He P, Yang Y, Yang J, Zhang Y, et al. Triptolide sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through the DNA damage response inhibition. Mol Carcinog. 2018; 57:807–814.
Article19. Banks JL, Beard HS, Cao Y, Cho AE, Damm W, Farid R, et al. Integrated modeling program, applied chemical theory (IMPACT). J Comput Chem. 2005; 26:1752–1780.
Article20. Deng Y, Li H, Yin X, Liu H, Liu J, Guo D, et al. C-terminal binding protein 1 modulates cellular redox via feedback regulation of MPC1 and MPC2 in melanoma cells. Med Sci Monit. 2018; 24:7614–7624.
Article21. Bergman LM, Birts CN, Darley M, Gabrielli B, Blaydes JP. CtBPs promote cell survival through the maintenance of mitotic fidelity. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29:4539–4551.
Article22. Blevins MA, Huang M, Zhao R. The role of CtBP1 in oncogenic processes and its potential as a therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017; 16:981–990.
Article23. Hilbert BJ, Grossman SR, Schiffer CA, Royer WE Jr. Crystal structures of human CtBP in complex with substrate MTOB reveal active site features useful for inhibitor design. FEBS Lett. 2014; 588:1743–1748.
Article24. Hilbert BJ, Morris BL, Ellis KC, Paulsen JL, Schiffer CA, Grossman SR, et al. Structure-guided design of a high affinity inhibitor to human CtBP. ACS Chem Biol. 2015; 10:1118–1127.
Article25. Birts CN, Nijjar SK, Mardle CA, Hoakwie F, Duriez PJ, Blaydes JP, et al. A cyclic peptide inhibitor of C-terminal binding protein dimerization links metabolism with mitotic fidelity in breast cancer cells. Chem Sci (Camb). 2013; 4:3046–3057.
Article26. Blevins MA, Kouznetsova J, Krueger AB, King R, Griner LM, Hu X, et al. Small molecule, NSC95397, inhibits the CtBP1-protein partner interaction and CtBP1-mediated transcriptional repression. J Biomol Screen. 2015; 20:663–672.
Article27. Straza MW, Paliwal S, Kovi RC, Rajeshkumar B, Trenh P, Parker D, et al. Therapeutic targeting of C-terminal binding protein in human cancer. Cell Cycle. 2010; 9:3740–3750.
Article28. Stankiewicz TR, Gray JJ, Winter AN, Linseman DA. C-terminal binding proteins: central players in development and disease. Biomol Concepts. 2014; 5:489–511.
Article29. Choi J, Jiang X, Jeong JB, Lee SH. Anticancer activity of protocatechualdehyde in human breast cancer cells. J Med Food. 2014; 17:842–848.
Article30. Moon CY, Ku CR, Cho YH, Lee EJ. Protocatechuic aldehyde inhibits migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and intravascular thrombosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 423:116–121.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- AC092127.1-miR-451a-AE binding protein 2 Signaling Facilitates Malignant Properties of Breast Cancer
- Inhibitor of DNA-binding 4 contributes to the maintenance and expansion of cancer stem cells in 4T1 mouse mammary cancer cell line
- Dioscin Decreases Breast Cancer Stem-like Cell Proliferation via Cell Cycle Arrest by Modulating p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways
- Long Noncoding-RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA Processing Endoribonuclease Promotes Carcinogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via the Competing Endogenous RNA Mechanism
- Artesunate Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating the SLC7A11-GPX4 Pathway via the p300-p53 Axis