Korean J Radiol.
2020 Mar;21(3):356-364. 10.3348/kjr.2019.0413.
Low-Dose Abdominal CT Using a Deep Learning-Based Denoising Algorithm: A Comparison with CT Reconstructed with Filtered Back Projection or Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. changwon1981@gmail.com
- 3Bio Imaging and Signal Processing Lab, Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Interdisciplinary Program in Bioengineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2470759
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2019.0413
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
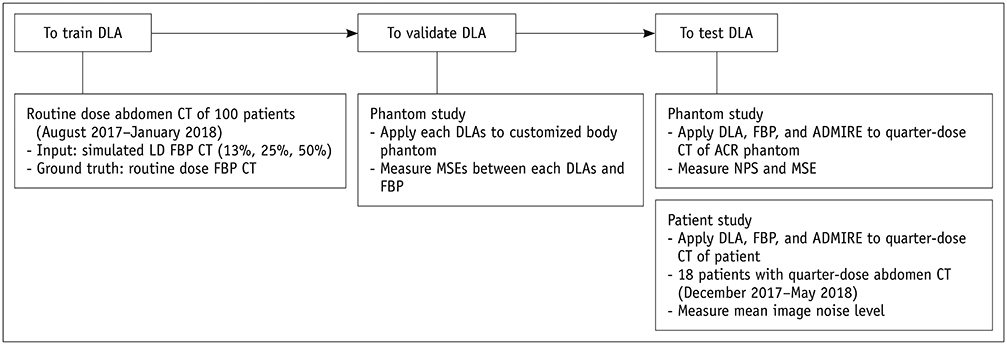
To compare the image quality of low-dose (LD) computed tomography (CT) obtained using a deep learning-based denoising algorithm (DLA) with LD CT images reconstructed with a filtered back projection (FBP) and advanced modeled iterative reconstruction (ADMIRE).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
One hundred routine-dose (RD) abdominal CT studies reconstructed using FBP were used to train the DLA. Simulated CT images were made at dose levels of 13%, 25%, and 50% of the RD (DLA-1, -2, and -3) and reconstructed using FBP. We trained DLAs using the simulated CT images as input data and the RD CT images as ground truth. To test the DLA, the American College of Radiology CT phantom was used together with 18 patients who underwent abdominal LD CT. LD CT images of the phantom and patients were processed using FBP, ADMIRE, and DLAs (LD-FBP, LD-ADMIRE, and LD-DLA images, respectively). To compare the image quality, we measured the noise power spectrum and modulation transfer function (MTF) of phantom images. For patient data, we measured the mean image noise and performed qualitative image analysis. We evaluated the presence of additional artifacts in the LD-DLA images.
RESULTS
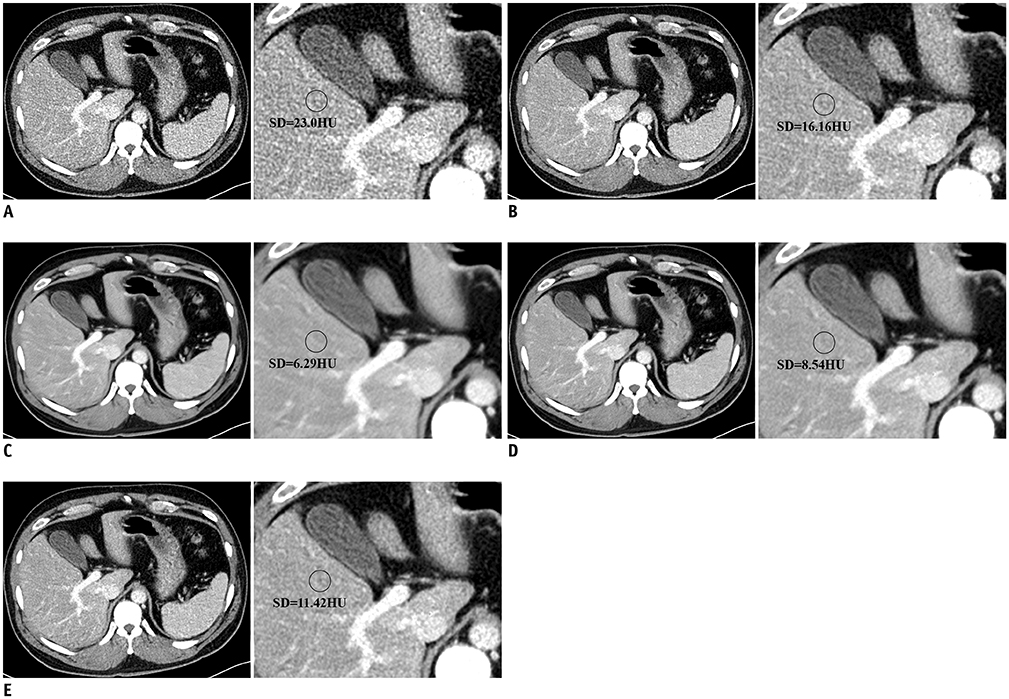
LD-DLAs achieved lower noise levels than LD-FBP and LD-ADMIRE for both phantom and patient data (all p < 0.001). LD-DLAs trained with a lower radiation dose showed less image noise. However, the MTFs of the LD-DLAs were lower than those of LD-ADMIRE and LD-FBP (all p < 0.001) and decreased with decreasing training image dose. In the qualitative image analysis, the overall image quality of LD-DLAs was best for DLA-3 (50% simulated radiation dose) and not significantly different from LD-ADMIRE. There were no additional artifacts in LD-DLA images.
CONCLUSION
DLAs achieved less noise than FBP and ADMIRE in LD CT images, but did not maintain spatial resolution. The DLA trained with 50% simulated radiation dose showed the best overall image quality.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smith-Bindman R, Lipson J, Marcus R, Kim KP, Mahesh M, Gould R, et al. Radiation dose associated with common computed tomography examinations and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:2078–2086.
Article2. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography — An increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2277–2284.
Article3. Berrington de González A, Mahesh M, Kim KP, Bhargavan M, Lewis R, Mettler F, et al. Projected cancer risks from computed tomographic scans performed in the United States in 2007. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:2071–2077.
Article4. Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, Kujak JL, Lawder HJ, Pavlicek W. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:764–771.
Article5. Nakayama Y, Awai K, Funama Y, Hatemura M, Imuta M, Nakaura T, et al. Abdominal CT with low tube voltage: preliminary observations about radiation dose, contrast enhancement, image quality, and noise. Radiology. 2005; 237:945–951.
Article6. Sagara Y, Hara AK, Pavlicek W, Silva AC, Paden RG, Wu Q. Abdominal CT: comparison of low-dose CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction and routine-dose CT with filtered back projection in 53 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:713–719.
Article7. Geyer LL, Schoepf UJ, Meinel FG, Nance JW Jr, Bastarrika G, Leipsic JA, et al. State of the art: iterative CT reconstruction techniques. Radiology. 2015; 276:339–357.
Article8. Holmquist F, Nyman U, Siemund R, Geijer M, Söderberg M. Impact of iterative reconstructions on image noise and low-contrast object detection in low kVp simulated abdominal CT: a phantom study. Acta Radiol. 2016; 57:1079–1088.
Article9. Prakash P, Kalra MK, Kambadakone AK, Pien H, Hsieh J, Blake MA, et al. Reducing abdominal CT radiation dose with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Invest Radiol. 2010; 45:202–210.
Article10. Yu L, Liu X, Leng S, Kofler JM, Ramirez-Giraldo JC, Qu M, et al. Radiation dose reduction in computed tomography: techniques and future perspective. Imaging Med. 2009; 1:65–84.
Article11. Jain V, Seung S. Natural image denoising with convolutional networks. In : 23rd annual conference on neural information processing systems 22; 2009 December 7–10; Vancouver, Canada.12. Nasri M, Nezamabadi-pour H. Image denoising in the wavelet domain using a new adaptive thresholding function. Neurocomputing. 2009; 72:1012–1025.
Article13. Xie J, Xu L, Chen E. Image denoising and inpainting with deep neural networks. In : 26th annual conference on neural information processing systems 25; 2012 December 3–6; Lake Tahoe, NV, USA.14. Kang E, Min J, Ye JC. A deep convolutional neural network using directional wavelets for low-dose X-ray CT reconstruction. Med Phys. 2017; 44:e360–e375.
Article15. Chen H, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Liao P, Li K, Zhou J, et al. Low-dose CT via convolutional neural network. Biomed Opt Express. 2017; 8:679–694.16. McCollough C. TU-FG-207A-04: overview of the low dose CT grand challenge. Med Phys. 2016; 43(Part 35):3759–3760.
Article17. Chen H, Zhang Y, Kalra MK, Lin F, Chen Y, Liao P, et al. Low-dose CT with a residual encoder-decoder convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2017; 36:2524–2535.
Article18. Kang E, Chang W, Yoo J, Ye JC. Deep convolutional framelet denosing for low-dose CT via wavelet residual network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2018; 37:1358–1369.
Article19. Ellmann S, Kammerer F, Brand M, Allmendinger T, May MS, Uder M, et al. A novel pairwise comparison-based method to determine radiation dose reduction potentials of iterative reconstruction algorithms, exemplified through circle of Willis computed tomography angiography. Invest Radiol. 2016; 51:331–339.
Article20. Ehman EC, Yu L, Manduca A, Hara AK, Shiung MM, Jondal D, et al. Methods for clinical evaluation of noise reduction techniques in abdominopelvic CT. Radiographics. 2014; 34:849–862.
Article21. Richard S, Husarik DB, Yadava G, Murphy SN, Samei E. Towards task-based assessment of CT performance: system and object MTF across different reconstruction algorithms. Med Phys. 2012; 39:4115–4122.
Article22. Friedman SN, Fung GS, Siewerdsen JH, Tsui BM. A simple approach to measure computed tomography (CT) modulation transfer function (MTF) and noise-power spectrum (NPS) using the American College of Radiology (ACR) accreditation phantom. Med Phys. 2013; 40:051907.
Article23. Kim K, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim S, Lee YJ, Kim KP, et al. Low-dose abdominal CT for evaluating suspected appendicitis. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1596–1605.
Article24. Kim SY, Lee KH, Kim K, Kim TY, Lee HS, Hwang SS, et al. Acute appendicitis in young adults: low- versus standard-radiation-dose contrast-enhanced abdominal CT for diagnosis. Radiology. 2011; 260:437–445.
Article25. Christianson O, Chen JJ, Yang Z, Saiprasad G, Dima A, Filliben JJ, et al. An improved index of image quality for task-based performance of CT iterative reconstruction across three commercial implementations. Radiology. 2015; 275:725–734.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of a Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction Algorithm with Filtered Back Projection and Iterative Reconstruction Algorithms for Pediatric Abdominopelvic CT
- Effects of Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm, Automatic Exposure Control on Image Quality, and Radiation Dose: Phantom Experiments with Coronary CT Angiography Protocols
- Contrast-Enhanced CT with Knowledge-Based Iterative Model Reconstruction for the Evaluation of Parotid Gland Tumors: A Feasibility Study
- Quantitative Image Quality and Histogram-Based Evaluations of an Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm at Low-to-Ultralow Radiation Dose Levels: A Phantom Study in Chest CT
- Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction Algorithm in CT: Effect on Image Quality Compared with Filtered Back Projection in Body Phantoms of Different Sizes