Prog Med Phys.
2015 Mar;26(1):28-35. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.1.28.
Effects of Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm, Automatic Exposure Control on Image Quality, and Radiation Dose: Phantom Experiments with Coronary CT Angiography Protocols
- Affiliations
-
- 1Yonsei - Cedars-Sinai, Integrative Cardiovascular Imaging Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Graduate School of Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Toshiba Medical Systems Korea, Seoul, Korea. hackjoon.shim@toshiba-medical.co.kr
- KMID: 2315775
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.1.28
Abstract
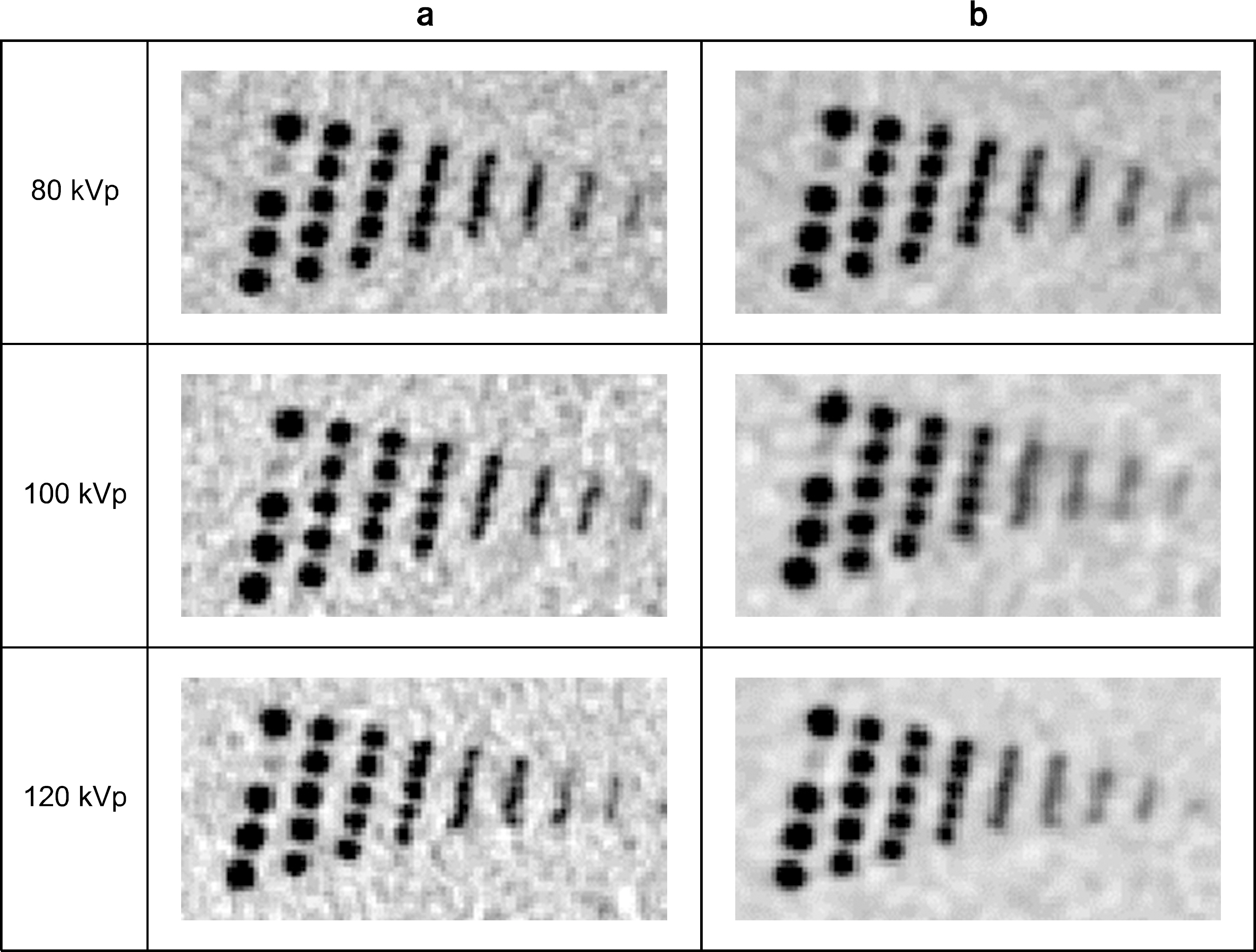
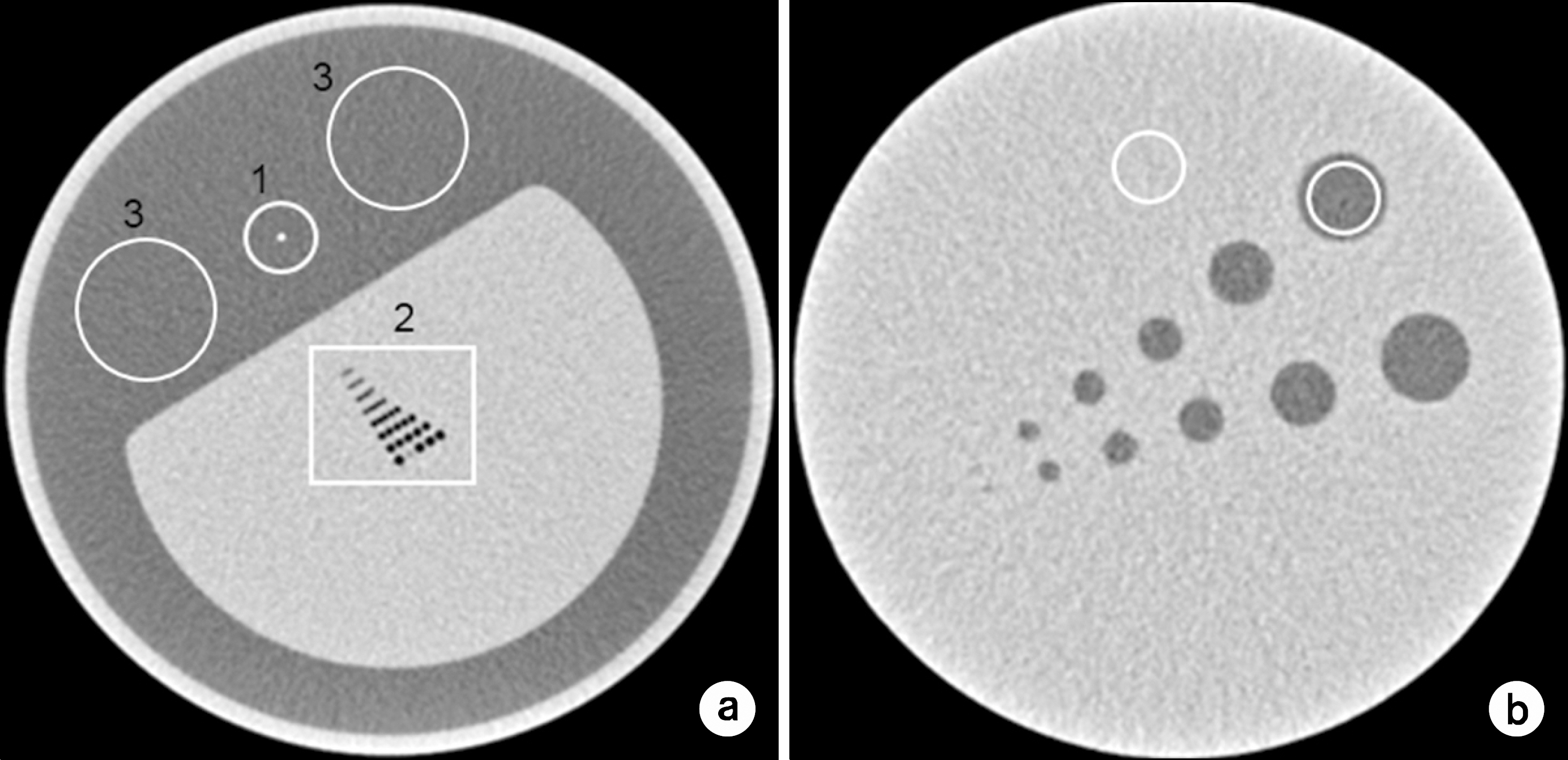
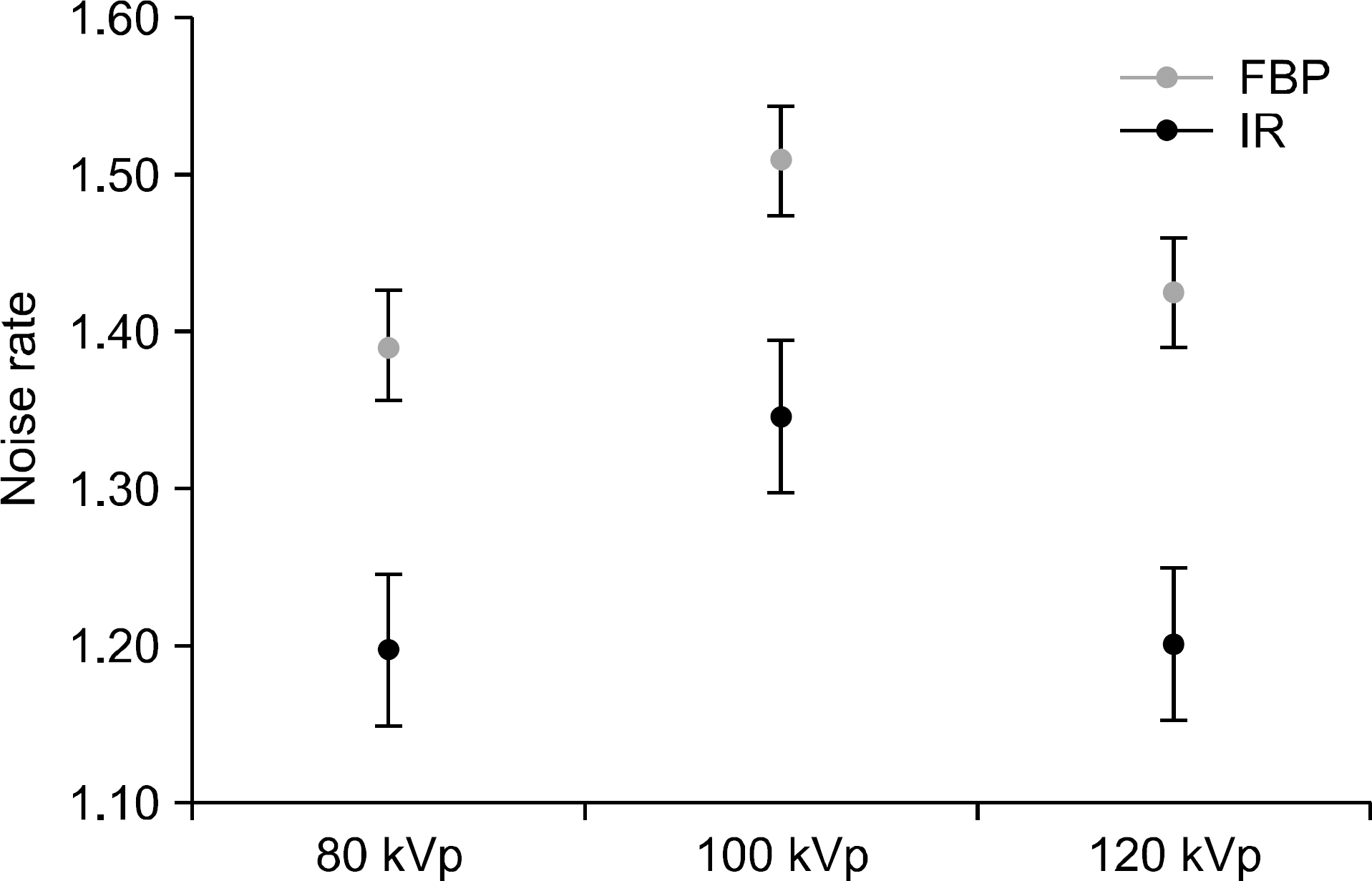
- In this study, we investigated the effects of an iterative reconstruction algorithm and an automatic exposure control (AEC) technique on image quality and radiation dose through phantom experiments with coronary computed tomography (CT) angiography protocols. We scanned the AAPM CT performance phantom using 320 multi-detector-row CT. At the tube voltages of 80, 100, and 120 kVp, the scanning was repeated with two settings of the AEC technique, i.e., with the target standard deviations (SD) values of 33 (the higher tube current) and 44 (the lower tube current). The scanned projection data were reconstructed also in two ways, with the filtered back projection (FBP) and with the iterative reconstruction technique (AIDR-3D). The image quality was evaluated quantitatively with the noise standard deviation, modulation transfer function, and the contrast to noise ratio (CNR). More specifically, we analyzed the influences of selection of a tube voltage and a reconstruction algorithm on tube current modulation and consequently on radiation dose. Reduction of image noise by the iterative reconstruction algorithm compared with the FBP was revealed eminently, especially with the lower tube current protocols, i.e., it was decreased by 46% and 38%, when the AEC was established with the lower dose (the target SD=44) and the higher dose (the target SD=33), respectively. As a side effect of iterative reconstruction, the spatial resolution was decreased by a degree that could not mar the remarkable gains in terms of noise reduction. Consequently, if coronary CT angiogprahy is scanned and reconstructed using both the automatic exposure control and iterative reconstruction techniques, it is anticipated that, in comparison with a conventional acquisition method, image noise can be reduced significantly with slight decrease in spatial resolution, implying clinical advantages of radiation dose reduction, still being faithful to the ALARA principle.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Estimation of Noise Level and Edge Preservation for Computed Tomography Images: Comparisons in Iterative Reconstruction
Sihwan Kim, Chulkyun Ahn, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Jong Hyo Kim, Minsoo Chun
Prog Med Phys. 2021;32(4):92-98. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2021.32.4.92.
Reference
-
References
1. MEDPAC: A Data Book: Healthcare Spending and the Medicare Program. Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, (. 2013.2. Smith-Bindman R, Lipson J, Marcus R, et al. Radiation dose associated with common computed tomography examinations and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer, Arch Intern Med. 169(22):2079–2086. 2009.3. ICRP Publication 102. Managing patient dose in multi-detector computed tomography(MDCT).Ann ICRP. 37(1):1–79. 2006.4. Hsieh J. Computed tomography: principles, design, artifacts, and recent advances, SPIE, (. 2009.5. Dougeni E, Faulkner K, Panayiotakis G. A review of patient dose and optimisation methods in adult and paediatric CT scanning, Eur J Radiol. 81(4):665–683. 2011.6. Payne JT. CT radiation dose and image quality, Radiol Clin North Am. 43(6):953–962. 2005.7. Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, et al. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study, AJR Am J Roentgenology. 193(3):764–771. 2009.8. Xu J, Mahesh M, Tsui BM. Is iterative reconstruction ready for MDCT?, J Am Coll Radiol. 6(4):274–276. 2009.9. Denis T, Kalra MK, Gevenois PA. Radiation dose from multidetector CT. 2nd ed.Springer;2012. ), pp.p. 152–154.10. Von Spiczak J1. Morsbach F, Winklhofer S, et al. Coronary artery stent imaging with CT using an integrated electronics detector and iterative reconstructions: first in vitro experience, J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 7(4):215–222. 2013.11. Ohashi K, Ichikawa K, Hara M. Examination of the optimal temporal resolution required for computed tomography coronary angiography, Radiol Phys Technol. 6(2):453–460. 2013.12. Gervaise A, Osemont B, Lecocq S. CT image quality improvement using adaptive iterative dose reduction with widevolume acquisition on 320-detector CT, European radiology. 22(2):295–301. 2012.13. Nakaya Y, Kawata Y, Niki N, et al. A method for determining the modulation transfer function from thick microwire profiles measured with x-ray microcomputed tomography, Medical Physics. 39(7):4347–4364. 2012.14. Ohkubo M, Wada S, Matsumoto T, et al. An effective method to verify line and point spread functions measured in computed tomography, Medical physics. 33(8):2757–2764. 2006.15. L. del Risco Norrlid, C. Rönnqvist, K. Fransson, et al: Calculation of the modulation transfer function for the X-ray imaging detector DIXI using Monte Carlo simulation data, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A. 466(1):209–217. (. 2001.16. Samei E, Ranger NT, Dobbins JT 3rd, et al. Intercomparison of methods for image quality characterization. I. Modulation transfer function, Medical physics. 33(5):1454–1465. 2006.17. Kenneth AF, Nicholas JH, Beth AS, et al. Measurement of the presampled two-dimensional modulation transfer function of digital imaging systems, Medical physics 29 (5) 913–921 (. 2002.18. Kalra MK, Maher MM, Toth TL, et al. Strategies for CT radiation dose optimization. Radiology. 230(3):619–628. 2004.
Article19. ICRP publication 103. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, Ann ICRP 37 (2–4): (. 2007.20. Halliburton SS, Abbara S, Chen MY, et al. SCCT guidelines on radiation dose and dose-optimization strategies in cardiovascular CT, Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. 5(4):198–224. 2011.21. Sharma RK, Voelker DJ, Sharma RK. Coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) in community hospitals: "current and emerging role", Vasc Health Risk Manag. 25(6):307–316. 2010.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dosimetric Effects of Low Dose 4D CT Using a Commercial Iterative Reconstruction on Dose Calculation in Radiation Treatment Planning: A Phantom Study
- Quantitative Image Quality and Histogram-Based Evaluations of an Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm at Low-to-Ultralow Radiation Dose Levels: A Phantom Study in Chest CT
- Quantitative Analysis of the Effect of Iterative Reconstruction Using a Phantom: Determining the Appropriate Blending Percentage
- Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction Algorithm in CT: Effect on Image Quality Compared with Filtered Back Projection in Body Phantoms of Different Sizes
- Low-Dose Abdominal CT Using a Deep Learning-Based Denoising Algorithm: A Comparison with CT Reconstructed with Filtered Back Projection or Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm