Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Dec;43(6):635-641. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.6.635.
Safe Needle Insertion Locations for Motor Point Injection of the Triceps Brachii Muscle: A Pilot Cadaveric and Ultrasonography Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, National Traffic Injury Rehabilitation Hospital, Yangpyeong, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. lafolia@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2468690
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.6.635
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
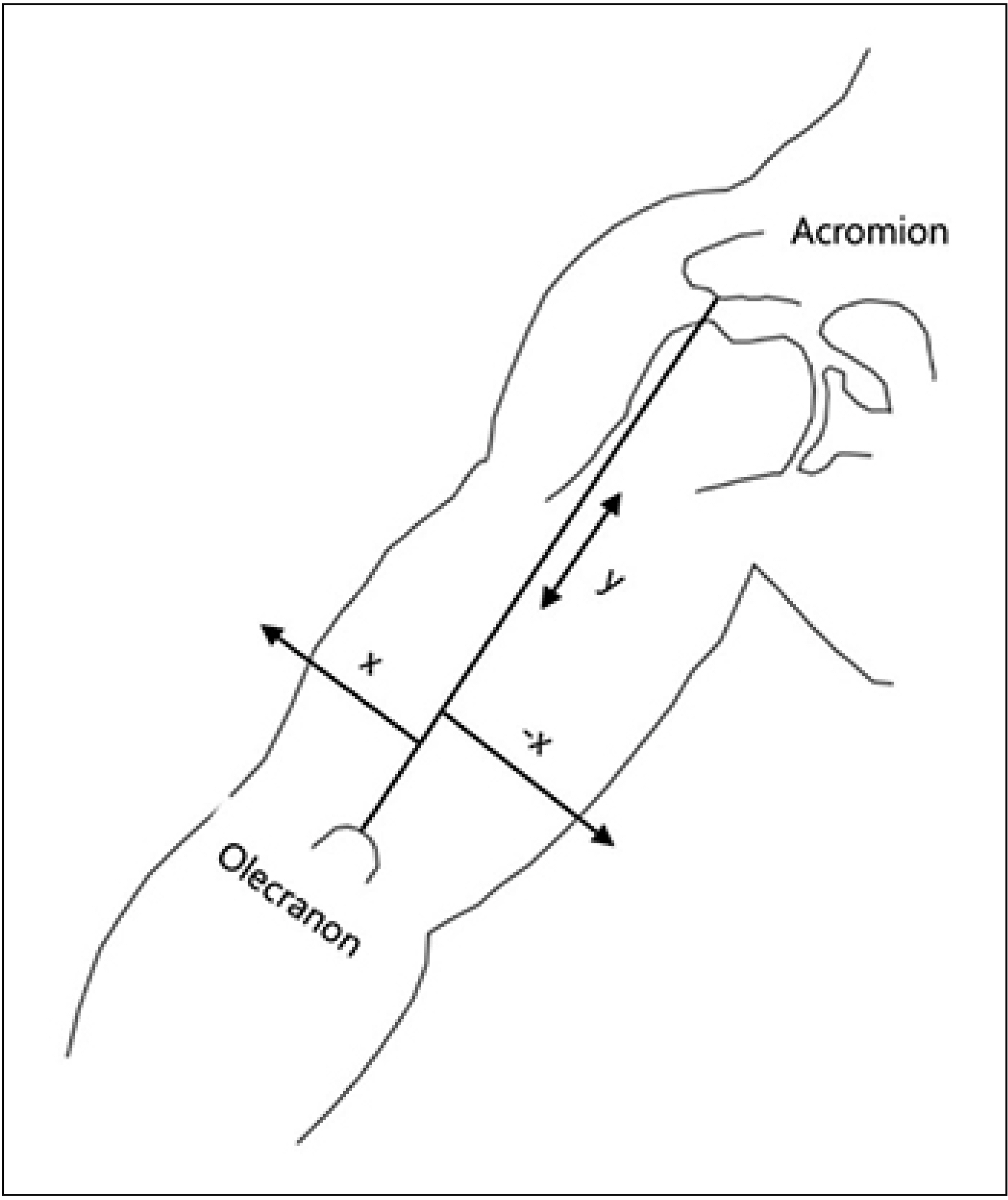
To determine the location of the motor endplate zones (MoEPs) for the three heads of the triceps brachii muscles during cadaveric dissection and estimate the safe injection zone using ultrasonography.
METHODS
We studied 12 upper limbs of 6 fresh cadavers obtained from body donations to the medical school anatomy institution in Seoul, Korea. The locations of MoEPs were expressed as the percentage ratio of the vertical distance from the posterior acromion angle to the midpoint of the olecranon process. By using the same reference line as that used for cadaveric dissection, the safe injection zone away from the neurovascular bundle was identified in 6 healthy volunteers via ultrasonography. We identified the neurovascular bundle and its location with respect to the distal end of the humerus and measured its depth from the skin surface.
RESULTS
The MoEPs for the long, lateral, and medial heads were located at a median of 43.8%, 54.8%, and 60.4% of the length of the reference line in cadaver dissection. The safe injection zone of the medial head MoEPs corresponded to a depth of approximately 3.5 cm from the skin surface and 1.4 cm away from the humerus, as determined by sonography.
CONCLUSION
Correct identification of the motor points for each head of the triceps brachii would increase the precision and efficacy of motor point injections to manage elbow extensor spasticity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ward AB. Spasticity treatment with botulinum toxins. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008; 115:607–16.
Article2. Bai YL, Hu YS, Wu Y, Zhu YL, Zhang B, Jiang CY, et al. Long-term three-stage rehabilitation intervention alleviates spasticity of the elbows, fingers, and plantar flexors and improves activities of daily living in ischemic stroke patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Neuroreport. 2014; 25:998–1005.3. Atiyeh BS, Hayek SN. Pressure sores with associated spasticity: a clinical challenge. Int Wound J. 2005; 2:77–80.
Article4. Hefter H, Jost WH, Reissig A, Zakine B, Bakheit AM, Wissel J. Classification of posture in poststroke upper limb spasticity: a potential decision tool for botulinum toxin A treatment? Int J Rehabil Res. 2012; 35:227–33.5. Hierner R, Rollnik JD, Berger AC, Dengler R. Botulinum toxin type a for the treatment of biceps/triceps co-contraction in obstetrical brachial plexus lesions. Eur J Plast Surg. 2001; 24:2–6.
Article6. Thibaut A, Chatelle C, Ziegler E, Bruno MA, Laureys S, Gosseries O. Spasticity after stroke: physiology, assessment and treatment. Brain Inj. 2013; 27:1093–105.
Article7. Parratte B, Tatu L, Vuillier F, Diop M, Monnier G. Intramuscular distribution of nerves in the human triceps surae muscle: anatomical bases for treatment of spastic drop foot with botulinum toxin. Surg Radiol Anat. 2002; 24:91–6.
Article8. Shaari CM, Sanders I. Quantifying how location and dose of botulinum toxin injections affect muscle paralysis. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:964–9.
Article9. Van Campenhout A, Bar-On L, Desloovere K, Molenaers G. Role of motor end plate-targeted botulinum toxin type A injections in children with cerebral palsyitle. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015; 81:167–71.10. Im S, Han SH, Choi JH, Lee JH, Ko YJ, Lee JI, et al. Anatomic localization of motor points for the neuromuscular blockade of hand intrinsic muscles involved in thumb-in-palm. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 87:703–9.
Article11. Alter KE, Karp BI. Ultrasound guidance for botulinum neurotoxin chemodenervation procedures. Toxins (Basel). 2017; 10.
Article12. Brashear A, Elovic E. Spasticity: diagnosis and management. New York: Demos Medical Publishing;2010.13. Hamill J, Knutzen KM. Biomechanical basis of human movement. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2009.14. Starkweather KJ, Gu Y, Gudas S, Murtaugh H, Frykberg B. PR_065: Localization of radial nerve motor points in the triceps muscle: a descriptive study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:e16.15. Cho H, Lee HY, Gil YC, Choi YR, Yang HJ. Topographical anatomy of the radial nerve and its muscular branches related to surface landmarks. Clin Anat. 2013; 26:862–9.
Article16. Mayer NH, Whyte J, Wannstedt G, Ellis CA. Comparative impact of 2 botulinum toxin injection techniques for elbow flexor hypertonia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:982–7.
Article17. Berweck S, Schroeder AS, Fietzek UM, Heinen F. Sonography-guided injection of botulinum toxin in children with cerebral palsy. Lancet. 2004; 363:249–50.
Article18. Seok J, Oh CT, Kwon HJ, Kwon TR, Choi EJ, Choi SY, et al. Investigating skin penetration depth and shape following needle-free injection at different pressures: a cadaveric study. Lasers Surg Med. 2016; 48:624–8.
Article19. Rha DW, Im SH, Lee SC, Kim SK. Needle insertion into the tibialis posterior: ultrasonographic evaluation of an anterior approach. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:283–7.
Article20. Rha DW, Han SH, Kim HJ, Won SY, Lee SC. Ultrasound-guided lateral approach for needle insertion into the subscapularis for treatment of spasticity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 93:1147–52.
Article21. Opheim A, Danielsson A, Alt Murphy M, Persson HC, Sunnerhagen KS. Upper-limb spasticity during the first year after stroke: stroke arm longitudinal study at the University of Gothenburg. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 93:884–96.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anatomical Locations of the Motor Points of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- Anatomical Locations of the Motor Points of the Triceps Surae Muscles
- Anatomic Motor Point Localization of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- Surface Mapping of Motor Points in Biceps Brachii Muscle
- Appropriate Depth of Needle Insertion During Rhomboid Major Trigger Point Block