Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Apr;36(2):187-196. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.187.
Surface Mapping of Motor Points in Biceps Brachii Muscle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Eunpyeong Hospital, Seoul 122-913, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, CHA University, Seongnam 463-070, Korea. hwangtaesun@cha.ac.kr
- 3Department of Dentistry, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam 463-070, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam 463-070, Korea.
- KMID: 2266756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.187
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
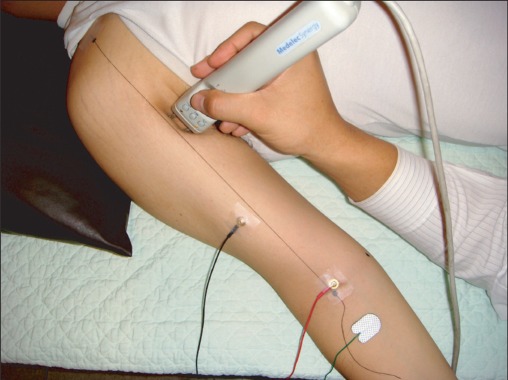
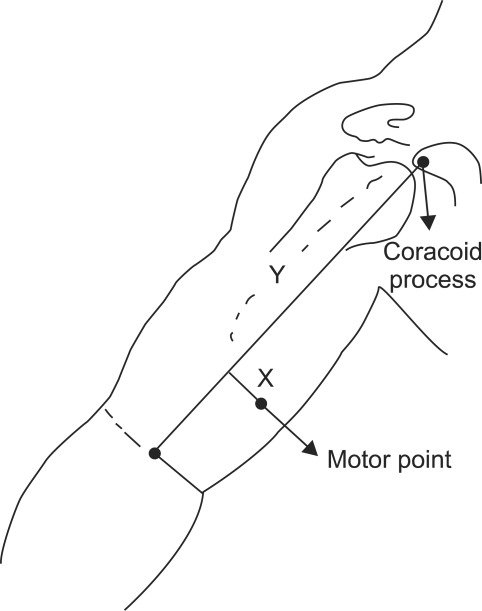
To localize the site of motor points within human biceps brachii muscles through surface mapping using electrophysiological method. METHOD: We recorded the compound muscle action potentials of each lattice of the biceps brachii in 40 healthy subjects. Standardized reference lines were made as the following: 1) a horizontal reference line (elbow crease) and 2) a vertical reference line connecting coracoid process and mid-point of the horizontal reference line. The Compound muscle action potentials were mapped in reference to the standardized reference lines. The locations of motor points were mapped to the skin surface, in the ratio to the length of the vertical and the half of the horizontal reference lines.
RESULTS
The motor point of the short head of biceps was located at 69.0+/-4.9% distal and 19.1+/-9.5% medial to the mid-point of horizontal reference line. The location of the motor point of the long head of the biceps was 67.3+/-4.3% distal and 21.4+/-8.7% lateral. The motor point of the short head of the biceps was located more medially and distally in the male subjects compared to that in the female (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
This study showed electrophysiological motor points of the biceps brachii muscles through surface mapping. This data might improve the clinical efficacy and the feasibility of motor point targeting, when injecting botulinum neurotoxin in biceps brachii.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bang MS, Han TR, Lim JY. Motor point block by phenol in spastic cerebral palsy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1997; 21:71–77.2. Rousseaux M, Kozlowski O, Froger J. Efficacy of botulinum toxin A in upper limb function of hemiplegic patients. J Neurol. 2002; 249:76–84. PMID: 11954872.
Article3. Shaari CM, Sanders I. Quantifying how location and dose of botulinum toxin injections affect muscle paralysis. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:964–969. PMID: 8355728.
Article4. Childers MK, Kornegay JN, Aoki R, Otaviani L, Bogan DJ, Petroski G. Evaluating motor end-plate-targeted injections of botulinum toxin type A in a canine model. Muscle Nerve. 1998; 21:653–655. PMID: 9572248.
Article5. Awad EA, Dykstra D. Kottke FJ, Lehmann JF, editors. Treatment of spasticity by neurolysis. Krusen's handbook of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 1990. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 1154–1161.6. Dumitru D. King JC, Robinson LR, Spielholz NI, Turk MA, editors. Nerve and muscle anatomy and physiology. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 1995. 1st ed. Philadelphia: Henley & Belfus Inc;p. 19.
Article7. Kim HS, Lee KW, Kim JM, Chung SH, Kim SY. Localization of the motor nerve branches and motor points of the hamstring muscles and triceps surae muscle. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1998; 22:1305–1311.8. Kim MW, Kim JH, Ko YJ, Moon JS, Yang YJ. Anatomical locations of the motor points of the triceps surae muscles. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2003; 27:581–584.9. Buchanan TS, Erickson JC. Selective block of the brachialis motor point. An anatomic investigation of musculocutaneous nerve branching. Reg Anesth. 1996; 21:89–92. PMID: 8829418.10. Kim JS, Kwon JY, Kang SY, Park JW. Anatomical locations of the motor points of the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2004; 28:592–595.11. Park BK, Shin YB, Ko HY, Park JH, Baek SY. Anatomic motor point localization of the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:459–462. PMID: 17596654.
Article12. Lee JH, Kim HW, Im S, An X, Lee MS, Lee UY, Han SH. Localization of motor entry points and terminal intramuscular nerve endings of the musculocutaneous nerve to biceps and brachialis muscles. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010; 32:213–220. PMID: 19779662.
Article13. Keenan MA. Management of the spastic upper extremity in the neurologically impaired adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 233:116–125. PMID: 3042230.
Article14. Keenan MA, Tomas ES, Stone L, Gersten LM. Percutaneous phenol block of the musculocutaneous nerve to control elbow flexor spasticity. J Hand Surg Am. 1990; 15:340–346. PMID: 2324468.
Article15. Bang IK, Kim C, Ahn JK, Park YK, Reu HW, Jung IT. Sonographically guided musculocutaneous nerve phenol block for elbow flexor spasticity: case report. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007; 31:371–374.16. Chin TY, Duncan JA, Johnstone BR, Graham HK. Management of the upper limb in cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005; 14:389–404. PMID: 16200013.
Article17. Gracies JM, Lugassy M, Weisz DJ, Vecchio M, Flanagan S, Simpson DM. Botulinum toxin dilution and endplate targeting in spasticity: a double-blind controlled study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:9–16. PMID: 19154823.
Article18. Mayer NH, Whyte J, Wannstedt G, Ellis CA. Comparative impact of 2 botulinum toxin injection techniques for elbow flexor hypertonia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:982–987. PMID: 18452749.
Article19. Francisco GE, Boake C, Vaughn A. Botulinum toxin in upper limb spasticity after acquired brain injury. A randomized trial comparing dilution techniques. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:355–363. PMID: 11964576.20. Ko HY, Park HJ, Park JH, Kim H. Surface mapping of motor points of gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:621–626.21. Aquilonius SM, Askmark H, Gillberg PG, Nandedkar S, Olsson Y, Stalberg E. Topographical localization of motor endplates in cryosections of whole human muscles. Muscle Nerve. 1984; 7:287–293. PMID: 6203034.
Article22. Amirali A, Mu L, Gracies JM, Simpson DM. Anatomical localization of motor endplate bands in the human biceps brachii. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2007; 9:306–312. PMID: 18090684.
Article23. Coërs C. Structural organization of the motor nerve endings in mammalian muscle spindles and other striated muscle fibers. Am J Phys Med. 1959; 38:166–175. PMID: 13810861.24. Christensen E. Topography of terminal motor innervation in striated muscles from stillborn infants. Am J Phys Med. 1959; 38:65–78. PMID: 13637190.
Article25. Deshpande S, Gormley ME, Carvey JR. Muscle fiber orientation in muscles commonly injected with botulinum toxin: an anatomical pilot study. Neurotox Res. 2006; 9:115–120. PMID: 16785107.
Article26. Masuda T, Miyano H, Sadoyama T. The distribution of myoneural junctions in the biceps brachii investigated by surface electromyography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1983; 56:597–603. PMID: 6197278.
Article27. Saitou K, Masuda T, Michikami D, Kojima R, Okada M. Innervation zones of the upper and lower limb muscles estimated by using multichannel surface EMG. J Hum Ergol (Tokyo). 2000; 29:35–52. PMID: 12696320.28. Chiarapattanakom P, Leechavengvongs S, Witoonchart K, Uerpairojkit C, Thuvasethakul P. Anatomy and internal topography of the musculocutaneous nerve: the nerves to the biceps and brachialis muscle. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23:250–255. PMID: 9556264.
Article29. Gaertner E, Kern O, Mahoudeau G, Freys G, Golfetto T, Calon B. Block of brachial plexus branches by the humeral route. A prospective study in 503 ambulatory patients. Proposal of a nerve-blocking sequence. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1999; 43:609–613. PMID: 10408813.30. O'Brien CF. Injection techniques for botulinum toxin using electromyography and electrical simulation. Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1997; 6:S176–S180. PMID: 9826989.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anatomical Locations of the Motor Points of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- Anatomic Motor Point Localization of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- Accessory Tendon of Biceps Brachii Originated from Pectoralis Major
- Bilateral asymmetric supernumerary heads of biceps brachii
- The Third Head of the Biceps Brachii Muscle Originated from the Pectoralis Major Muscle