J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Jun;22(3):459-462. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.3.459.
Anatomic Motor Point Localization of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, 1-10 Ami-dong, Seo-gu, Busan, Korea. yi0314@medimail.co.kr
- 3Department of Anatomy, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, HakjangKeunsol Medical Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1778354
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.3.459
Abstract
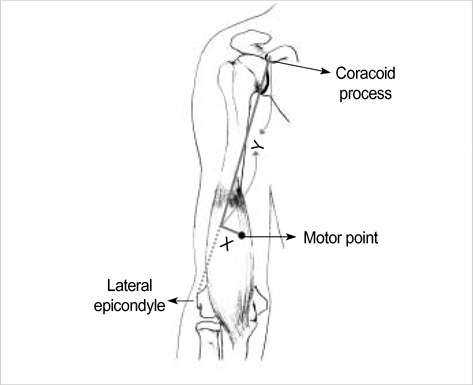
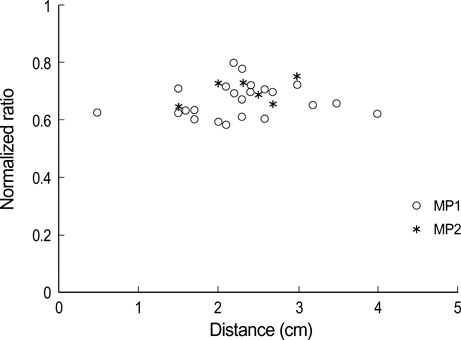
- Injection of the neurolytic agents into motor points of the biceps brachii or brachialis muscles is an effective treatment of spasticity of the elbow flexors in many stroke survivors. Accurate localization of the motor points of each muscle is necessary for enhancing the efficacy of motor point blocks. To identify the precise locations of the motor points (terminal nerve endings) of the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles in relation to anatomic surface landmarks for motor point blocks, we dissected 23 limbs from 12 cadavers. A reference line was defined as a line connecting the coracoid process with the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. The location of the motor points of the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles was identified in reference to the reference line. The motor point of the biceps brachii muscle was found to be approximately half of the reference line. In the brachialis muscle, the location of the motor point was 70% of the reference line from the coracoid process and 2 cm medial to the line. The results are expected to facilitate effective localization of the motor point block of these muscles in selective motor nerve block.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Surface Mapping of Motor Points in Biceps Brachii Muscle
Ja-Young Moon, Tae-Sun Hwang, Seon-Ju Sim, Sae-il Chun, Minyoung Kim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2012;36(2):187-196. doi: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.187.
Reference
-
1. Mizrahi EM, Angel RW. Impairment of voluntary movement by spasticity. Ann Neurol. 1979. 5:594–595.
Article2. Calais-Germain B. Anderson S, editor. The elbow. Anatomy of movement. 1993. Seattle: Eastland Press;131–146.3. Keenan MA, Tomas ES, Stone L, Gersten LM. Percutaneous phenol block of the musculocutaneous nerve to control elbow flexor spasticity. J Hand Surg Am. 1990. 15:340–346.
Article4. Garland DE, Rhoades ME. Orthopedic management of brain-injured adults. Part II. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978. 131:111–122.5. Keenan MA. Management of the spastic upper extremity in the neurologically impaired adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 233:116–125.
Article6. Khalili AA, Betts HB. Isolated block of musculocutaneous and perineal nerves in the management of spasticity with special reference to the use of a nerve stimulator. Anesthesiology. 1967. 28:219–222.7. Garland DE, Thompson R, Waters RL. Musculocutaneous neurectomy for spastic elbow flexion in non-functional upper extremities in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980. 62:108–112.
Article8. Glenn MB. Katz RT, editor. Nerve blocks for the treatment of spasticity. Physical medicine and rehabilitation: state of the art reviews. 1994. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;481–505.9. Johnson ME, Sill JC, Brown DL, Halsey TJ, Uhl CB. The effect of the neurolytic agent ethanol on cytoplasmic calcium in arterial smooth muscle and endothelium. Reg Anesth. 1996. 21:6–13.10. Kong KH, Chua KS. Neurolysis of the musculocutaneous nerve with alcohol to treat poststroke elbow flexor spasticity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999. 80:1234–1236.
Article11. Albert T, Yelnik A, Colle F, Bonan I, Lassau JP. Anatomic motor point localization for partial quadriceps block in spasticity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000. 81:285–287.
Article12. Kim HS, Hwang JH, Lee PK, Kwon JY, Oh-Park MY, Kim JM, Chun MH. Localization of the motor nerve branches and motor points of the triceps surae muscles in Korean cadavers. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002. 81:765–769.13. Buchanan TS, Erickson JC. Selective block of the brachialis motor point. An anatomic investigation of musculocutaneous nerve branching. Reg Anesth. 1996. 21:89–92.14. Kim JS, Kwon JY, Kang SY, Park JW. Anatomical locations of the motor points of the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2004. 28:592–595.15. Jenkins DB. Hollinshead's functional anatomy of the limbs and back. 2002. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.16. Johnson D, Ellis H. Standring S, Ellis H, Healy JC, Johnson D, Williams A, Collins P, Wigley C, editors. Upper arm. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 2005. 39th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;851–858.17. Ip MC, Chang KS. A study on the radial supply of the human brachialis muscle. Anat Rec. 1968. 162:363–371.
Article18. Mahakkanukrauh P, Somsarp V. Dual innervation of the brachialis muscle. Clin Anat. 2002. 15:206–209.
Article19. Blackburn SC, Wood CP, Evans DJ, Watt DJ. Radial nerve contribution to brachialis in the UK Caucasian population: position is predictable based on surface landmarks. Clin Anat. 2007. 20:64–67.
Article20. DeLagi EF, Perotto A, Iazzetti J, Morrison D. Anatomic guide for the electromyographer the limbs. 1981. 2nd ed. Springfield (IL): Charles C Thomas.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anatomical Locations of the Motor Points of the Biceps Brachii and Brachialis Muscles
- Surface Mapping of Motor Points in Biceps Brachii Muscle
- Bilateral asymmetric supernumerary heads of biceps brachii
- Three Cases of Rare Anatomic Variations of the Long Head of Biceps Brachii
- Medial Accessory Belly of the Brachialis Muscle in the Korean Population: A Case Report