Perinatology.
2019 Dec;30(4):200-207. 10.14734/PN.2019.30.4.200.
Evaluation of the Early Onset Neonatal Sepsis according to Two Antenatal Group B Streptococcus Screening Methods: Risk-Based versus Universal Screening
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. crroh@skku.edu
- KMID: 2468540
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2019.30.4.200
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The standard antenatal screening method for Group B Streptococcus (GBS) has not been established yet. Therefore, many practitioners in South Korea offer GBS screening to all pregnant women without solid clinical evidence. The aim of this study was to compare the rates of early onset neonatal sepsis (EONS) according to two different antenatal GBS screening methods - risk-based versus universal screening.
METHODS
This is a retrospective cohort study from January 2014 to April 2017. The study period was divided into two 16-month periods: from January 2014 to April 2015 in which risk-based screening was performed (period 1), and from January 2016 to April 2017 in which universal screening was performed (period 2). We compared the rates of EONS caused by GBS and other bacterial species between the two periods.
RESULTS
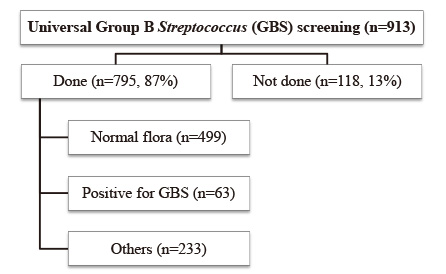
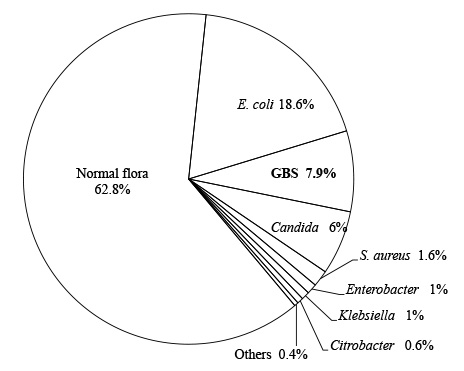
1,301 neonates from 1,293 deliveries and 924 neonates from 913 deliveries were enrolled in period 1 and period 2, respectively. Suspected or culture-proven EONS caused by any organisms were more frequently observed in period 2 (0.7% in period 1 vs. 1.8% in period 2, P=0.013). The causative organism was not confirmed by culture in most cases, except for GBS, Escherichia coli, and Enterococcus. Intrapartum administration of antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP) was more frequently performed in period 2 (10.9% in period 1 vs. 21.5% in period 2, P < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
In spite of the significant increase in IAP rate in the period 2, EONS rates did not decrease by the universal antenatal GBS screening method.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Homer CS, Scarf V, Catling C, Davis D. Culture-based versus risk-based screening for the prevention of group B streptococcal disease in newborns: a review of national guidelines. Women Birth. 2014; 27:46–51.
Article2. Sun HD, Su WH, Chang WH, Wen L, Huang BS, Wang PH. Rupture of a pregnant unscarred uterus in an early secondary trimester: a case report and brief review. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2012; 38:442–445.
Article3. Money D, Allen VM. Infectious Diseases Committee. The prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013; 35:939–948.
Article4. Schrag SJ, Verani JR. Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for the prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease: experience in the United States and implications for a potential group B streptococcal vaccine. Vaccine. 2013; 31:Suppl 4. D20–D26.
Article5. Fairlie T, Zell ER, Schrag S. Effectiveness of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2013; 121:570–577.
Article6. Kurz E, Davis D. Routine culture-based screening versus risk-based management for the prevention of early-onset group B Streptococcus disease in the neonate: a systematic review. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015; 13:206–246.
Article7. Verani JR, McGee L, Schrag SJ. Division of Bacterial Diseases, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease--revised guidelines from CDC, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010; 59:1–36.8. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG committee opinion: number 279, December 2002. Prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal disease in newborns. Obstet Gynecol. 2002; 100:1405–1412.9. Van Dyke MK, Phares CR, Lynfield R, Thomas AR, Arnold KE, Craig AS, et al. Evaluation of universal antenatal screening for group B Streptococcus. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2626–2636.
Article10. Berardi A, Di Fazzio G, Gavioli S, Di Grande E, Groppi A, Papa I, et al. Universal antenatal screening for group B Streptococcus in Emilia-Romagna. J Med Screen. 2011; 18:60–64.
Article11. Prevention of. green-top guideline No. 36. BJOG. 2017; 124:e280–e305.12. Melin P, Efstratiou A. Group B streptococcal epidemiology and vaccine needs in developed countries. Vaccine. 2013; 31:Suppl 4. D31–D42.
Article13. Edmond KM, Kortsalioudaki C, Scott S, Schrag SJ, Zaidi AK, Cousens S, et al. Group B streptococcal disease in infants aged younger than 3 months: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012; 379:547–556.
Article14. Anderson EL, Cole JN, Olson J, Ryba B, Ghosh P, Nizet V. The fibrinogen-binding M1 protein reduces pharyngeal cell adherence and colonization phenotypes of M1T1 group A Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:3539–3539.
Article15. Barcaite E, Bartusevicius A, Tameliene R, Kliucinskas M, Maleckiene L, Nadisauskiene R. Prevalence of maternal group B streptococcal colonisation in European countries. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008; 87:260–271.
Article16. Uh Y, Jang IH, Yoon KJ, Lee CH, Kwon JY, Kim MC. Colonization rates and serotypes of group B streptococci isolated from pregnant women in a Korean tertiary hospital. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997; 16:753–756.
Article17. Hong JS, Choi CW, Park KU, Kim SN, Lee HJ, Lee HR, et al. Genital group B Streptococcus carrier rate and serotype distribution in Korean pregnant women: implications for group B streptococcal disease in Korean neonates. J Perinat Med. 2010; 38:373–377.
Article18. Bang SM, Seo JW, Park KU, Kim SJ, Kim K, Kim SH, et al. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of Korean patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010; 197:117–121.
Article19. Woo HI, Kim HJ, Lee SH, Yoo KH, Koo HH, Kim SH. Acute myeloid leukemia with complex hypodiploidy and loss of heterozygosity of 17p in a boy with Fanconi anemia. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2011; 41:66–70.20. Yook JH, Kim MY, Kim EJ, Yang JH, Ryu HM, Oh KY, et al. Risk factors associated with group B Streptococcus resistant to clindamycin and erythromycin in pregnant Korean women. Infect Chemother. 2013; 45:299–307.
Article21. Lee BK, Song YR, Kim MY, Yang JH, Shin JH, Seo YS, et al. Epidemiology of group B Streptococcus in Korean pregnant women. Epidemiol Infect. 2010; 138:292–298.
Article22. Rhie K, Choi EH, Cho EY, Lee J, Kang JH, Kim DS, et al. Etiology of invasive bacterial infections in immunocompetent children in Korea (2006-2010): a retrospective multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci. 2018; 33:e45.
Article23. Konrad G, Katz A. Epidemiology of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal infection: implications for screening. Can Fam Physician. 2007; 53:1054–1055.24. Lee JH, Kim SM, Lee HS, Kim SY, Choi SD, Sung IK, et al. A clinical study of group B streptococcal infection: five years experience. Neonatal Med. 2003; 10:226–234.25. Gerdes JS. Diagnosis and management of bacterial infections in the neonate. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2004; 51:939–959.
Article26. Luo Y, Siu GK, Yeung AS, Chen JH, Ho PL, Leung KW, et al. Performance of the VITEK MS matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry system for rapid bacterial identification in two diagnostic centres in China. J Med Microbiol. 2015; 64:18–24.
Article27. Schrag SJ, Zell ER, Lynfield R, Roome A, Arnold KE, Craig AS, et al. A population-based comparison of strategies to prevent early-onset group B streptococcal disease in neonates. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:233–239.
Article28. Ki M, Srinivasan U, Oh KY, Kim MY, Shin JH, Hong HL, et al. Emerging fluoroquinolone resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae in South Korea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:3199–3205.
Article29. Seo YS, Srinivasan U, Oh KY, Shin JH, Chae JD, Kim MY, et al. Changing molecular epidemiology of group B Streptococcus in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:817–823.
Article30. Gibbs RS, Schrag S, Schuchat A. Perinatal infections due to group B streptococci. Obstet Gynecol. 2004; 104:1062–1076.
Article31. Burgess APH, Katz JE, Moretti M, Lakhi N. Risk factors for intrapartum fever in term gestations and associated maternal and neonatal sequelae. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2017; 82:508–516.
Article32. Klingenberg C, Kornelisse RF, Buonocore G, Maier RF, Stocker M. Culture- negative early-onset neonatal sepsis - at the crossroad between efficient sepsis care and antimicrobial stewardship. Front Pediatr. 2018; 6:285.
Article33. Choi KU, Koh SK, Lee JY, Park JH, Hwang SO, Lee BI, et al. Clinical significance of group B streptococcal infection in pregnant women. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2002; 45:811–815.34. Kim MW, Jang HO, Chang DY, Cho JR, Kim YA, Choi HM, et al. Group B streptococcal colonization rate in Korean pregnant women. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2006; 49:337–344.35. Kim EJ, Oh KY, Kim MY, Seo YS, Shin JH, Song YR, et al. Risk factors for group B Streptococcus colonization among pregnant women in Korea. Epidemiol Health. 2011; 33:e2011010.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Utility of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator in risk-based group B Streptococcus screening approach
- Risk-based maternal group B Streptococcus screening strategy is compatible with the implementation of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator
- Epidemiology of Early and Late Onset Neonatal Sepsis
- A Case of Neonatal Death due to Group B beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal Sepsis
- Prevalence of group B streptococcus colonization in pregnant women in a tertiary care center in Korea