J Cardiovasc Imaging.
2020 Jan;28(1):74-76. 10.4250/jcvi.2019.0082.
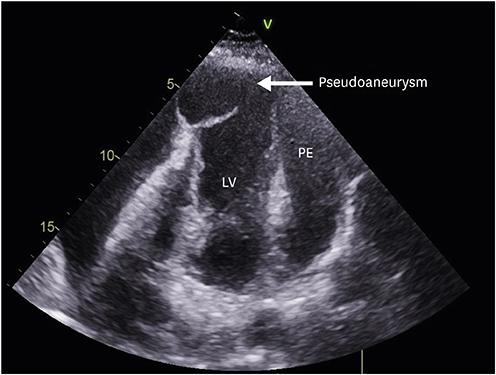
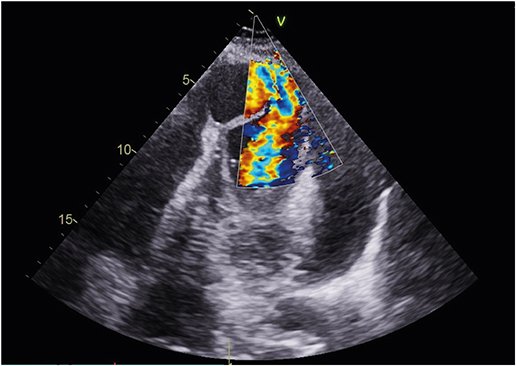
Left Ventricular Apical Pseudoaneurysm with Cardiac Tamponade
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Apex Heart Institute, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. pradyot.arian@gmail.com
- KMID: 2468386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcvi.2019.0082
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brown SL, Gropler RJ, Harris KM. Distinguishing left ventricular aneurysm from pseudoaneurysm. A review of the literature. Chest. 1997; 111:1403–1409.2. Gatewood RP Jr, Nanda NC. Differentiation of left ventricular pseudoaneurysm from true aneurysm with two dimensional echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 1980; 46:869–878.
Article3. Kawakami Y, Hirose K, Watanabe Y, et al. Myocardial free wall rupture and thrombolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction. Kokyu To Junkan. 1989; 37:1109–1112.4. Vlodaver Z, Coe JI, Edwards JE. True and false left ventricular aneurysms. Propensity for the altter to rupture. Circulation. 1975; 51:567–572.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Cases of Tuberculous Pericarditis Associated with Pseudoaneurysm of the Left Ventricle
- Operative Treatment for Cardiac Tamponade with Ventricular Rupture of PostMyocardial Infarction without Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A case report
- Huge Multilobulated Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Pseudoaneurysm Presenting with Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular dyssynchrony in patients with permanent pacemaker
- Acute Heart Failure after Relief of Massive Pericardial Effusion