J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Sep;31(9):1472-1478. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1472.
Ultrasound Dimensions of the Rotator Cuff and Other Associated Structures in Korean Healthy Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, St. Paul's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. coltrane@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2468282
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1472
Abstract
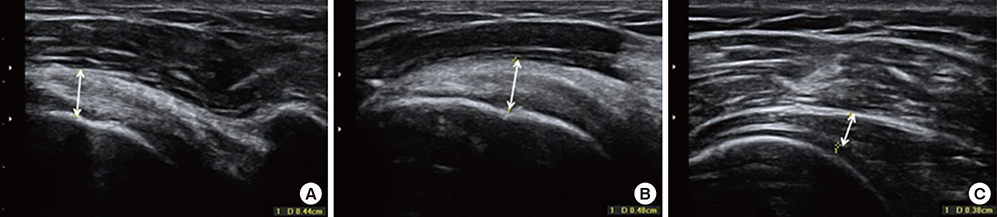
- In evaluating patients complaining of shoulder pain, ultrasonography is an emerging imaging tool due to convenience, low cost, high sensitivity and specificity. However, normative values of ultrasound dimensions of the shoulder to be compared with pathologic findings in Korean adults are not provided yet. We evaluated the ultrasound dimensions of the rotator cuff, long head of biceps tendon, deltoid muscle and acromioclavicular joint in Korean healthy adults. Shoulder ultrasonography was performed on 200 shoulders from 100 healthy adults. The dimensions of the thickness of rotator cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis tendon), deltoid muscle, long head of biceps tendon, subacromial subdeltoid bursa, and acromioclavicular joint interval were measured in a standardized manner. Differences in measurements among sex, age, and dominant arms were compared. The thickness of rotator cuff tendons (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis) and deltoid muscle were significantly different between men and women. The thickness of subacromial subdeltoid bursa was significantly different between men and women for non-dominant side. In rotator cuff tendon measurements, the differences between dominant and non-dominant shoulders were not significant, which means the asymptomatic contralateral shoulder can be used to estimate the normal reference values. When stratified by age divided by 10 years, the measurements of supraspinatus, subscapularis and deltoid thickness showed tendency of increase with the age. The acromioclavicular joint interval, on the other hand, revealed decreasing tendency. This report suggests normative values of ultrasound dimensions of healthy Korean population with varying age, and can be useful as reference values in evaluating shoulder pathology, especially in rotator cuff tendon pathology.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acromioclavicular Joint/anatomy & histology/diagnostic imaging
Adult
Aged
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Deltoid Muscle/anatomy & histology/diagnostic imaging
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Reference Values
Republic of Korea
Rotator Cuff/*anatomy & histology/diagnostic imaging
Shoulder/diagnostic imaging
Tendons/anatomy & histology/diagnostic imaging
Ultrasonography/standards
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chard MD, Hazleman R, Hazleman BL, King RH, Reiss BB. Shoulder disorders in the elderly: a community survey. Arthritis Rheum. 1991; 34:766–769.2. de Jesus JO, Parker L, Frangos AJ, Nazarian LN. Accuracy of MRI, MR arthrography, and ultrasound in the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears: a meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:1701–1707.3. Lenza M, Buchbinder R, Takwoingi Y, Johnston RV, Hanchard NC, Faloppa F. Magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance arthrography and ultrasonography for assessing rotator cuff tears in people with shoulder pain for whom surgery is being considered. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013; CD009020.4. Roy JS, Braën C, Leblond J, Desmeules F, Dionne CE, MacDermid JC, Bureau NJ, Frémont P. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography, MRI and MR arthrography in the characterisation of rotator cuff disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2015; 49:1316–1328.5. Smith TO, Back T, Toms AP, Hing CB. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound for rotator cuff tears in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2011; 66:1036–1048.6. de Miguel E, Cobo T, Muñoz-Fernández S, Naredo E, Usón J, Acebes JC, Andréu JL, Martín-Mola E. Validity of enthesis ultrasound assessment in spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:169–174.7. Maffulli N, Regine R, Angelillo M, Capasso G, Filice S. Ultrasound diagnosis of Achilles tendon pathology in runners. Br J Sports Med. 1987; 21:158–162.8. Bang IK, Lee JP, Kim YJ, Kim C, Kim GH, Reu HW, Oh JK. Tendon diameter of rotator cuff and strength of the shoulder external/internal rotator muscles in elite thrower. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007; 31:730–734.9. Karthikeyan S, Rai SB, Parsons H, Drew S, Smith CD, Griffin DR. Ultrasound dimensions of the rotator cuff in young healthy adults. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23:1107–1112.10. Teunis T, Lubberts B, Reilly BT, Ring D. A systematic review and pooled analysis of the prevalence of rotator cuff disease with increasing age. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23:1913–1921.11. Abate M, Schiavone C, Salini V. Sonographic evaluation of the shoulder in asymptomatic elderly subjects with diabetes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010; 11:278.12. Cho SH, Cho HL, Lee JS, Kim JW. Ultrasonographic findings of the shoulder in asymptomatic high school overhead athletes. J Korean Orthop Ultrasound Soc. 2012; 5:81–88.13. Milgrom C, Schaffler M, Gilbert S, van Holsbeeck M. Rotator-cuff changes in asymptomatic adults. The effect of age, hand dominance and gender. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:296–298.14. Yu TY, Tsai WC, Cheng JW, Yang YM, Liang FC, Chen CH. The effects of aging on quantitative sonographic features of rotator cuff tendons. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012; 40:471–478.15. Stein BE, Wiater JM, Pfaff HC, Bigliani LU, Levine WN. Detection of acromioclavicular joint pathology in asymptomatic shoulders with magnetic resonance imaging. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001; 10:204–208.16. Nicholson GP, Goodman DA, Flatow EL, Bigliani LU. The acromion: morphologic condition and age-related changes. A study of 420 scapulas. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996; 5:1–11.17. Le Corroller T, Cohen M, Aswad R, Pauly V, Champsaur P. Sonography of the painful shoulder: role of the operator's experience. Skeletal Radiol. 2008; 37:979–986.18. Wall LB, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Dahiya N, Steger-May K, Kim HM, Wessell D, Yamaguchi K. Diagnostic performance and reliability of ultrasonography for fatty degeneration of the rotator cuff muscles. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:e83.19. Wendelboe AM, Hegmann KT, Gren LH, Alder SC, White GL Jr, Lyon JL. Associations between body-mass index and surgery for rotator cuff tendinitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A:743–747.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound Images after Rotator Cuff Surgery: Usefulness of Postoperative Follow-Up
- Biological Characteristics of Rotator Cuff Tendon
- Controversy in Pathophysiology of Rotator Cuff Tear: Degenerative Tear
- Revisional Rotator Cuff Repair
- Postoperative Ultrasound Findings of the Rotator Cuff Tendon after Arthroscopic Repair of a Rotator Cuff Tear