Nat Prod Sci.
2019 Dec;25(4):334-340. 10.20307/nps.2019.25.4.334.
Development and Validation of HPLC-PDA Method and Pattern Recognition Analyses Using Eight Marker Compounds for the Quality Control Between the Seeds of Cuscuta chinensis Lam. and Cuscuta japonica Choisy
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Drug Research and Development Center, Daegu Catholic University, Gyeongsan 38430, Republic of Korea. woomh@cu.ac.kr
- 2Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Thanh Dong University, Hai Duong city, Viet Na.
- 3School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China.
- 4Division of Computational Physics, Institute for Computational Science, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
- 5Faculty of Pharmacy, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
- KMID: 2468067
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.4.334
Abstract
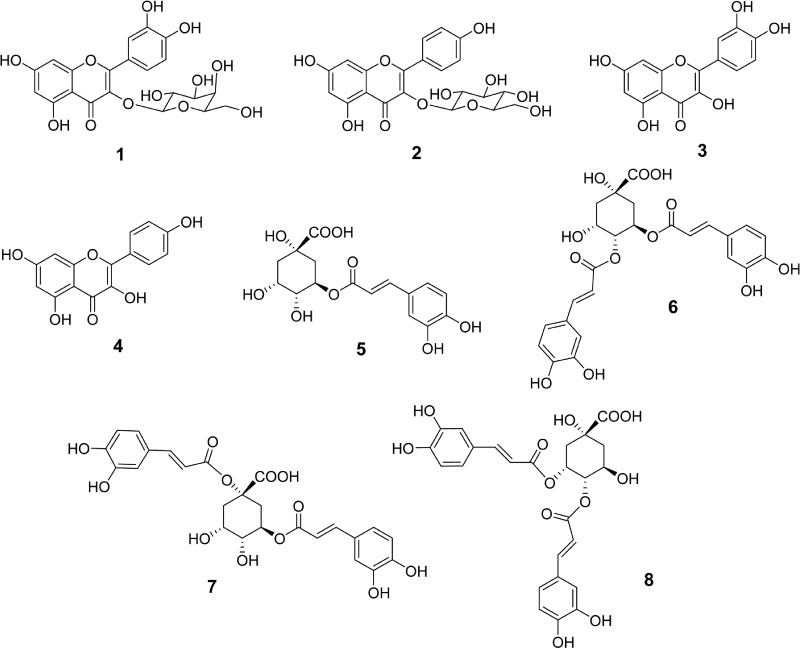
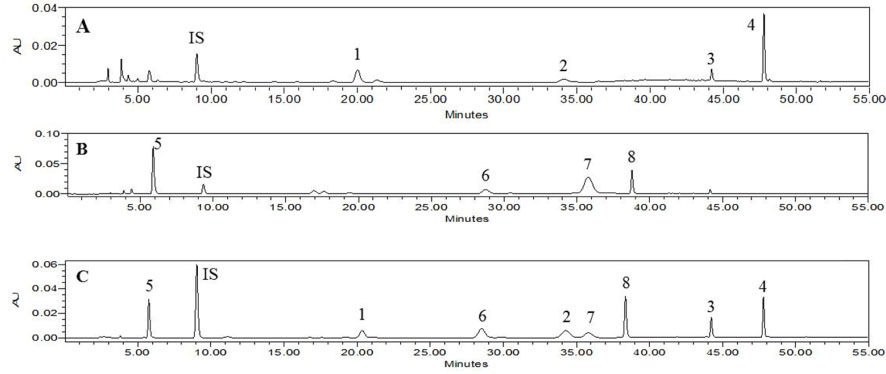
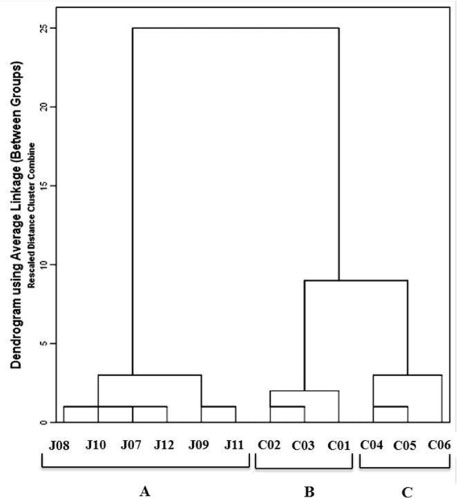
- Cuscuta chinensis Lam. and Cuscuta japonica Choisy are parasitic plants. C. chinensis seeds were traditionally used for treatment of kidney and liver deficiencies. C. japonica seeds were used as tonic medicine to improve liver function and strengthen kidneys, treatment of high blood pressure, chronic diarrhea, and sore eyes. Cuscutae Semen are seeds of only C. chinensis in Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia (K.H.P.). The developed HPLC-PDA method easily, accurately, and sensitively quantified using eight marker compounds [hyperoside (1), astragalin, (2), quercetin (3), kaempferol (4), chlorogenic acid (5), 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (6), 1,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (7), and 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (8)]. In addition, the method may be used to distinguish seeds between C. chinensis Lam. and C. japonica Choisy. Furthermore, the result from the current study was applied to clarify samples between steam processed and unprocessed samples of C. chinensis by pattern analysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Donnapee S, Li J, Yang X, Ge AH, Donkor PO, Gao XM, Chang YX. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014; 157:292–308.2. He XH, Yang WZ, Meng AH, He WN, Guo DA, Ye M. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2010; 12:934–939.3. Sam HV, Baas P, Kebler PJA. Blumea. 2008; 53:569–601.4. Zhen GH, Jiang B, Bao YM, Li DX, An LJ. J Chin Med Mat. 2006; 29:1051–1055.5. Jian-Hui L, Jiang B, Bao Y, An L. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2003; 21:277–281.
Article6. Yen FL, Wu TH, Lin LT, Lin CC. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007; 111:123–128.7. Yao CH, Tsai HM, Chen YS, Liu BS. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005; 75:277–288.8. Chauhan A, Sharma PK, Srivastava P, Kumar N, Dudhe R. Pharm Lett. 2010; 2:369–387.9. Cheng P, Shi J, Du P, Liu D, Cao X, Wen X. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing. 2013; 8:116–118.10. Liao GI, Chen MY, Kuoh CS. Bot Bull Acad Sin. 2005; 46:75–81.11. Araujo P. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009; 877:2224–2234.12. Le DD, Nguyen DH, Zhao BT, Min BS, Song SW, Woo MH. Nat Prod Sci. 2019; 25:122–129.13. Hajimehdipoor H, kondori BM, Amin GR, Adib N, Rastegar H, Shekarchi M. Daru. 2012; 20:57–63.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of an HPTLC Method for Differentiating the Botanical Origins of Cuscutae Semen
- Development of Analytical Method and Validation using HPLC/PDA for Discrimination between Artemisiae Argyi Folium and Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba
- Simultaneous Quantification of Eight Compounds of Lonicera japonica by HPLC-DAD
- Development and Validation of an HPLC-PDA Method for Quantitation of Ten Marker Compounds from Eclipta prostrata (L.) and Evaluation of Their Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B, α-Glucosidase, and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activities
- Preliminary Report on the Safety of a New Herbal Formula and Its Effect on Sperm Quality