Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2019 Dec;23(4):351-360. 10.13104/imri.2019.23.4.351.
Noninvasive Biomarker for Predicting Treatment Response to Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. radpms@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsseong@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2468052
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2019.23.4.351
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate noninvasive biomarkers for predicting treatment response in patients with locally advanced HCC who underwent concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRTx).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
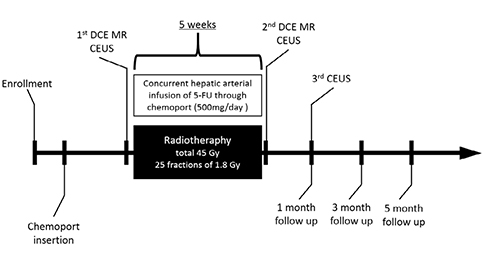
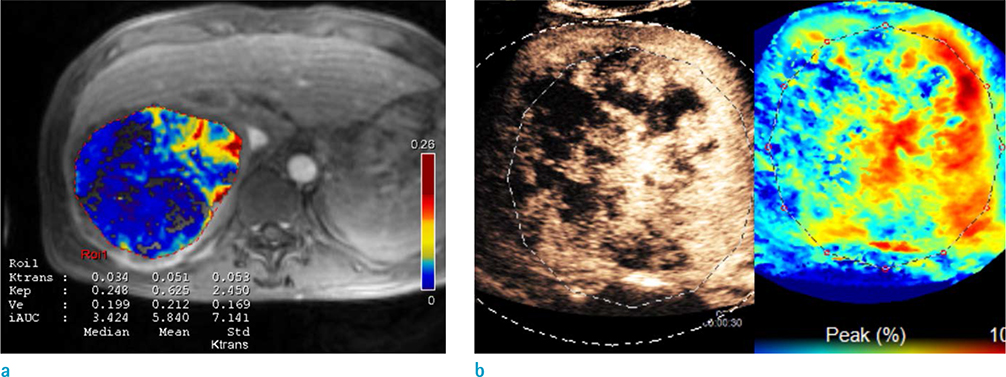
Thirty patients (55.5 ± 10.2 years old, M:F = 24:6) who underwent CCRTx due to advanced HCC were enrolled. Contrast-enhanced US (CEUS) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were obtained before and immediately after CCRTx. The third CEUS was obtained at one month after CCRTx was completed. Response was assessed at three months after CCRTx based on RECIST 1.1. Quantitative imaging biomarkers measured with CEUS and MRI were compared between groups. A cutoff value was calculated with ROC analysis. Overall survival (OS) was compared by the Breslow method.
RESULTS
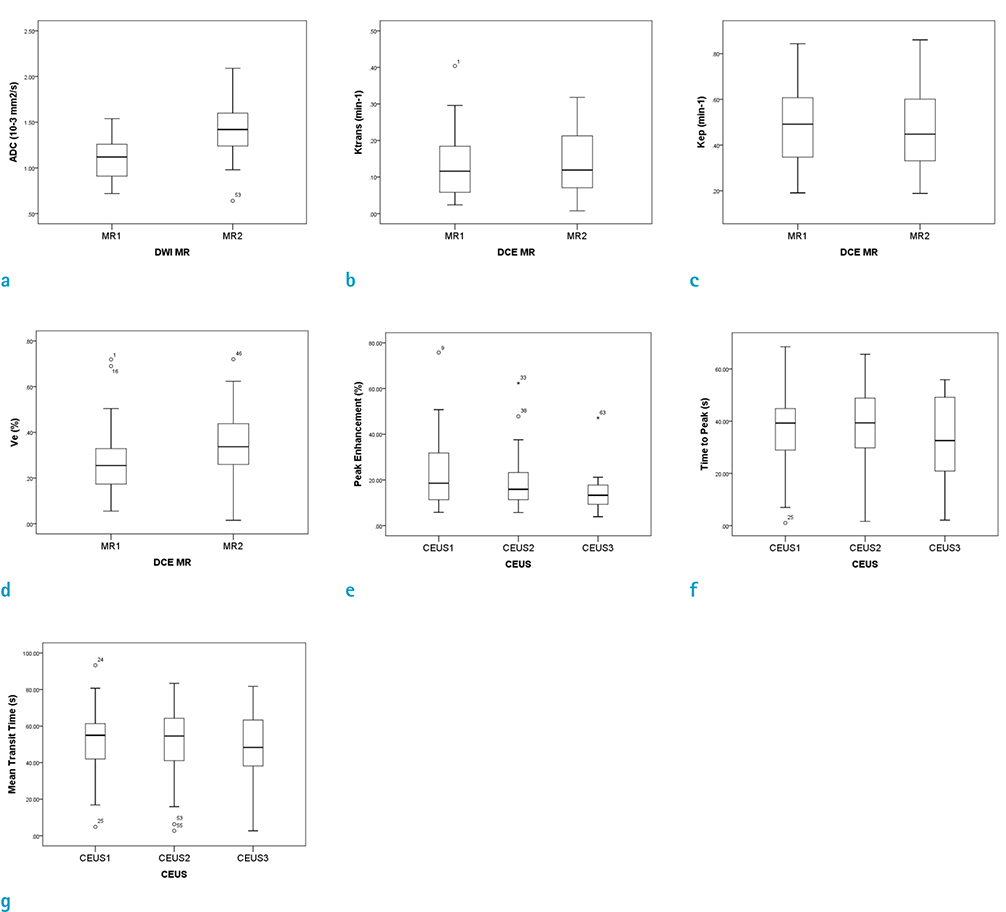
Twenty-five patients were categorized into the non-progression group and five patients were categorized into the progression group. Peak enhancement of the first CEUS before CCRTx (PE1) was significantly lower in the non-progression group (median, 18.6%; IQR, 20.9%) than that in the progression group (median, 59.1%; IQR, 13.5%; P = 0.002). There was no significant difference in other quantitative biomarkers between the two groups. On ROC analysis, with a cutoff value of 42.6% in PE1, the non-progression group was diagnosed with a sensitivity of 90.9% and a specificity of 100%. OS was also significantly longer in patients with PE1 < 42.6% (P = 0.014).
CONCLUSION
Early treatment response and OS could be predicted by PE on CEUS before CCRTx in patients with HCC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Johnson PJ. Non-surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 2005; 7:50–55.2. Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150:835–853.3. Lee HS, Choi GH, Choi JS, et al. Surgical resection after down-staging of locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma by localized concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:3646–3653.4. Choi Y, Kim JW, Cha H, Han KH, Seong J. Overall response of both intrahepatic tumor and portal vein tumor thrombosis is a good prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving concurrent chemoradiotherapy. J Radiat Res. 2014; 55:113–120.5. Cho IR, Lee HW, Song KJ, et al. Conditional survival estimate in patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B/C hepatocellular carcinoma treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with/without concurrent radiotherapy. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:79914–79926.6. Chong JU, Choi GH, Han DH, et al. Downstaging with localized concurrent chemoradiotherapy can identify optimal surgical candidates in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018; 25:3308–3315.7. Han DH, Joo DJ, Kim MS, et al. Living donor liver transplantation for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis after concurrent chemoradiation therapy. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:1276–1281.8. Jiang T, Zhu AX, Sahani DV. Established and novel imaging biomarkers for assessing response to therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:169–177.9. Hsu CY, Shen YC, Yu CW, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers predict survival and response in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib and metronomic tegafur/uracil. J Hepatol. 2011; 55:858–865.10. Zhu AX, Sahani DV, Duda DG, et al. Efficacy, safety, and potential biomarkers of sunitinib monotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3027–3035.11. Wang D, Gaba RC, Jin B, et al. Perfusion reduction at transcatheter intraarterial perfusion MR imaging: a promising intraprocedural biomarker to predict transplant-free survival during chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2014; 272:587–597.12. Liang PC, Ch'ang HJ, Hsu C, Chen LT, Shih TT, Liu TW. Perfusion parameters of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging predict outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma receiving radiotherapy with or without thalidomide. Hepatol Int. 2015; 9:258–268.13. Zhou JH, Cao LH, Zheng W, Liu M, Han F, Li AH. Contrast-enhanced gray-scale ultrasound for quantitative evaluation of tumor response to chemotherapy: preliminary results with a mouse hepatoma model. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:W13–W17.14. Zhou J, Zheng W, Cao L, Liu M, Han F, Li A. Antiangiogenic tumor treatment: noninvasive monitoring with contrast pulse sequence imaging for contrast-enhanced grayscale ultrasound. Acad Radiol. 2010; 17:646–651.15. Merz M, Komljenovic D, Semmler W, Bauerle T. Quantitative contrast-enhanced ultrasound for imaging antiangiogenic treatment response in experimental osteolytic breast cancer bone metastases. Invest Radiol. 2012; 47:422–429.16. Chung YE, Kim KW. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography: advance and current status in abdominal imaging. Ultrasonography. 2015; 34:3–18.17. Minami Y, Kudo M. Imaging modalities for assessment of treatment response to nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: contrast-enhanced US, CT, and MRI. Liver Cancer. 2015; 4:106–114.18. Han KH, Seong J, Kim JK, Ahn SH, Lee DY, Chon CY. Pilot clinical trial of localized concurrent chemoradiation therapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Cancer. 2008; 113:995–1003.19. Kim KA, Park MS, Ji HJ, et al. Diffusion and perfusion MRI prediction of progression-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 39:286–292.20. Korpisalo P, Hytonen JP, Laitinen JT, et al. Ultrasound imaging with bolus delivered contrast agent for the detection of angiogenesis and blood flow irregularities. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014; 307:H1226–H1232.21. Park HJ, Griffin RJ, Hui S, Levitt SH, Song CW. Radiation-induced vascular damage in tumors: implications of vascular damage in ablative hypofractionated radiotherapy (SBRT and SRS). Radiat Res. 2012; 177:311–327.22. Rockwell S, Dobrucki IT, Kim EY, Marrison ST, Vu VT. Hypoxia and radiation therapy: past history, ongoing research, and future promise. Curr Mol Med. 2009; 9:442–458.23. Zahra MA, Hollingsworth KG, Sala E, Lomas DJ, Tan LT. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI as a predictor of tumour response to radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2007; 8:63–74.24. Niizawa G, Ikegami T, Matsuzaki Y, et al. Monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma, following proton radiotherapy, with contrast-enhanced color Doppler ultrasonography. J Gastroenterol. 2005; 40:283–290.25. Thng CH, Koh TS, Collins D, Koh DM. Perfusion imaging in liver MRI. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2014; 22:417–432.26. Chen BB, Hsu CY, Yu CW, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with the liver parenchyma and correlation with the survival of patients receiving systemic therapy. Radiology. 2016; 281:454–464.27. Hsu C, Yang TS, Huo TI, et al. Vandetanib in patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:1097–1103.28. Liang PC, Ch'ang HJ, Hsu C, Tseng SS, Shih TT, Wu Liu T. Dynamic MRI signals in the second week of radiotherapy relate to treatment outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma: a preliminary result. Liver Int. 2007; 27:516–528.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Advanced Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Successfully Treated with Liver-directed Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy and Sequential Transarterial Radio-embolization
- Long-term survival after CCRT and HAIC followed by ALPPS for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: a case report
- Personalized approaches to the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma using immune checkpoint inhibitors: Editorial on “Genomic biomarkers to predict response to atezolizumab plus bevacizumab immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Insights from the IMbrave150 trial”
- A Case of Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Noninvasive diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma