Electrolyte Blood Press.
2019 Dec;17(2):54-61. 10.5049/EBP.2019.17.2.54.
Baseline High Blood Pressure is Associated with Clinico-Pathologic Findings and Later Renal Progression in Chronic Glomerulonephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nephrology, Kyung-Hee University Hospital, Kyung-Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cgihm@naver.com
- KMID: 2467961
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2019.17.2.54
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Several factors had been suggested to contribute to the development of hypertension in chronic glomerulonephritis (GN). This study was conducted to find the association of baseline blood pressure (BP) with pathophysiologic findings and later renal progression in chronic GN.
METHODS
Clinico-pathological findings including serum creatinine (Cr), proteinuria, pathological findings, and urinary Na excretion were analyzed in a total of 233 patients with IgA nephropathy from The Kyung-Hee Cohort of GN. Glomerular surface area (GSA) was measured by imaging analysis and urine angiotensinogen (AGT) concentrations by human ELISA kits.
RESULTS
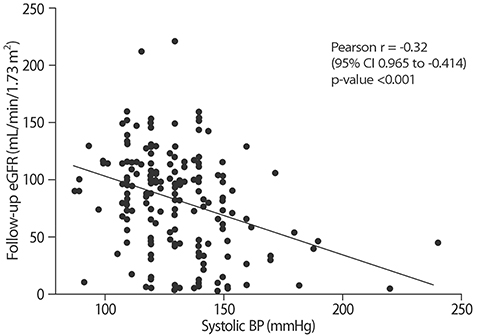
Systolic BP was ≥130mmHg in 124 patients (53%). Systolic BP was negatively correlated with follow-up eGFR (r=−0.32, p<0.0001) and positively serum uric acid concentrations, while it had no significant relationships with initial serum Cr and eGFR. As compared with patients with systolic BP<130 mmHg, those with ≥130 mmHg were older and showed higher serum Cr, proteinuria, 24 hr urinary Na excretion, mean GSA, and T-I fibrosis, lower follow-up eGFR, and steeper decline in slope of eGFR. The results in patients with normal serum Cr concentrations were comparable to those in whole group. Systolic BP was positively correlated with age, baseline and follow-up proteinuria, serum uric acid concentrations and IgM deposit and negatively with follow-up eGFR. In subgroup analysis, systolic BP was also positively correlated with mean GSA and urinary AGT concentrations.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that baseline systolic BP is related to urinary Na excretion, glomerulomegaly, T-I fibrosis and later renal progression in patients with IgA nephropathy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Orofino L, Quereda C, Lamas S, et al. Hypertension in primary chronic glomerulonephritis: analysis of 288 biopsied patients. Nephron. 1987; 45:22–26.
Article2. Glassock RJ AS, Ward HJ, Cohen AH. The kidney. 4 ed. 1991.3. Berthoux F, Mohey H, Laurent B, Mariat C, Afiani A, Thibaudin L. Predicting the risk for dialysis or death in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; 22:752–761.
Article4. Csiky B, Kovacs T, Wagner L, Vass T, Nagy J. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and progression in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999; 14:86–90.
Article5. Reich HN, Troyanov S, Scholey JW, Cattran DC, Toronto Glomerulonephritis R. Remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:3177–3183.
Article6. Valvo E, Gammaro L, Bedogna V, et al. Hypertension in primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy (Berger’s disease): hemodynamic alterations and mechanisms. Nephron. 1987; 45:219–223.
Article7. Joles JA, Koomans HA. Causes and consequences of incresed sympathetic activity in renal disease. Hypertension. 2004; 43:699–706.
Article8. Konishi Y, Okada N, Okamura M, et al. Sodium sensitivity of blood pressure appearing before hypertension and related to histological damage in immunoglobulin a nephropathy. Hypertension. 2001; 38:81–85.
Article9. Bazzi C, Stivali G, Rachele G, Rizza V, Casellato D, Nangaku M. Arteriolar hyalinosis and arterial hypertension as possible surrogate markers of reduced interstitial blood flow and hypoxia in glomerulonephritis. Nephrology (Carlton). 2015; 20:11–11.
Article10. Abdi-Ali A, Mann MC, Hemmelgarn BR, et al. IgA nephropathy with early kidney disease is associated with increased arterial stiffness and renin-angiotensin system activity. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015; 16:521–528.
Article11. Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, et al. Expressing the Modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate with standardized serum creatinine values. Clin Chem. 2007; 53:766–772.
Article12. Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Greene T, et al. Comparative performance of the CKD epidemiology collaboration (CKD-EPI) and the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) study equations for estimating GFR levels above 60mL/min/1.73m2. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010; 56:486–489.13. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:604–612.
Article14. Lee HS, Lee MS, Lee SM, et al. Histological grading of IgA nephropathy predicting renal outcome: revisiting H. S. Lee’s glomerular grading system. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005; 20:342–348.
Article15. Kanetsuna Y, Hirano K, Nagata M, et al. Characterization of diabetic nephropathy in a transgenic model of hypoinsulinemic diabetes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006; 291:F1315–F1322.
Article16. Helal I, Fick-Brosnahan GM, Reed-Gitomer B, Schrier RW. Glomerular hyperfiltration: definitions, mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012; 8:293–300.
Article17. Neuringer JR, Brenner BM. Glomerular hypertension: cause and consequence of renal injury. J Hypertens Suppl. 1992; 10:S91–S97.18. Kataoka H, Ohara M, Honda K, Mochizuki T, Nitta K. Maximal glomerular diameter as a 10-year prognostic indicator for IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:3937–3943.
Article19. Rennke HG, Klein PS. Pathogenesis and significance of nonprimary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1989; 13:443–456.
Article20. Nishiyama A, Konishi Y, Ohashi N, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen reflects the activity of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:170–177.
Article21. Kim YG, Song SB, Lee SH, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a predictive marker in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011; 15:720–726.
Article22. Sanchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Santamaria J, et al. Mild hyperuricemia induces vasoconstriction and maintains glomerular hypertension in normal and remnant kidney rats. Kidney Int. 2005; 67:237–247.
Article23. Srivastava A, Kaze AD, McMullan CJ, Isakova T, Waikar SS. Uric Acid and the Risks of Kidney Failure and Death in Individuals With CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018; 71:362–370.
Article24. Sedaghat S, Hoorn EJ, van Rooij FJ, et al. Serum uric acid and chronic kidney disease: the role of hypertension. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e76827.
Article