J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2019 Dec;26(4):151-159. 10.4184/jkss.2019.26.4.151.
Factors Associated with the Effect of Conservative Treatment in Surgically Indicated Single-Level Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea. osahnyj@nate.com
- KMID: 2467944
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2019.26.4.151
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study of date collected prospectively.
OBJECTIVES
To report analytic results about association factors related to effect of conservative treatment in surgically indicated single level lumbar spinal stenosis patient. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: There have been various reports about clinical outcomes and relative factors after surgical treatment of spinal stenosis. However, there are few reports about factors related to effect of conservative treatment in surgically indicated lumbar spinal stenosis patient.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
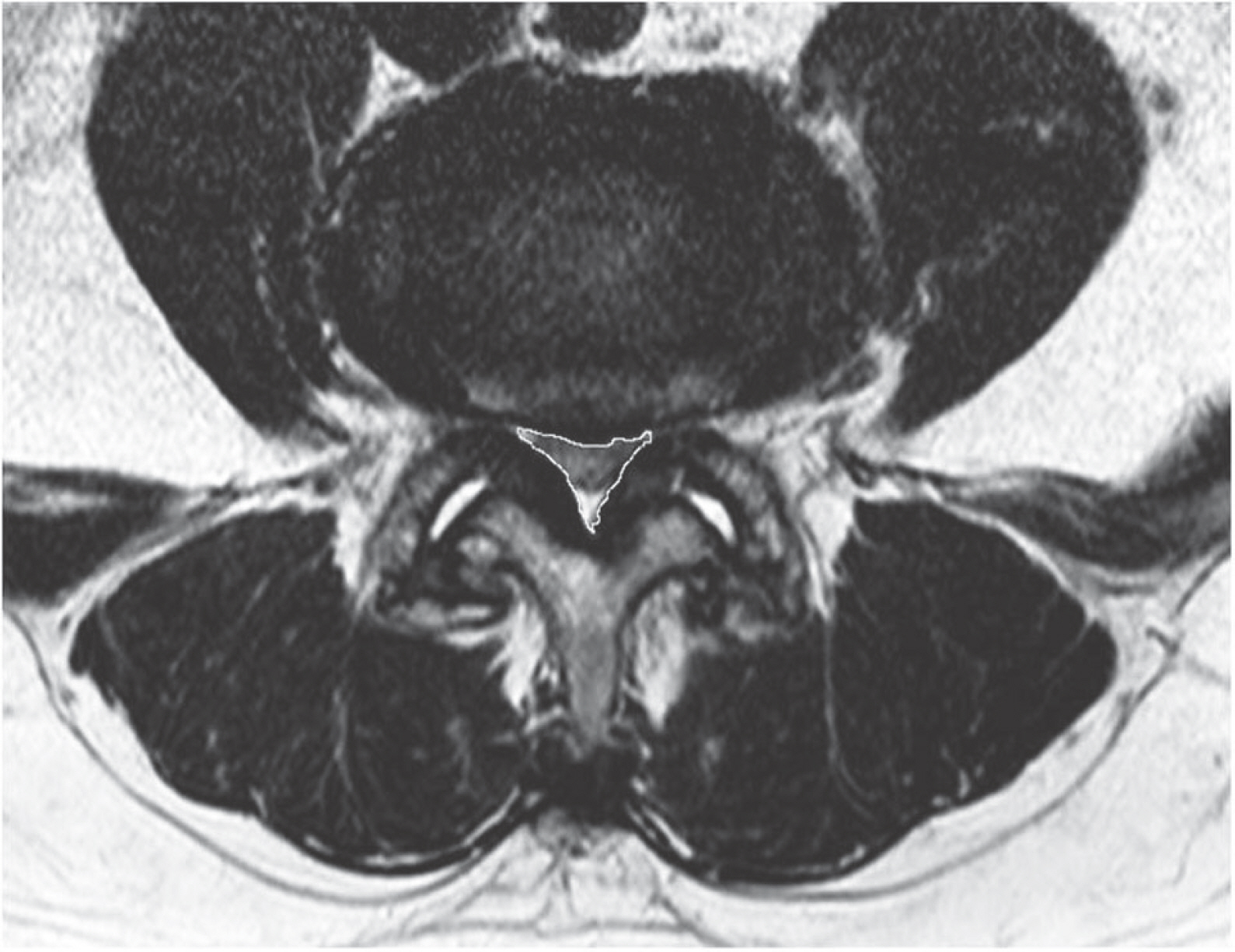
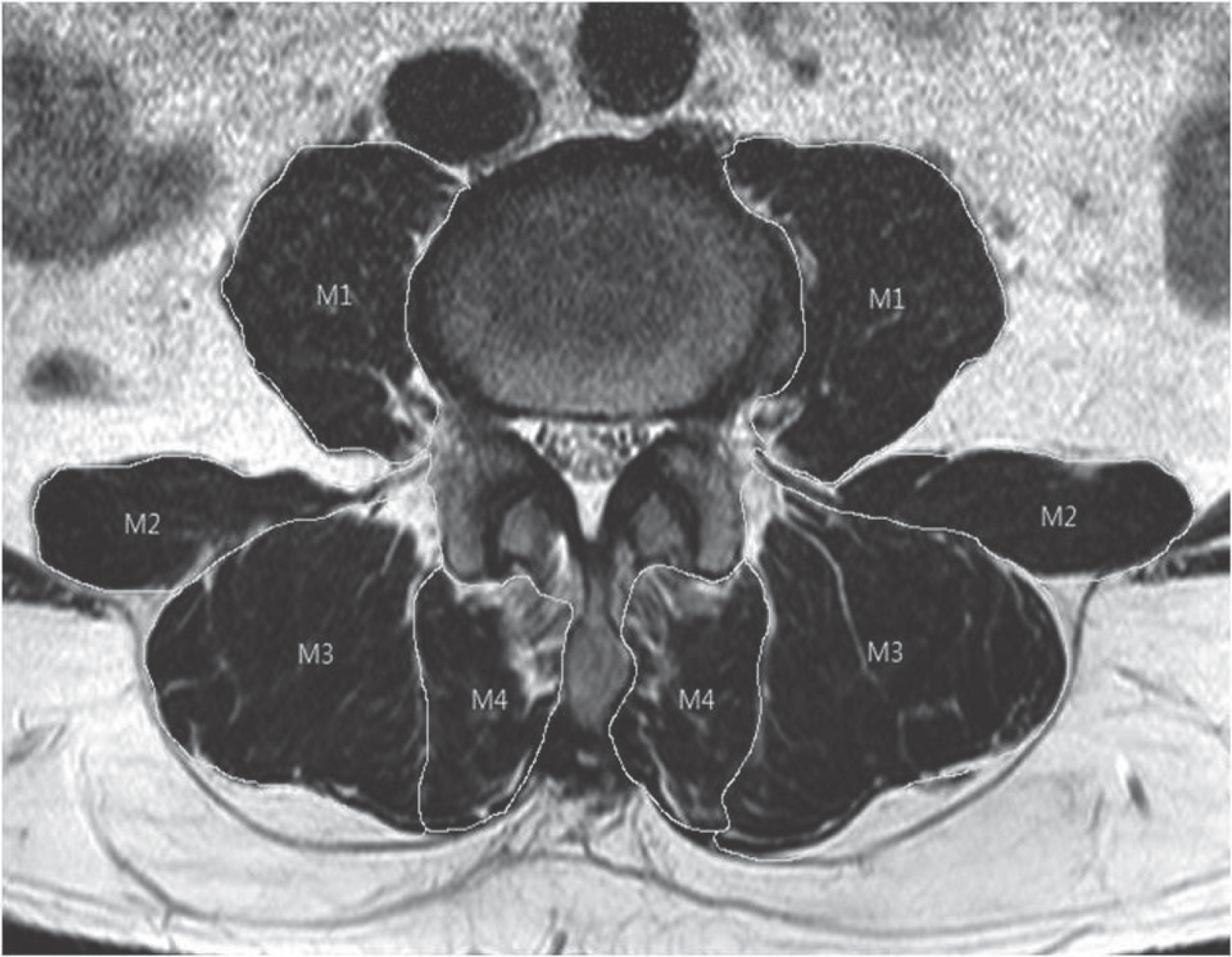
We based on 40 patients who had visited our hospital from May 2010 to April 2016 who were traceable for at least three years. We analysed 20 patients who improved symptom and who didn't improved symptom then investigated association factors related to effect of conservative treatment. Clinical assessment was conducted using questionnaire and spinal canal's area and muscle amount were measured in the MRI.
RESULTS
Average of the spinal canal of not-improved group is 91.29(±34.26) mm², improved group is 130.70 (±32.18) mm² and impoved group is wider (p=0.001). Muscle mass of improved group is 91.47(±9.43) cm², not-improved group is 79.26 (±14.35) cm², and improved group is wider (p=0.003). Repetitive strain and traffic accident were related in not-improved group (p=0.028). However, practiced stretching continuously were related to symptom improvement (p=0.022).
CONCLUSIONS
Association factors related to effect of conservative treatment are cases of wide spinal canal, wide muscle amount, repetitive sprain, traffic accident and stretching. A small muscle amount can be considered as a key factor related to surgical conversion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Katz JN, Harris MB. Clinical practice. Lumbar spinal stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2008 Feb; 358(8):818–25. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMcp0708097.2. Ishimoto Y, Kawakami M, Curtis E, et al. The Impact of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis, Knee Osteoarthritis, and Loss of Lumbar Lordosis on the Quality of Life: Findings from the Katsuragi Low Back Pain Study. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018 Aug 25; 3(2):157–162. DOI: 10.22603/ssrr.2018-0051. eCollection 2019 Apr 27.
Article3. Antti Malmivaara, Par Slatis, Paivi Sainio, et al. Surgical or Nonoperative Treatment for Lumbar Spinal stenosis? A Randomized Controlled Trial. Spine. 2007 Jan; 32(1):1–8.4. Matsudaira K, Hara N, Oka H, et al. Predictive Factors for Subjective Improvement in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Patients with Nonsurgical Treatment: A 3-Year Prospective Co-hort Study. PLoS ONE. 2016 Feb; 11(2):e0148584. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148584.
Article5. Jeon CH, Kim DJ, Kim SK, et al. Validation in the Cross-cultural Adaptation of the Korean Version Of the Oswestry Disability Index. J Korean Med Sci. 2006 Dec; 21(6):1092–7.
Article6. Shim DM, Choi YH, Yang JH, et al. Analysis and measurement of the lumbar spinal canal dimension using magnetic resonance imaging. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2008; 43(5):588–94.
Article7. WAN Q, LIN C, LI X, et al. MRI assessment of paraspinal muscles in patients with acute and chronic unilateral low back pain. Br J Radiol. 2015 Sep; 88(1053):20140546. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20140546. Epub 2015 Jun 24.
Article8. Zaina F, Tomkins-Lane C, Carragee E., et al. Surgical Ver-sus Nonsurgical Treatment for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016 Jul 15; 41(14):E857–68. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001635.
Article9. Porter RW, Wicks M, Ottewell D. Measurement of the spinal canal by diagnostic ultrasound. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1978 Nov; 60-B(4):481–4.
Article10. Ahn YJ, Im SH, Park SH. Short-Term Effects of Selective Nerve Root Block in Spinal Stenosis Patients According to Spinal Canal Dimensions. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2017 Jun; 24(2):72–9. https://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.2.72.
Article11. Hides JA, Stokes MJ, Saide M, et al. Evidence of lumbar multifidus muscle wasting ipsilateral to symptoms in patients with acute/subacute low back pain. Spine. 1994 Jan 15; 19(2):165–72.
Article12. Hodges PW, Holm AK, Hansson T, et al. Rapid atrophy of the lumbar multifidus follows experimental disc or nerve root injury. Spine. 2006 Dec 1; 31(25):2926–33.
Article13. Boutin RD, Yao L, Canter RJ. Sarcopenia: Current Con-cepts and Imaging Implications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Sep; 205(3):W255–66.
Article14. Twomey L, Taylor J. Exercise and spinal manipulation in the treatment of low back pain. Spine. 1995 Mar 1; 20(5):615–9.
Article15. Saal JA, Saal JS. Nonoperative treatment of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc with radiculopathy. An outcome study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989 Apr; 14(4):431–7.16. Hides JA, Stanton WR, McMahon S, et al. Effect of stabilization training on multifidus muscle cross-sectional area among young elite cricketers with low back pain. J Orthop Phys Ther. 2008 Mar; 38(3):101–8. DOI: 10.2519/jospt.2008.2658. Epub 2007 Dec 7.
Article17. Hides JA, Jull GA, Richardson CA. Long-term effects of specific stabilizing exercises for first-episode low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001 Jun 1; 26(11):E243–8.
Article18. Mannion AF, Taimela S, Muntener M, et al. Active therapy for chronic low back pain. part 1. Effects on back muscle activation, fatigability, and strength. Spine. 2001 Apr 15; 26(8):920–9.19. Videman T, Levä lahti E, Battié MC. The effects of anthro-pometrics, lifting strength, and physical activities in disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Jun 1; 32(13):1406–13.
Article20. Callaghan JP, Gunning JL, McGill SM. The relationship between lumbar spine load and muscle activity during extensor exercises. Phys Ther. 1998 Jan; 78(1):8–18.
Article21. Elliott JM, Jull G, Noteboom JT, et al. Fatty infiltration in the cervical extensor muscles in persistent whiplash-associated disorders. a magnetic resonance imaging analysis. Spine. 2006 Oct; 31(22):E847–55.22. Wessberg P, Frennered K. Central lumbar spinal stenosis: natural history of non-surgical patients. Eur Spine J. 2017 Oct; 26(10):2536–2542. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-017-5075-x. Epub 2017 Apr 17.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Associated with Conversion from Conservative to Surgical Treatment in Single-Level Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Patients
- A Case of Coexisting Cervical and Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Result of Pedicle Screw Fixation in Lumbar Stenosis with: A Comparison of Degenerative Type Lumbar Stenosis with Spondylolisthetic type Lumbar Stenosis
- The Pathomorphologic Study of Spinal Stenosis as Seen on CT - Myelography of the Lumbar
- Anterior Epidural Irrigation in a Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Patient