J Clin Neurol.
2019 Oct;15(4):429-437. 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.429.
Clinical and Radiographic Characteristics of Neuro-Behçet's Disease in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hayshin@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Dermatology, Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatoloy, Catholic Kwandong University International St. Mary's Hospital, Incheon, Korea. dbang@ish.or.kr
- KMID: 2467750
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.429
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Neurological involvement in Behçet's disease [neuro-Behçet's disease (NBD)] is uncommon, but it is worth investigating since it can cause substantial disability. However, difficulties exist in understanding the clinical features of NBD due to regional variations and the lack of studies utilizing well-established diagnostic criteria. We therefore analyzed the clinical features of patients with NBD based on the recent international consensus recommendation.
METHODS
We retrospectively searched electronic databases for patients with Behçet's disease (BD) between 2000 and 2017, and reviewed their medical records. Based on the recent international consensus recommendation, patients with definite or probable NBD were included.
RESULTS
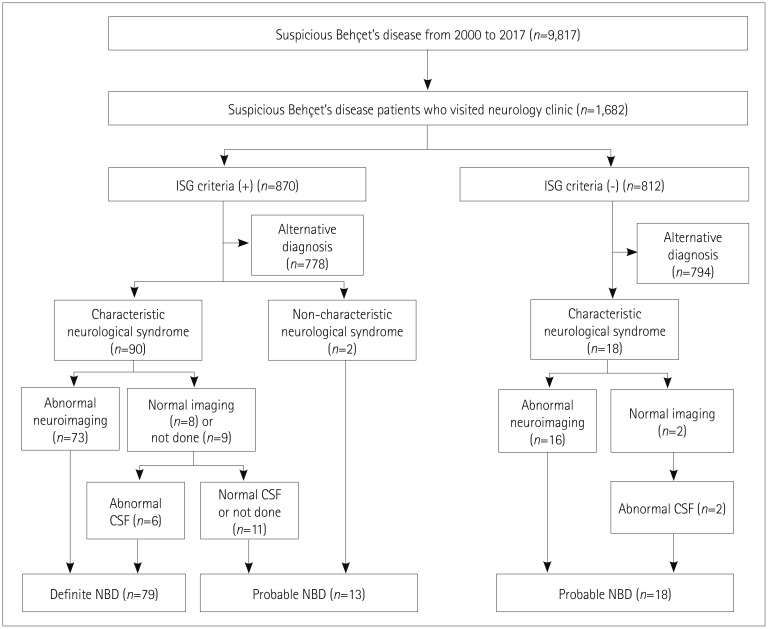
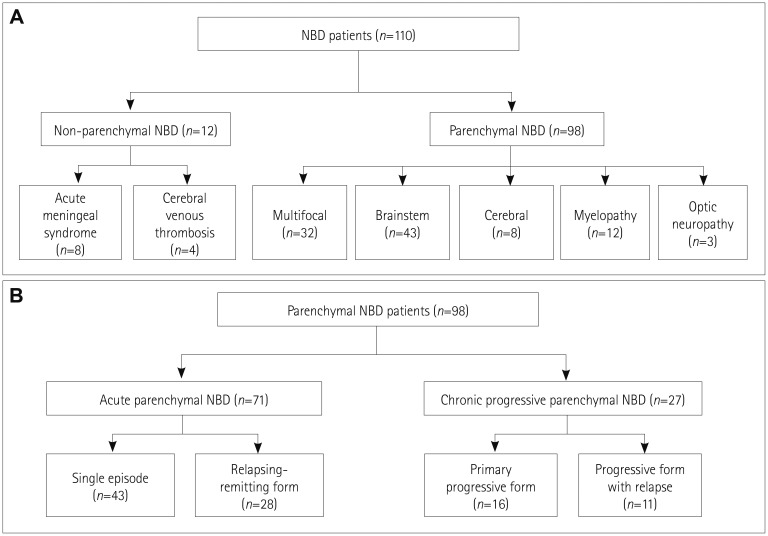
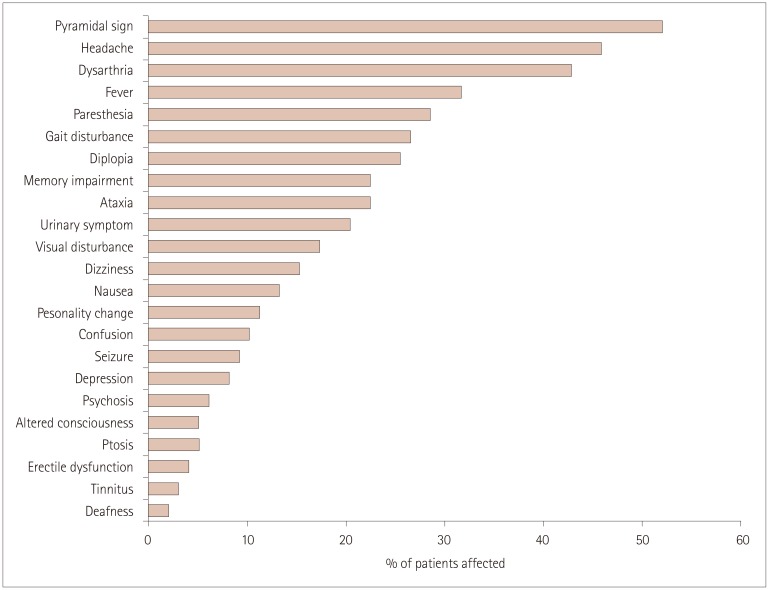
Of 9,817 patients with the diagnosis code for BD, 1,682 (17.1%) visited the neurology clinic and 110 (1.1%) were classified as NBD. Ninety-eight patients exhibited parenchymal NBD and 12 exhibited nonparenchymal NBD. Their age at the onset of NBD was 37.6±10.6 years and the male-to-female ratio was 1.24:1. Brainstem syndrome (43.9%) was the most common condition in the 98 patients with parenchymal NBD, followed by multifocal (32.7%) and spinal cord (12.2%) syndromes. 72.4% exhibited acute NBD and 27.6% exhibited a progressive disease course. Frequent manifestations included pyramidal signs (52.0%), headache (45.9%), dysarthria (42.9%), and fever (31.6%). A frequent pattern in brain MRI was an upper brainstem lesion extending to the thalamus and basal ganglia.
CONCLUSIONS
Approximately 1% of the patients with suspected BD exhibited NBD. Neurologists must understand the clinical characteristics of NBD in order to perform the differential diagnosis and management of these patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Epidemiologic and Etiological Features of Korean Patients With Behçet’s Disease
Soo Hyun Choi, BA, Do-Young Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2021;28(4):183-191. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.183.
Reference
-
1. Al-Araji A, Kidd DP. Neuro-Behçet's disease: epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:192–204. PMID: 19161910.
Article2. Tursen U, Gurler A, Boyvat A. Evaluation of clinical findings according to sex in 2313 Turkish patients with Behçet's disease. Int J Dermatol. 2003; 42:346–351. PMID: 12755969.3. Siva A, Kantarci OH, Saip S, Altintas A, Hamuryudan V, Islak C, et al. Behçet's disease: diagnostic and prognostic aspects of neurological involvement. J Neurol. 2001; 248:95–103. PMID: 11284141.
Article4. Akman-Demir G, Serdaroglu P, Tasçi B. Clinical patterns of neurological involvement in Behçet's disease: evaluation of 200 patients. The Neuro-Behçet Study Group. Brain. 1999; 122:2171–2182. PMID: 10545401.5. Farah S, Al-Shubaili A, Montaser A, Hussein JM, Malaviya AN, Mukhtar M, et al. Behçet's syndrome: a report of 41 patients with emphasis on neurological manifestations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 64:382–384. PMID: 9527155.6. Ikeda K, Abe M, Iwasaki Y, Kinoshita M. Neuro-Behçet's disease in Japan. Neurology. 1996; 47:614–615. PMID: 8757065.7. Joseph FG, Scolding NJ. Neuro-Behçet's disease in Caucasians: a study of 22 patients. Eur J Neurol. 2007; 14:174–180. PMID: 17250726.
Article8. Kalra S, Silman A, Akman-Demir G, Bohlega S, Borhani-Haghighi A, Constantinescu CS, et al. Diagnosis and management of neuro-Behçet's disease: international consensus recommendations. J Neurol. 2014; 261:1662–1676. PMID: 24366648.
Article9. Hirohata S, Kikuchi H, Sawada T, Nagafuchi H, Kuwana M, Takeno M, et al. Clinical characteristics of Neuro-Behcet's disease in Japan: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:405–413. PMID: 21935641.
Article10. Ideguchi H, Suda A, Takeno M, Kirino Y, Ihata A, Ueda A, et al. Neurological manifestations of Behçet's disease in Japan: a study of 54 patients. J Neurol. 2010; 257:1012–1020. PMID: 20127350.
Article11. Houman MH, Bellakhal S, Ben Salem T, Hamzaoui A, Braham A, Lamloum M, et al. Characteristics of neurological manifestations of Behçet's disease: a retrospective monocentric study in Tunisia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:2015–2018. PMID: 23830180.
Article12. Talarico R, D'Ascanio A, Figus M, Stagnaro C, Ferrari C, Elefante E, et al. Behçet's disease: features of neurological involvement in a dedicated centre in Italy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012; 30:S69–S72. PMID: 23009765.13. Yoon DL, Kim YJ, Koo BS, Kim YG, Lee CK, Yoo B. Neuro-Behçet's disease in South Korea: clinical characteristics and treatment response. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014; 17:453–458. PMID: 24506839.
Article14. Lee SH, Yoon PH, Park SJ, Kim DI. MRI findings in neuro-Behçet's disease. Clin Radiol. 2001; 56:485–494. PMID: 11428799.
Article15. Davatchi F, Shahram F, Chams-Davatchi C, Sadeghi Abdollahi B, Shams H, Nadji A, et al. Behcet's disease: is there a gender influence on clinical manifestations. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012; 15:306–314. PMID: 22709493.
Article16. Noel N, Bernard R, Wechsler B, Resche-Rigon M, Depaz R, Le Thi Huong Boutin D, et al. Long-term outcome of neuro-Behçet's disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014; 66:1306–1314. PMID: 24782188.
Article17. Borhani Haghighi A, Pourmand R, Nikseresht AR. Neuro-Behçet disease: a review. Neurologist. 2005; 11:80–89. PMID: 15733330.18. Hatemi I, Hatemi G, Celik AF, Melikoglu M, Arzuhal N, Mat C, et al. Frequency of pathergy phenomenon and other features of Behçet's syndrome among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008; 26:S91–S95. PMID: 19026122.19. Al-Araji A, Sharquie K, Al-Rawi Z. Prevalence and patterns of neurological involvement in Behcet's disease: a prospective study from Iraq. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003; 74:608–613. PMID: 12700303.
Article20. Ashjazadeh N, Borhani Haghighi A, Samangooie S, Moosavi H. Neuro-Behcet's disease: a masquerader of multiple sclerosis. A prospective study of neurologic manifestations of Behcet's disease in 96 Iranian patients. Exp Mol Pathol. 2003; 74:17–22. PMID: 12645628.21. Serdaroğlu P, Yazici H, Ozdemir C, Yurdakul S, Bahar S, Aktin E. Neurologic involvement in Behçet's syndrome. A prospective study. Arch Neurol. 1989; 46:265–269. PMID: 2919979.22. Borhani-Haghighi A, Samangooie S, Ashjazadeh N, Nikseresht A, Shariat A, Yousefipour G, et al. Neurological manifestations of Behçet's disease. Saudi Med J. 2006; 27:1542–1546. PMID: 17013480.23. Moghaddassi M, Togha M, Shahram F, Hanif H, Dadkhah S, Jahromi SR, et al. Headache in Behcet's disease: types and characteristics. Springerplus. 2016; 5:1077. PMID: 27462525.
Article24. Fountain EM, Dhurandhar A. Neuro-Behçet's disease: an unusual cause of headache. J Gen Intern Med. 2014; 29:956–960. PMID: 24549519.
Article25. Kidd D. The prevalence of headache in Behçet's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006; 45:621–623. PMID: 16368730.
Article26. Saip S, Siva A, Altintas A, Kiyat A, Seyahi E, Hamuryudan V, et al. Headache in Behçet's syndrome. Headache. 2005; 45:911–919. PMID: 15985109.
Article27. Borhani Haghighi A, Aflaki E, Ketabchi L. The prevalence and characteristics of different types of headache in patients with Behçet's disease, a case-control study. Headache. 2008; 48:424–429. PMID: 18205799.28. Gökçay F, Celebisoy N, Gökçay A, Aksu K, Keser G. Neurological symptoms and signs in Behçet disease: a Western Turkey experience. Neurologist. 2011; 17:147–150. PMID: 21532383.29. Lee HS, Kim DY, Shin HY, Choi YC, Kim SM. Spinal cord involvement in Behçet's disease. Mult Scler. 2016; 22:960–963. PMID: 26480923.
Article30. Kidd D, Steuer A, Denman AM, Rudge P. Neurological complications in Behçet's syndrome. Brain. 1999; 122:2183–2194. PMID: 10545402.
Article31. Lo Monaco A, La Corte R, Caniatti L, Borrelli M, Trotta F. Neurological involvement in North Italian patients with Behçet disease. Rheumatol Int. 2006; 26:1113–1119. PMID: 16794844.
Article32. Akman-Demir G, Tüzün E, Içöz S, Yeşilot N, Yentür SP, Kürtüncü M, et al. Interleukin-6 in neuro-Behçet's disease: association with disease subsets and long-term outcome. Cytokine. 2008; 44:373–376. PMID: 19010690.
Article33. Coban O, Bahar S, Akman-Demir G, Taşci B, Yurdakul S, Yazici H, et al. Masked assessment of MRI findings: is it possible to differentiate neuro-Behçet's disease from other central nervous system diseases? [corrected]. Neuroradiology. 1999; 41:255–260. PMID: 10344509.34. Sumita Y, Murakawa Y, Sugiura T, Wada Y, Nagai A, Yamaguchi S. Elevated BAFF levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuro-Behçet's disease: BAFF is correlated with progressive dementia and psychosis. Scand J Immunol. 2012; 75:633–640. PMID: 22340436.
Article35. Aykutlu E, Baykan B, Serdaroglu P, Gökyigit A, Akman-Demir G. Epileptic seizures in Behçet disease. Epilepsia. 2002; 43:832–835. PMID: 12181001.
Article36. Farahangiz S, Sarhadi S, Safari A, Borhani-Haghighi A. Magnetic resonance imaging findings and outcome of neuro-Behçet's disease: the predictive factors. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012; 15:e142–e149. PMID: 23253242.
Article37. Borhani Haghighi A, Sarhadi S, Farahangiz S. MRI findings of neuro-Behcet's disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2011; 30:765–770. PMID: 21165752.
Article38. Kotake S, Higashi K, Yoshikawa K, Sasamoto Y, Okamoto T, Matsuda H. Central nervous system symptoms in patients with Behçet disease receiving cyclosporine therapy. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:586–589. PMID: 10080218.
Article39. Kikuchi H, Aramaki K, Hirohata S. Effect of infliximab in progressive neuro-Behçet's syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2008; 272:99–105. PMID: 18550081.
Article40. Hirohata S, Kikuchi H, Sawada T, Nagafuchi H, Kuwana M, Takeno M, et al. Retrospective analysis of long-term outcome of chronic progressive neurological manifestations in Behcet's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 349:143–148. PMID: 25601769.
Article41. Santos Lacomba M, Marcos Martín C, Gallardo Galera JM, Gómez Vidal MA, Collantes Estévez E, Ramírez Chamond R, et al. Aqueous humor and serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha in clinical uveitis. Ophthalmic Res. 2001; 33:251–255. PMID: 11586057.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Blepharoptosis in Behçet's Disease
- Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms Associated with Behçet's Disease
- Rupture of Renal Artery in a Patient with Behçet's Disease
- Elevated Serum Levels of Neopterin in Patients with Behçet's Disease
- Behçet's Disease with Deep Vaginal Ulcer Diagnosed for the First Time during Pregnancy