Infect Chemother.
2016 Sep;48(3):209-215. 10.3947/ic.2016.48.3.209.
Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Piperacillin/Tazobactam in Korean Patients with Acute Infections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. smkimkor@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Cheongju St. Mary's Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2466433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2016.48.3.209
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
For more effective and safer usage of antibiotics, the dosing strategy should be individualized based on the patients' characteristics, including race. The aim of this study was to investigate the population pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles of piperacillin and tazobactam in Korean patients with acute infections.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
At least four consecutive 2/0.25 g or 4/0.5 g doses of piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP) were intravenously infused over 1 h every 8 h for patients with creatinine clearance (CL(cr)) ≤50 ml/min or CL(cr) >50 mL/min, respectively. Blood samples from 33 patients at a steady-state were taken pre-dose and at 0 min, 30 min, and 4-6 h after the fourth infusion. The population PK analysis was conducted using a non-linear mixed-effects method. A likelihood ratio test was used to select significant covariates, with significance levels of P <0.05 for selection and P <0.01 for elimination.
RESULTS
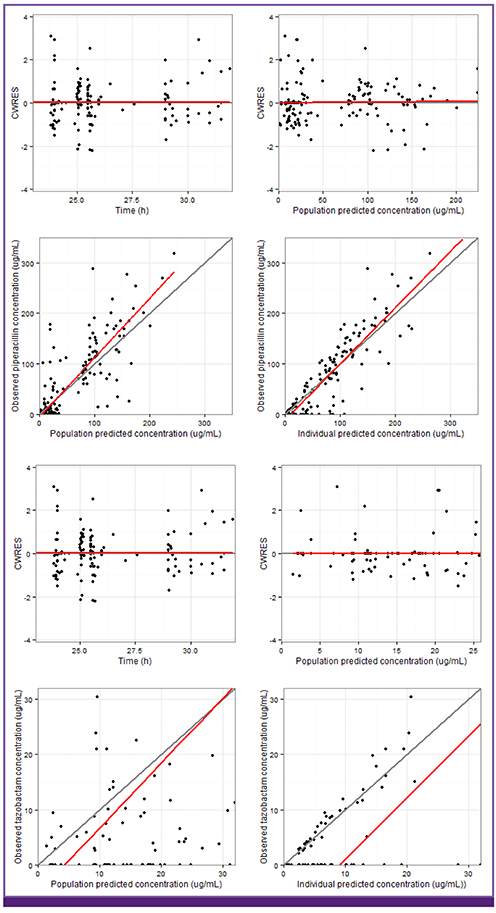
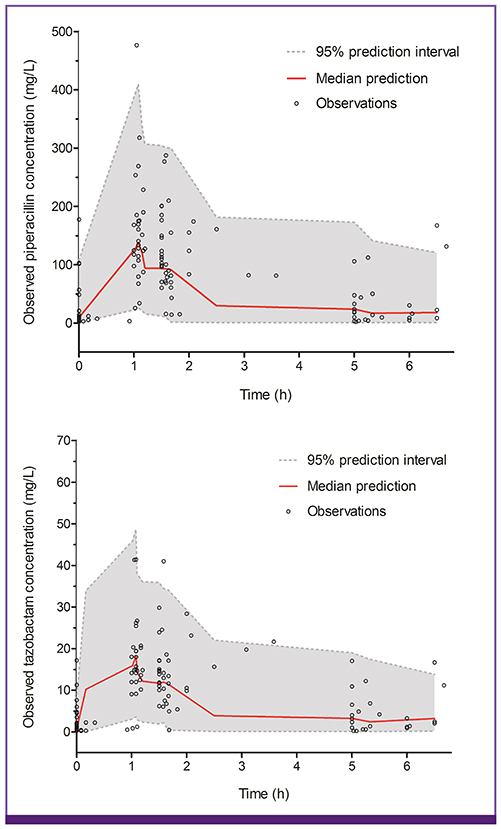
Both piperacillin PK and tazobactam PK were well described by a two-compartment model with first-order elimination. Creatinine clearance and body weight, as covariates on clearance (CL) and volume of central compartment (V1), were selected among the covariates possibly affecting PK parameters of both drugs. CL was defined as CL = 2.9 + 4.03 × CL(cr)/47 for piperacillin and CL = 1.76 + 4.81 × CL(cr)/47 for tazobactam. V1 was defined as V1 = 19.5 × weight/60 for piperacillin and V1 = 22.6 × weight/60 for tazobactam.
CONCLUSION
The PK profiles of TZP at a steady-state in Korean patients with acute infections were well described by a two-compartment model with first-order elimination. Both piperacillin and tazobactam clearances were significantly influenced by creatinine clearance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Collaborative Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic Research for Optimization of Antimicrobial Therapy
Seunghoon Han
Infect Chemother. 2016;48(3):254-256. doi: 10.3947/ic.2016.48.3.254.
Reference
-
1. Gin A, Dilay L, Karlowsky JA, Walkty A, Rubinstein E, Zhanel GG. Piperacilin-tazobactam: a beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combination. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2007; 5:365–383.2. Maltezou HC, Nikolaidis P, Lebesii E, Dimitriou L, Androulakakis E, Kafetzis DA. Piperacillin/tazobactam versus cefotaxime plus metronidazole for treatment of children with intra-abdominal infections requiring surgery. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001; 20:643–646.
Article3. Tumbarello M, Sanguinetti M, Montuori E, Trecarichi EM, Posteraro B, Fiori B, Citton R, D’Inzeo T, Fadda G, Cauda R, Spanu T. Predictors of mortality in patients with bloodstream infections caused by extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: importance of inadequate initial antimicrobial treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007; 51:1987–1994.
Article4. Peralta G, Lamelo M, Alvarez-García P, Velasco M, Delgado A, Horcajada JP, Montero M, Roiz MP, Fariñas MC, Alonso J, Martínez LM, Gutiérrez-Macías A, Alava JA, Rodríguez A, Fleites A, Navarro V, Sirvent E, Capdevila JA; SEMI- BLEE STUDY GROUP. Impact of empirical treatment in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp bacteremia. A multicentric cohort study. BMC Infect Dis. 2012; 12:245.5. Turnidge JD. The pharmacodynamics of β-lactams. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 27:10–22.
Article6. Mckinnon PS, Paladino JA, Schentag JJ. Evaluation of area under the inhibitory curve (AUIC) and time above the minimum inhibitory concentration (T>MIC) as predictors of outcome for cefepime and ceftazidime in serious bacterial infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008; 31:345–351.
Article7. Lodise TP, Lomaestro BM, Drusano GL; Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Application of antimicrobial pharmacodynamics concepts into clinical practice: focus onββ -lactam antibiotics: insights form the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy. 2006; 26:1320–1332.
Article8. Patel N, Scheetz MH, Drusano GL, Lodise TP. Identification of optimal renal dosage adjustments for traditional and extended-infusion piperacillin-tazobactam dosing refimens in hospitalized patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:460–465.
Article9. Dulhunty JM, Roberts JA, Davis JS, Webb SA, Bellomo R, Gomersall C, Shirwadkar C, Eastwood GM, Myburgh J, Paterson DL, Lipman J. Continous infusion of beta-lactam antibiotics in severe sepsis: a multicenter double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56:236–244.
Article10. Roberts JA, Ulldemolins M, Roberts MS, McWhinney BC, Ungerer J, Paterson DL, Lipman J. Therapeutic drug monitoring of β-lactams in critically ill patients: proof of concept. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010; 36:332–339.
Article11. Johnson JA. Influence of race or ethnicity on pharmacokinetics of drugs. J Pharm Sci. 1997; 86:1328–1333.
Article12. Chen ML. Ethnic or racial differences revisited: impact of dosage regimen form on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006; 45:957–964.13. Jeon S, Han S, Lee J, Hong T, Paek J, Woo H, Yim DS. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of piperacillin in burn patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58:3744–3751.
Article14. Oh KH, Kim C, Lee H, Lee H, Jung JY, Kim NJ, Yu KS, Shin KH, Jang IJ, Ahn C. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous piperacillin administration in patients undergoing on-line hemodiafiltration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:3266–3268.
Article15. Kiem S, Ryu SM, Lee YM, Schentag JJ, Kim YW, Kim HK, Jang HJ, Joo YD, Jin K, Shin JG, Ghim JL. Population pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin in Korean patients. J Chemother. 2016; 28:308–313.
Article16. Li C, Kuti JL, Nightingale CH, Mansfield DL, Dana A, Nicolau DP. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piperacillin/tazobactam in patients with complicated intra-abdominal infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 56:388–395.
Article17. Felton TW, Roberts JA, Lodise TP, Guilder MV, Boselli E, Neely MN, Hope WW. Indivisualization of piperacillin dosing for critically ill patients: dosing software to optimize antimicrobial therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58:4094–4102.
Article18. Hayashi Y, Roberts JA, Paterson DL, Lipman J. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of piperacillin-tazobactam. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010; 6:1017–1031.
Article19. Cheymol G. Effects of obesity on pharmacokinetics implications for drug therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000; 39:215–231.20. Morgan DJ, Bray KM. Lean body mass as a predictor of drug dosage. Implications for drug therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994; 26:292–307.21. Cheatham SC, Fleming MR, Healy DP, Chung CE, Shea KM, Humphrey ML, Kays MB. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piperacillin and tazobactam administered by prolonged infusion in obese patients. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013; 41:52–56.
Article22. Chung EK, Cheatham SC, Fleming MR, Healy DP, Shea KM, Kays MB. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piperacillin and tazobactam administered by prolonged infusion in obese and nonobese patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015; 55:899–908.
Article23. Tamma PD, Turnbull AE, Milstone AM, Hsu AJ, Carroll KC, Cosgrove SE. Does the piperacillin minimum inhibitory concentration for Pseudomonas aeruginosa influence clinical outcomes of children with pseudomonal bacteremia? Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 55:799–806.
Article24. Karino F, Nishimura N, Ishihara N, Moriyama H, Miura K, Hamaguchi S, Sutani A, Kuraki T, Morikawa N. Nephrotoxicity induced by piperacillin-tazobactam in late elderly Japanese patients with nursing and healthcare associated pneumonia. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014; 37:1971–1976.
Article25. Huang WT, Hsu YJ, Chu PL, Lin SH. Neurotoxicity associated with standard doses of piperacillin in an elderly patient with renal failure. Infection. 2009; 37:374–376.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In vitro Susceptibility of Imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa against Piperacillin/tazobactam
- Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Associated Hypersensitivity Syndrome with Overlapping Features of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis and Drug-Related Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome
- Comparison of Cefepime Monotherapy with Piperacillin-Tazobactam, Gentamicin Combination Therapy in Pediatric Cancer Patients with Febrile Neutropenia
- In Vitro Susceptibility of piperacillin/tazobactam Against extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Drug Fever Due to Piperacillin/Tazobactam Loaded into Bone Cement