Yonsei Med J.
2016 Jan;57(1):138-145. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.138.
Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient Predicts Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. sonjh@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Ajou University Hospital, Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2466363
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.138
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The present study aimed to investigate the role of hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) for prediction of long-term mortality in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical data from 97 non-critically-ill cirrhotic patients with HVPG measurements were retrospectively and consecutively collected between 2009 and 2012. Patients were classified according to clinical stages and presence of ascites. The prognostic accuracy of HVPG for death, survival curves, and hazard ratios were analyzed.
RESULTS
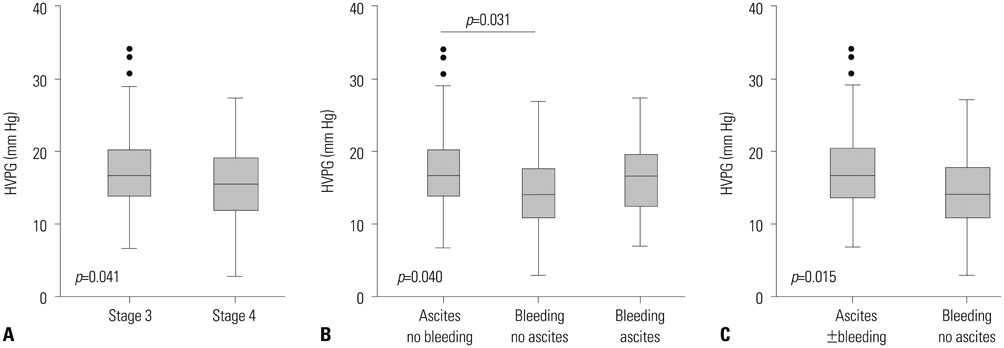
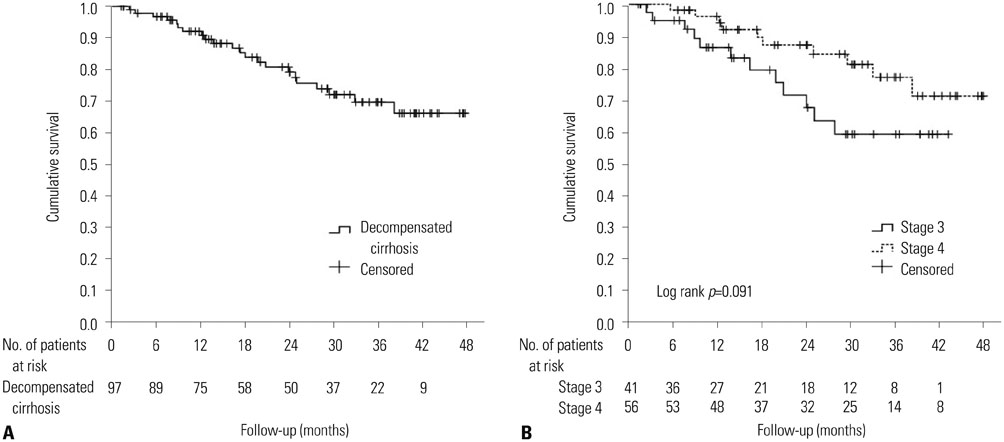
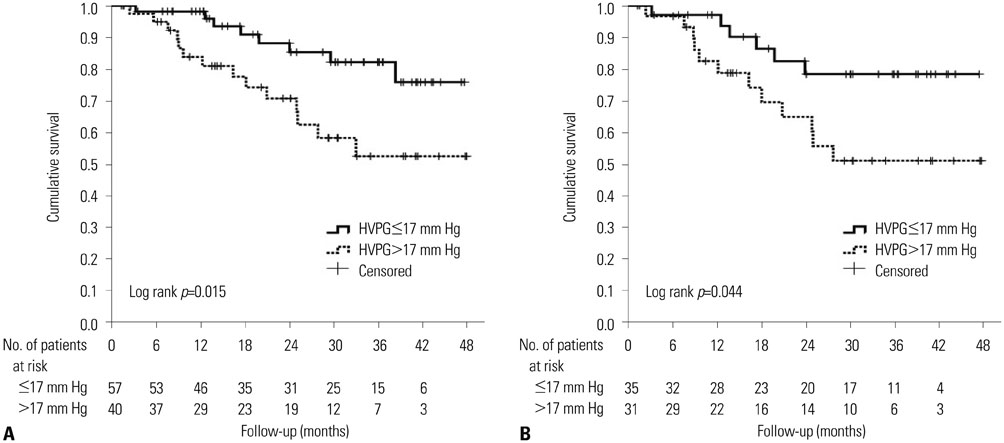
During a median follow-up of 24 (interquartile range, 13-36) months, 22 patients (22.7%) died. The area under the receiver operating characteristics curves of HVPG for predicting 1-year, 2-year, and overall mortality were 0.801, 0.737, and 0.687, respectively (all p<0.01). The best cut-off value of HVPG for predicting long-term overall mortality in all patients was 17 mm Hg. The mortality rates at 1 and 2 years were 8.9% and 19.2%, respectively: 1.9% and 11.9% with HVPG < or =17 mm Hg and 16.2% and 29.4% with HVPG >17 mm Hg, respectively (p=0.015). In the ascites group, the mortality rates at 1 and 2 years were 3.9% and 17.6% with HVPG < or =17 mm Hg and 17.5% and 35.2% with HVPG >17 mm Hg, respectively (p=0.044). Regarding the risk factors for mortality, both HVPG and model for end-stage liver disease were positively related with long-term mortality in all patients. Particularly, for the patients with ascites, both prothrombin time and HVPG were independent risk factors for predicting poor outcomes.
CONCLUSION
HVPG is useful for predicting the long-term mortality in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, especially in the presence of ascites.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Ascites/mortality
Female
Hepatic Veins/*physiopathology
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Liver Cirrhosis/blood/complications/diagnosis/*mortality/*physiopathology
Liver Failure/diagnosis/*mortality/physiopathology
Male
Middle Aged
Predictive Value of Tests
Prognosis
Proportional Hazards Models
ROC Curve
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Severity of Illness Index
Venous Pressure
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Presence of Sarcopenia and Its Rate of Change Are Independently Associated with Long-term Mortality in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Jae Yoon Jeong, Sanghyeok Lim, Joo Hyun Sohn, Jae Gon Lee, Dae Won Jun, Yongsoo Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(50):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e299.
Reference
-
1. Suk KT, Baik SK, Yoon JH, Cheong JY, Paik YH, Lee CH, et al. Revision and update on clinical practice guideline for liver cirrhosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2012; 18:1–21.
Article2. Albilllos A, Garcia-Tsao G. Classification of cirrhosis: the clinical use of HVPG measurements. Dis Markers. 2011; 31:121–128.
Article3. Salerno F, Merli M, Cazzaniga M, Valeriano V, Rossi P, Lovaria A, et al. MELD score is better than Child-Pugh score in predicting 3-month survival of patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. J Hepatol. 2002; 36:494–500.
Article4. Huo TI, Wu JC, Lin HC, Lee FY, Hou MC, Lee PC, et al. Evaluation of the increase in model for end-stage liver disease (DeltaMELD) score over time as a prognostic predictor in patients with advanced cirrhosis: risk factor analysis and comparison with initial MELD and Child-Turcotte-Pugh score. J Hepatol. 2005; 42:826–832.
Article5. Bambha KM, Biggins SW. Inequities of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease: an examination of current components and future additions. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2008; 13:227–233.
Article6. Lee SH, Park SH, Kim GW, Lee WJ, Hong WK, Ryu MS, et al. [Comparison of the Model for End-stage Liver Disease and hepatic venous pressure gradient for predicting survival in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis]. Korean J Hepatol. 2009; 15:350–356.
Article7. Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV, Vangeli M, Terreni N, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Systematic review: The model for end-stage liver disease--should it replace Child-Pugh's classification for assessing prognosis in cirrhosis? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 22:1079–1089.
Article8. Kim HJ, Lee HW. Important predictor of mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013; 19:105–115.
Article9. Suk KT. Hepatic venous pressure gradient: clinical use in chronic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2014; 20:6–14.
Article10. Gluud C, Henriksen JH, Nielsen G. Prognostic indicators in alcoholic cirrhotic men. Hepatology. 1988; 8:222–227.
Article11. Merkel C, Bolognesi M, Bellon S, Zuin R, Noventa F, Finucci G, et al. Prognostic usefulness of hepatic vein catheterization in patients with cirrhosis and esophageal varices. Gastroenterology. 1992; 102:973–979.
Article12. Ripoll C, Bañares R, Rincón D, Catalina MV, Lo Iacono O, Salcedo M, et al. Influence of hepatic venous pressure gradient on the prediction of survival of patients with cirrhosis in the MELD Era. Hepatology. 2005; 42:793–801.
Article13. Moitinho E, Escorsell A, Bandi JC, Salmerón JM, García-Pagán JC, Rodés J, et al. Prognostic value of early measurements of portal pressure in acute variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:626–631.
Article14. Zipprich A, Garcia-Tsao G, Rogowski S, Fleig WE, Seufferlein T, Dollinger MM. Prognostic indicators of survival in patients with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2012; 32:1407–1414.
Article15. Suk KT, Kim CH, Park SH, Sung HT, Choi JY, Han KH, et al. Comparison of hepatic venous pressure gradient and two models of end-stage liver disease for predicting the survival in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012; 46:880–886.
Article16. Park SH, Park HY, Kang JW, Park JS, Shin KJ, Kim CH, et al. Identification of patients with decompensated cirrhosis at high risk for death: improving the prediction by hepatic venous pressure gradient? Hepatogastroenterology. 2012; 59:2548–2551.17. D'Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006; 44:217–231.18. The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1994; 20(1 Pt 1):15–20.19. Sanyal AJ, Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Kowdley KV, Chalasani N, Lavine JE, et al. Endpoints and clinical trial design for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2011; 54:344–353.
Article20. Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. National Cancer Center, Korea. [Practice guidelines for management of hepatocellular carcinoma 2009]. Korean J Hepatol. 2009; 15:391–423.21. D'Amico G, Garcia-Pagan JC, Luca A, Bosch J. Hepatic vein pressure gradient reduction and prevention of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:1611–1624.22. Albillos A, Bañares R, González M, Ripoll C, Gonzalez R, Catalina MV, et al. Value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient to monitor drug therapy for portal hypertension: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1116–1126.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The relation between hepatic venous pressure gradient and complications of liver cirrhosis
- Combined effect of hepatic venous pressure gradient and liver stiffness on long-term mortality in patients with cirrhosis
- Comparison of the Model for End-stage Liver Disease and hepatic venous pressure gradient for predicting survival in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis
- Pharmacological Therapy of Portal Hypertension: Focused on Korean Data
- Pathophysiology and diagnosis of portal hypertension