Endocrinol Metab.
2019 Dec;34(4):398-405. 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.398.
Short-Term Effects of Beraprost Sodium on the Markers for Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Microalbuminuria
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea. hegletter@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2466259
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.398
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To evaluate the changes in cardiovascular risk markers including pulse wave velocity (PWV), microalbuminuria, inflammatory cytokines, and adhesion molecules after treatment with beraprost sodium (BPS) in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
METHODS
This was a multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with microalbuminuria were included. The primary endpoints were changes in microalbuminuria in spot urine and PWV after BPS or placebo (PCB) treatment for 24 weeks. The secondary endpoints were changes in clinical and metabolic parameters.
RESULTS
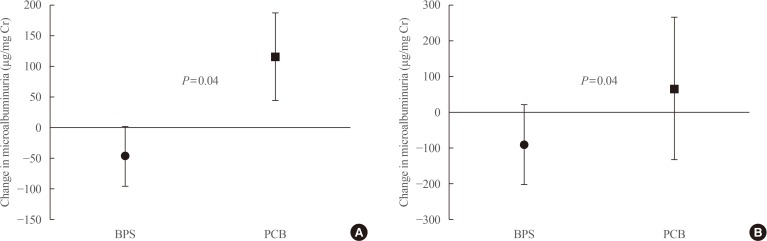
A total of 52 patients completed the 24-week trial. Changes in PWV were not different significantly in the BPS and PCB groups (right, P=0.16; left, P=0.11). Changes in microalbuminuria were 14.2±157.0 and 34.5±146.6 (µg/mg Cr) in the BPS and PCB groups, respectively (P=0.63). Subgroup analysis in the high blood pressure (BP) group (baseline systolic BP >120 mm Hg and diastolic BP >80 mm Hg), showed that microalbuminuria decreased by −47.6 in the BPS group compared with an increase by 116.4 (µg/mg Cr) in the PCB group (P=0.04). Also, in the large waist circumference group (>95 cm), microalbuminuria decreased significantly in the BPS group (P=0.04).
CONCLUSION
Short-term treatment of BPS for patients with diabetic nephropathy did not show significant improvement in various cardiovascular risk factors. However, BPS significantly decreased microalbuminuria in study subjects with higher cardiovascular risk such as high BP or large waist circumference.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Melian EB, Goa KL. Beraprost: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of peripheral arterial disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Drugs. 2002; 62:107–133. PMID: 11790158.2. Goya K, Otsuki M, Xu X, Kasayama S. Effects of the prostaglandin I2 analogue, beraprost sodium, on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human vascular endothelial cells and circulating vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2003; 52:192–198. PMID: 12601631.
Article3. Shin S, Kim KJ, Chang HJ, Lee BW, Yang WI, Cha BS, et al. The effect of oral prostaglandin analogue on painful diabetic neuropathy: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:185–188.
Article4. Guan J, Long L, Chen YQ, Yin Y, Li L, Zhang CX, et al. Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy. Genet Mol Res. 2014; 13:4154–4158. PMID: 25036159.
Article5. Watanabe M, Nakashima H, Mochizuki S, Abe Y, Ishimura A, Ito K, et al. Amelioration of diabetic nephropathy in OLETF rats by prostaglandin I(2) analog, beraprost sodium. Am J Nephrol. 2009; 30:1–11. PMID: 19158439.6. Yamashita T, Shikata K, Matsuda M, Okada S, Ogawa D, Sugimoto H, et al. Beraprost sodium, prostacyclin analogue, attenuates glomerular hyperfiltration and glomerular macrophage infiltration by modulating ecNOS expression in diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002; 57:149–161. PMID: 12126764.
Article7. Arima S, Ren Y, Juncos LA, Carretero OA, Ito S. Glomerular prostaglandins modulate vascular reactivity of the downstream efferent arterioles. Kidney Int. 1994; 45:650–658. PMID: 8196266.
Article8. Owada A, Suda S, Hata T. Effect of long-term administration of prostaglandin I(2) in incipient diabetic nephropathy. Nephron. 2002; 92:788–796. PMID: 12399622.9. Lehmann ED, Riley WA, Clarkson P, Gosling RG. Non-invasive assessment of cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1997; 350 Suppl 1:SI14–SI19. PMID: 9250278.
Article10. Amar J, Ruidavets JB, Chamontin B, Drouet L, Ferrieres J. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a population-based study. J Hypertens. 2001; 19:381–387. PMID: 11288807.
Article11. Shima A, Miyamoto M, Kubota Y, Takagi G, Shimizu W. Beraprost sodium protects against diabetic nephropathy in patients with arteriosclerosis obliterans: a prospective, randomized, open-label study. J Nippon Med Sch. 2015; 82:84–91. PMID: 25959199.
Article12. Nakayama T, Hironaga T, Ishima H, Maruyama T, Masubuchi Y, Kokubun S. The prostacyclin analogue beraprost sodium prevents development of arterial stiffness in elderly patients with cerebral infarction. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2004; 70:491–494. PMID: 15120711.
Article13. Nakayama T, Masubuchi Y, Kawauchi K, Masaki R, Hironaga T, Ishima H, et al. Beneficial effect of beraprost sodium plus telmisartan in the prevention of arterial stiffness development in elderly patients with hypertension and cerebral infarction. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2007; 76:309–314. PMID: 17616452.
Article14. Chapleau CE, White RP. Effects of prostacyclin on the canine isolated basilar artery. Prostaglandins. 1979; 17:573–580. PMID: 379918.
Article15. Cecelja M, Chowienczyk P. Dissociation of aortic pulse wave velocity with risk factors for cardiovascular disease other than hypertension: a systematic review. Hypertension. 2009; 54:1328–1336. PMID: 19884567.16. Kim HK, Kim CH, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Choe J, Park JY, et al. Impaired fasting glucose and risk of cardiovascular disease in Korean men and women: the Korean Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:328–335. PMID: 23002083.17. Cruickshank K, Riste L, Anderson SG, Wright JS, Dunn G, Gosling RG. Aortic pulse-wave velocity and its relationship to mortality in diabetes and glucose intolerance: an integrated index of vascular function. Circulation. 2002; 106:2085–2090. PMID: 12379578.18. Grassi G, Giannattasio C. Obesity and vascular stiffness: when body fat has an adverse impact on arterial dynamics. J Hypertens. 2005; 23:1789–1791. PMID: 16148598.
Article19. Mauer SM, Steffes MW, Ellis EN, Sutherland DE, Brown DM, Goetz FC. Structural-functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1984; 74:1143–1155. PMID: 6480821.
Article20. Makino H, Yamasaki Y, Haramoto T, Shikata K, Hironaka K, Ota Z, et al. Ultrastructural changes of extracellular matrices in diabetic nephropathy revealed by high resolution scanning and immunoelectron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1993; 68:45–55. PMID: 8423676.21. Koh E, Morimoto S, Jiang B, Inoue T, Nabata T, Kitano S, et al. Effects of beraprost sodium, a stable analogue of prostacyclin, on hyperplasia, hypertrophy and glycosaminoglycan synthesis of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Artery. 1993; 20:242–252. PMID: 8141645.22. Villa E, Rabano A, Ruilope LM, Garcia-Robles R. Effects of cicaprost and fosinopril on the progression of rat diabetic nephropathy. Am J Hypertens. 1997; 10:202–208. PMID: 9037329.
Article23. Wang LN, Tang Z, Shou I, Fukui M, Tomino Y. Effects of the PGI2 analog beraprost sodium on glomerular prostanoid synthesis in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Nephron. 1996; 73:637–643. PMID: 8856263.24. Fujita T, Fuke Y, Satomura A, Hidaka M, Ohsawa I, Endo M, et al. PGl2 analogue mitigates the progression rate of renal dysfunction improving renal blood flow without glomerular hyperfiltration in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2001; 65:223–227. PMID: 11728176.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Diabetic Nephropathy without Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes
- Diagnosis and test for diabetic kidney disease
- Clinical Significance of Microalbuminuria in Korean Non-diabetic Subjects
- Efficacy and Safety of beraprost sodium in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Complicated with Arteriosclerosis Obliterans (ASO): A Prospective, Multicenter, Open Clinical Study
- Diabetic Nephropathy in Childhood and Adolescence (I) : Clinical Features