J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2019 Dec;60(12):1356-1362. 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.12.1356.
Report of Bilateral Acute Angle-closure Crisis Induced by Serotonin-norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Ophthalmology and Optometry, Department of Ophthalmology, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkeoph@gmail.com
- KMID: 2466196
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2019.60.12.1356
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study reports a case of bilateral acute angle-closure crisis induced by two kinds of serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), duloxetine and tramadol.
CASE SUMMARY
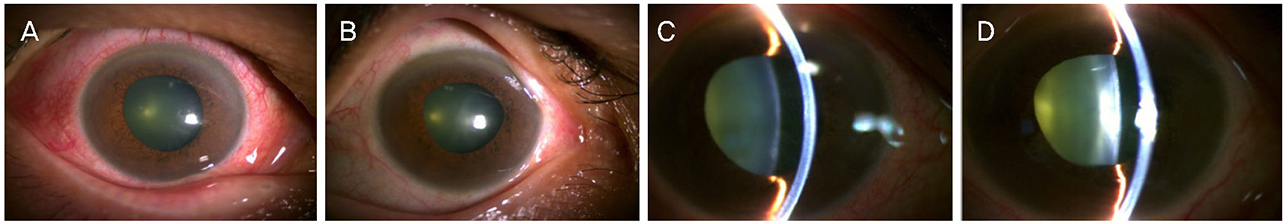
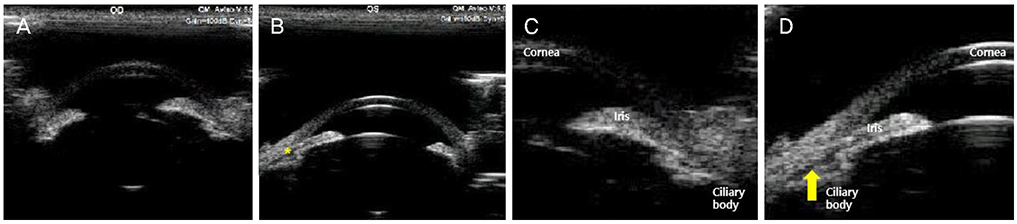
A 55-year-old female visited our clinic, complaining of bilateral visual impairment, ocular pain, and headache, which began 2 days after taking several drugs including duloxetine and tramadol for the purpose of back pain relief. On the day of the first visit, her uncorrected visual acuity was 0.04 in the right eye and 0.02 in the left eye, and the intraocular pressure (IOP) was 45 mmHg in the right eye and 51 mmHg in the left eye. The anterior chamber was shallow and the anterior chamber-angle was closed in both eyes on gonioscopy. There was mild nuclear sclerosis of both lenses. Assuming drug-induced bilateral acute angle-closure crisis, all medications were discontinued, and IOP-lowering agents were prescribed. The symptoms, visual acuity, and IOP improved; however, both anterior chambers were still shallow and the iridocorneal angle was still closed in both eyes. Laser iridotomy was tried in the right eye but failed because the pupils were not completely constricted, and iris bleeding occurred. Phacoemulsification and posterior chamber lens insertion were conducted in both eyes, and her visual acuity, IOP, anterior chamber depth, and iridocorneal angle have been stable at 9 months since her first visit.
CONCLUSIONS
The combined administration of SNRI may cause bilateral acute angle-closure attacks.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lachkar Y, Bouassida W. Drug-induced acute angle closure glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007; 18:129–133.2. Lai JS, Gangwani RA. Medication-induced acute angle closure attack. Hong Kong Med J. 2012; 18:139–145.3. Beakley BD, Kaye AM, Kaye AD. Tramadol, pharmacology, side effects, and serotonin syndrome: a review. Pain Physician. 2015; 18:395–400.4. Cackett P, Cameron JR, Morris B, et al. Bilateral angle-closure glaucoma secondary to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Therapy. 2006; 3:387–388.5. Chen VC, Ng MH, Chiu WC, et al. Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on glaucoma: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0173005. Accessed March 3, 2017. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173005.6. Ah-Kee EY, Egong E, Shafi A, et al. A review of drug-induced acute angle closure glaucoma for non-ophthalmologists. Qatar Med J. 2015; 2015:6.7. Seitz DP, Campbell RJ, Bell CM, et al. Short-term exposure to antidepressant drugs and risk of acute angle-closure glaucoma among older adults. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012; 32:403–407.8. Mahmoud A, Abid F, Ksiaa I, et al. Bilateral acute angle-closure glaucoma following tramadol subcutaneous administration. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018; 18:50.9. Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RB, Rosenbaum JT. Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group. Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the First International Workshop. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:509–516.10. Gündüz GU, Parmak Yener N, Kılınçel O, Gündüz CJC. Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on intraocular pressure and anterior segment parameters in open angle eyes? Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2018; 37:36–40.11. Wiciński M, Kaluzny BJ, Liberski S, et al. Association between serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors and acute angle closure: what is known? Surv Ophthalmol. 2019; 64:185–194.12. de Guzman MH, Thiagalingam S, Ong PY, Goldberg I. Bilateral acute angle closure caused by supraciliary effusions associated with venlafaxine intake. Med J Aust. 2005; 182:121–123.13. Aragona M, Inghilleri M. Increased ocular pressure in two patients with narrow angle glaucoma treated with venlafaxine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1998; 21:130–131.14. Shifera AS, Leoncavallo A, Sherwood M. Probable association of an attack of bilateral acute angle-closure glaucoma with duloxetine. Ann Pharmacother. 2014; 48:936–939.15. Mahmut A, Tunc V, Demiryurek E, Gursoy A. Bilateral acute angle-closure glaucoma induced by duloxetine. Ideggyogy Sz. 2017; 70:358–360.16. Ng B, Sanbrook GM, Malouf AJ, Agarwal SA. Venlafaxine and bilateral acute angle closure glaucoma. Med J Aust. 2002; 176:241.17. Ezra DG, Storoni M, Whitefield LA. Simultaneous bilateral acute angle closure glaucoma following venlafaxine treatment. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:128–129.18. Zhou N, Zhao JX, Zhu YN, et al. Acute angle-closure glaucoma caused by venlafaxine. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018; 131:1502–1503.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacological Treatment of Depression
- Comparison of Bleeding Tendency Between Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors Using Platelet Function Analyzer
- Two Cases of Hyponatremia Induced by Duloxetine for Treating Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
- Triple Reuptake Inhibitors: A Premise and Promise
- Structural Requirements for Modulating 4-Benzylpiperidine Carboxamides from Serotonin/Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors to Triple Reuptake Inhibitors