Clin Endosc.
2019 Nov;52(6):533-540. 10.5946/ce.2018.156.
Elastography of the Pancreas, Current View
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ultrasound Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China. Christoph.dietrich@ckbm.de
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Caritas Hospital Bad Mergentheim, Bad Mergentheim, Germany.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, HELIOS Klinikum Meiningen, Meiningen, Germany.
- KMID: 2465795
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.156
Abstract
- Ultrasound elastography (USE) of the pancreas allows pancreatic tissue stiffness assessment by virtual palpation. Two main types of USE are used. For the pancreas strain elastography applying by endoscopic ultrasound has been established for the characterisation of small solid pancreatic lesions (SPL). In larger SPL >30 mm the results are less convincing mainly due to the heterogenicity of the lesions but also by concomitant changes of the surrounding pancreatic parenchyma. The current role of shear wave elastography has to be determined. This article reviews the current use of elastography of the pancreas.
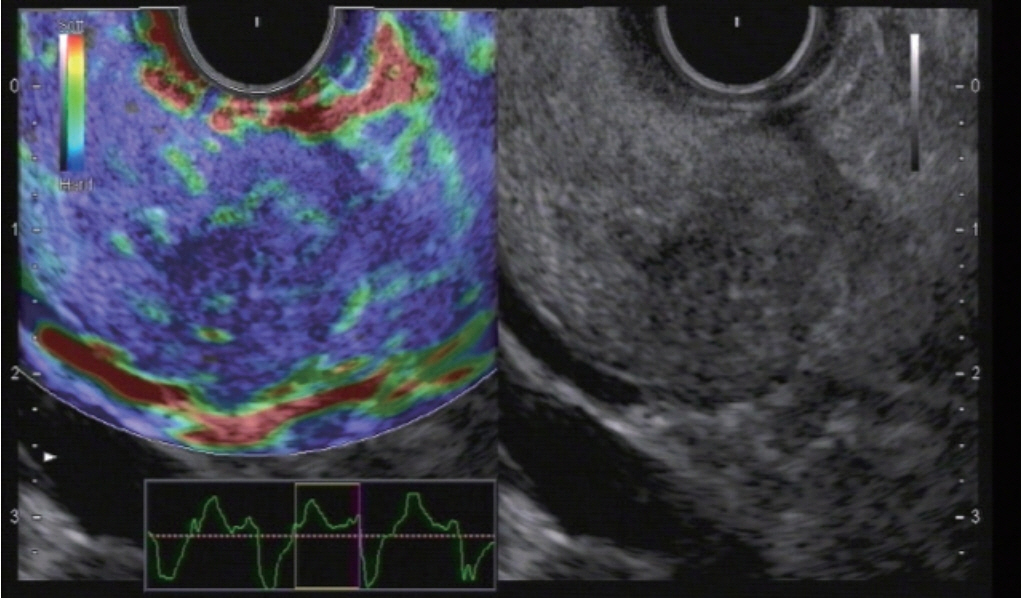
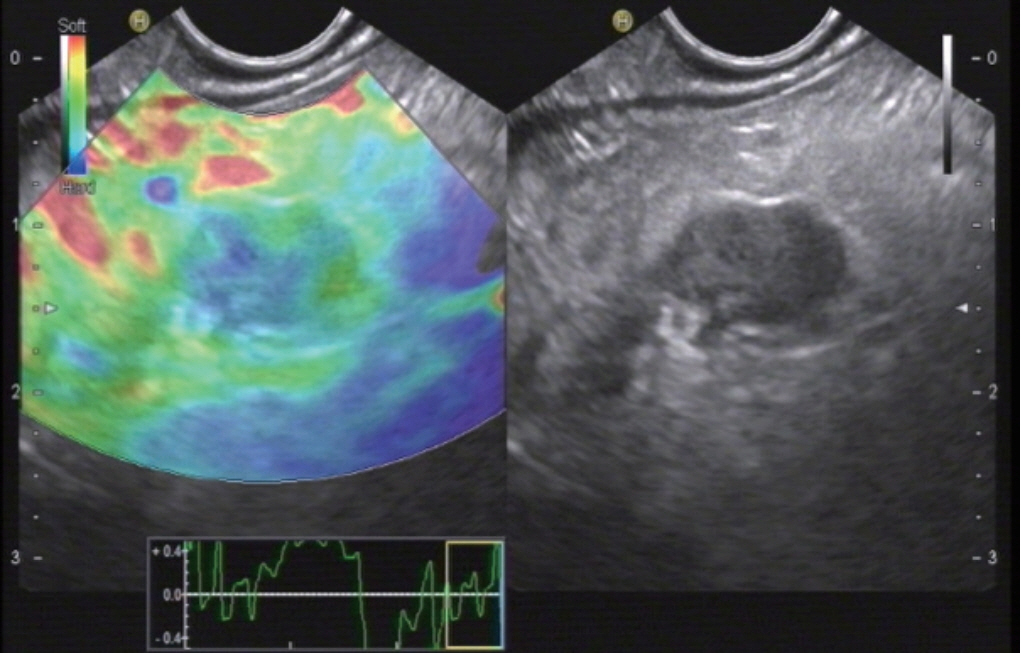
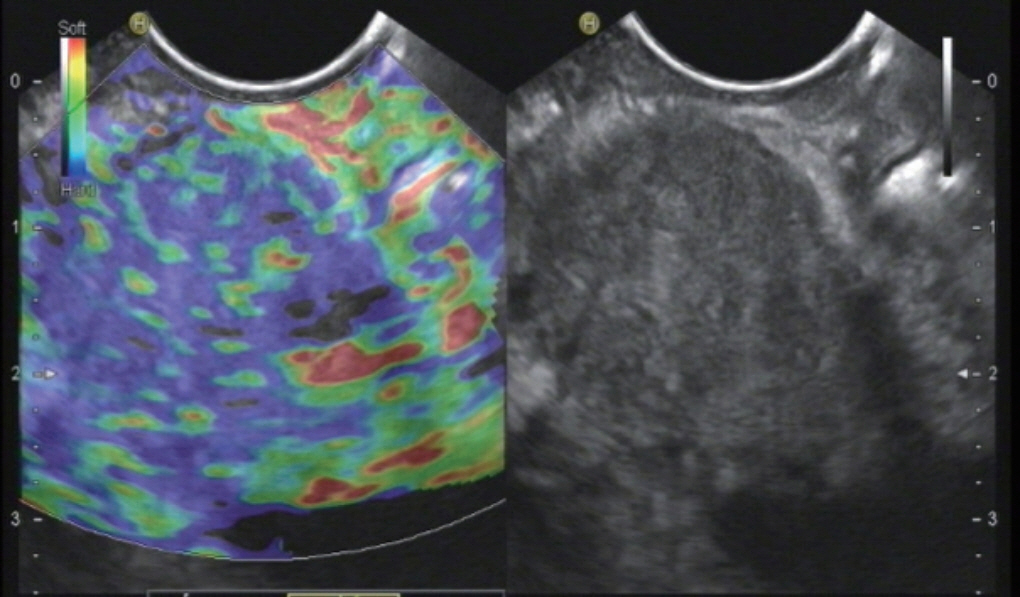
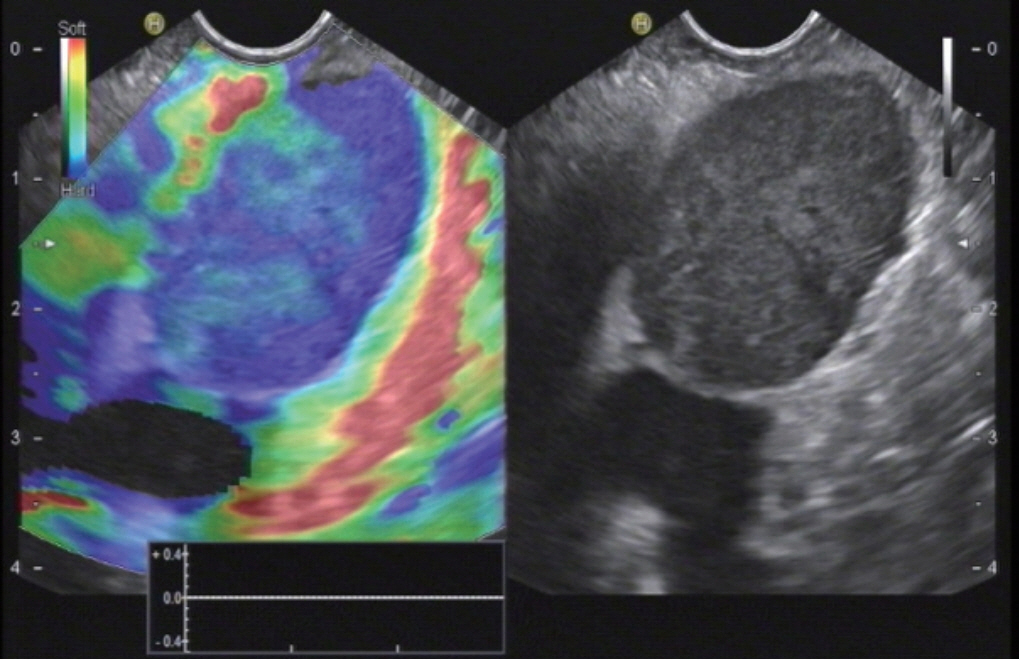
Figure
Reference
-
1. De Molo C, Cui XW, Pirri C, et al. Pancreas mobile. Z Gastroenterol. 2013; 51:1165–1170.
Article2. Pirri C, Cui XW, De Molo C, Ignee A, Schreiber-Dietrich DG, Dietrich CF. The pancreatic head is larger than often assumed. Z Gastroenterol. 2013; 51:390–394.
Article3. Sienz M, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. [Reference values in abdominal ultrasound - biliopancreatic system and spleen]. Z Gastroenterol. 2011; 49:845–870.4. Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med. 2013; 34:169–184.
Article5. Shiina T, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 1: basic principles and terminology. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015; 41:1126–1147.
Article6. Hocke M, Braden B, Jenssen C, Dietrich CF. Present status and perspectives of endosonography 2017 in gastroenterology. Korean J Intern Med. 2018; 33:36–63.
Article7. Saftoiu A, Vilman P. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography-- a new imaging technique for the visualization of tissue elasticity distribution. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2006; 15:161–165.8. Săftoiu A, Vilmann P, Gorunescu F, et al. Efficacy of an artificial neural network-based approach to endoscopic ultrasound elastography in diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:84–90. e1.
Article9. Săftoiu A, Vilmann P, Gorunescu F, et al. Accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound elastography used for differential diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses: a multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:596–603.
Article10. Săftoiu A, Vilmann P. Differential diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses by semiquantitative EUS elastography: between strain ratios and strain histograms. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:188–189.
Article11. Săftoiu A, Vilmann P, Gorunescu F, et al. Neural network analysis of dynamic sequences of EUS elastography used for the differential diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:1086–1094.
Article12. Cosgrove D, Piscaglia F, Bamber J, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: clinical applications. Ultraschall Med. 2013; 34:238–253.13. Ferraioli G, Filice C, Castera L, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 3: liver. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015; 41:1161–1179.
Article14. Dong Y, Sirli R, Ferraioli G, et al. Shear wave elastography of the liver - review on normal values. Z Gastroenterol. 2017; 55:153–166.
Article15. Berzigotti A, Ferraioli G, Bota S, Gilja OH, Dietrich CF. Novel ultrasound-based methods to assess liver disease: the game has just begun. Dig Liver Dis. 2018; 50:107–112.
Article16. Dietrich CF, Bamber J, Berzigotti A, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of liver ultrasound elastography, update 2017 (short version). Ultraschall Med. 2017; 38:377–394.
Article17. Dietrich CF, Bamber J, Berzigotti A, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of liver ultrasound elastography, update 2017 (long version). Ultraschall Med. 2017; 38:e16–e47.
Article18. Ferraioli G, Wong VW, Castera L. Liver ultrasound elastography: an update to the world federation for ultrasound in medicine and biology guidelines and recommendations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2018; 44:2419–2440.
Article19. Dietrich CF, Barr RG, Farrokh A, et al. Strain elastography - how to do it? Ultrasound Int Open. 2017; 3:E137–E149.
Article20. Dietrich CF, Hirche TO, Ott M, Ignee A. Real-time tissue elastography in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:718–720.
Article21. Hirche TO, Ignee A, Barreiros AP, et al. Indications and limitations of endoscopic ultrasound elastography for evaluation of focal pancreatic lesions. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:910–917.
Article22. Havre RF, Ødegaard S, Gilja OH, Nesje LB. Characterization of solid focal pancreatic lesions using endoscopic ultrasonography with real-time elastography. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:742–751.
Article23. Ignee A, Jenssen C, Arcidiacono PG, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography of small solid pancreatic lesions: a multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:1071–1079.
Article24. Chiorean L, Barr RG, Braden B, et al. Transcutaneous ultrasound: elastographic lymph node evaluation. Current clinical applications and literature review. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016; 42:16–30.25. Havre RF, Leh SM, Gilja OH, et al. Differentiation of metastatic and non-metastatic mesenteric lymph nodes by strain elastography in surgical specimens. Ultraschall Med. 2016; 37:366–372.
Article26. Cui XW, Hocke M, Jenssen C, et al. Conventional ultrasound for lymph node evaluation, update 2013. Z Gastroenterol. 2014; 52:212–221.
Article27. Cui XW, Jenssen C, Saftoiu A, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. New ultrasound techniques for lymph node evaluation. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4850–4860.28. Dietrich CF, Hocke M, Jenssen C. [Ultrasound for abdominal lymphadenopathy]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013; 138:1001–1018.29. Dietrich CF, Ponnudurai R, Bachmann Nielsen M. [Is there a need for new imaging methods for lymph node evaluation?]. Ultraschall Med. 2012; 33:411–414.
Article30. Dietrich CF, Bojunga J. [Ultrasound of the thyroid]. Z Gastroenterol. 2015; 53:208–225.31. Cui XW, Chang JM, Kan QC, Chiorean L, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography: current status and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:13212–13224.
Article32. Dietrich CF, Săftoiu A, Jenssen C. Real time elastography endoscopic ultrasound (RTE-EUS), a comprehensive review. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:405–414.
Article33. Janssen J, Dietrich CF, Will U, Greiner L. Endosonographic elastography in the diagnosis of mediastinal lymph nodes. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:952–957.
Article34. Barr RG, Nakashima K, Amy D, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 2: breast. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015; 41:1148–1160.
Article35. Cosgrove D, Barr R, Bojunga J, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 4. Thyroid. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017; 43:4–26.
Article36. Barr RG, Cosgrove D, Brock M, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 5. Prostate. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017; 43:27–48.
Article37. Havre RF, Elde E, Gilja OH, et al. Freehand real-time elastography: impact of scanning parameters on image quality and in vitro intra- and interobserver validations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008; 34:1638–1650.
Article38. Cho N, Moon WK, Chang JM, Kim SJ, Lyou CY, Choi HY. Aliasing artifact depicted on ultrasound (US)-elastography for breast cystic lesions mimicking solid masses. Acta Radiol. 2011; 52:3–7.
Article39. Gallotti A, D’Onofrio M, Pozzi Mucelli R. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) technique in ultrasound with virtual touch tissue quantification of the upper abdomen. Radiol Med. 2010; 115:889–897.
Article40. Janssen J, Papavassiliou I. Effect of aging and diffuse chronic pancreatitis on pancreas elasticity evaluated using semiquantitative EUS elastography. Ultraschall Med. 2014; 35:253–258.
Article41. Chantarojanasiri T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Age-related changes in pancreatic elasticity: when should we be concerned about their effect on strain elastography? Ultrasonics. 2016; 69:90–96.
Article42. Kawada N, Tanaka S, Uehara H, et al. Potential use of point shear wave elastography for the pancreas: a single center prospective study. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:620–624.
Article43. Stumpf S, Jaeger H, Graeter T, et al. Influence of age, sex, body mass index, alcohol, and smoking on shear wave velocity (p-SWE) of the pancreas. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016; 41:1310–1316.
Article44. Yashima Y, Sasahira N, Isayama H, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for noninvasive assessment of chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47:427–432.
Article45. Arda K, Ciledag N, Aktas E, Aribas BK, Köse K. Quantitative assessment of normal soft-tissue elasticity using shear-wave ultrasound elastography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:532–536.
Article46. Goertz RS, Schuderer J, Strobel D, Pfeifer L, Neurath MF, Wildner D. Acoustic radiation force impulse shear wave elastography (ARFI) of acute and chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic tumor. Eur J Radiol. 2016; 85:2211–2216.
Article47. Xie J, Zou L, Yao M, et al. A preliminary investigation of normal pancreas and acute pancreatitis elasticity using virtual touch tissue quantification (VTQ) imaging. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21:1693–1699.
Article48. Mateen MA, Muheet KA, Mohan RJ, et al. Evaluation of ultrasound based acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) and eSie touch sonoelastography for diagnosis of inflammatory pancreatic diseases. JOP. 2012; 13:36–44.49. Göya C, Hamidi C, Hattapoğlu S, et al. Use of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography to diagnose acute pancreatitis at hospital admission: comparison with sonography and computed tomography. J Ultrasound Med. 2014; 33:1453–1460.50. D’Onofrio M, Tremolada G, De Robertis R, et al. Prevent pancreatic fistula after pancreatoduodenectomy: possible role of ultrasound elastography. Dig Surg. 2018; 35:164–170.
Article51. Harada N, Ishizawa T, Inoue Y, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the pancreas for estimation of pathologic fibrosis and risk of postoperative pancreatic fistula. J Am Coll Surg. 2014; 219:887–894. e5.
Article52. Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis using EUS elastography. J Gastroenterol. 2017; 52:868–874.
Article53. Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative evaluation of pancreatic tumor fibrosis using shear wave elastography. Pancreatology. 2016; 16:1063–1068.
Article54. Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography-elastography as a predictive tool for the occurrence of pancreatic fistula after pancreatoduodenectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2017; 24:649–656.
Article55. Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Usefulness of shear wave elastography as a quantitative diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33:756–761.
Article56. Pozzi R, Parzanese I, Baccarin A, et al. Point shear-wave elastography in chronic pancreatitis: a promising tool for staging disease severity. Pancreatology. 2017; 17:905–910.
Article57. Llamoza-Torres CJ, Fuentes-Pardo M, Álvarez-Higueras FJ, Alberca-de-Las-Parras F, Carballo-Álvarez F. Usefulness of percutaneous elastography by acoustic radiation force impulse for the non-invasive diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2016; 108:450–456.
Article58. Dominguez-Muñoz JE, Iglesias-Garcia J, Castiñeira Alvariño M, Luaces Regueira M, Lariño-Noia J. EUS elastography to predict pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:136–142.59. Harada N, Yoshizumi T, Maeda T, et al. Preoperative pancreatic stiffness by real-time tissue elastography to predict pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Anticancer Res. 2017; 37:1909–1915.60. Iglesias-Garcia J, Larino-Noia J, Abdulkader I, Forteza J, Dominguez-Munoz JE. Quantitative endoscopic ultrasound elastography: an accurate method for the differentiation of solid pancreatic masses. Gastroenterology. 2010; 139:1172–1180.
Article61. Rana SS, Dambalkar A, Chhabra P, et al. Is pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in celiac disease related to structural alterations in pancreatic parenchyma? Ann Gastroenterol. 2016; 29:363–366.
Article62. Janssen J, Schlörer E, Greiner L. EUS elastography of the pancreas: feasibility and pattern description of the normal pancreas, chronic pancreatitis, and focal pancreatic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:971–978.
Article63. Itoh Y, Itoh A, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative analysis of diagnosing pancreatic fibrosis using EUS-elastography (comparison with surgical specimens). J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:1183–1192.
Article64. Domínguez-Muñoz JE. Predicting pancreatic exocrine insufficiency with EUS elastography. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016; 12:511–512.65. Uchida H, Hirooka Y, Itoh A, et al. Feasibility of tissue elastography using transcutaneous ultrasonography for the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. Pancreas. 2009; 38:17–22.
Article66. Friedrich-Rust M, Schlueter N, Smaczny C, et al. Non-invasive measurement of liver and pancreas fibrosis in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2013; 12:431–439.
Article67. Sugimoto M, Takahashi S, Kojima M, et al. What is the nature of pancreatic consistency? Assessment of the elastic modulus of the pancreas and comparison with tactile sensation, histology, and occurrence of postoperative pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surgery. 2014; 156:1204–1211.
Article68. Hatano M, Watanabe J, Kushihata F, et al. Quantification of pancreatic stiffness on intraoperative ultrasound elastography and evaluation of its relationship with postoperative pancreatic fistula. Int Surg. 2015; 100:497–502.
Article69. Kim SY, Cho JH, Kim YJ, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of quantitative endoscopic ultrasound elastography for differentiating pancreatic disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32:1115–1122.
Article70. D’Onofrio M, Crosara S, De Robertis R, Canestrini S, Demozzi E, Pozzi Mucelli R. Elastography of the pancreas. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:415–419.
Article71. Dong Y, D’Onofrio M, Hocke M, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: imaging features. Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:196–203.
Article72. Dong Y, Potthoff A, Klinger C, Barreiros AP, Pietrawski D, Dietrich CF. Ultrasound findings in autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2018; 24:1583–1590.
Article73. Hocke M, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2011; 43 Suppl 2 UCTN:E381–E382.
Article74. Hocke M, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. Contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:163–165.
Article75. Dong Y, Jürgensen C, Puri R, et al. Ultrasound imaging features of isolated pancreatic tuberculosis. Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:119–127.
Article76. Barreiros AP, Braden B, Schieferstein-Knauer C, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. Characteristics of intestinal tuberculosis in ultrasonographic techniques. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008; 43:1224–1231.
Article77. Lee TK, Kang CM, Park MS, et al. Prediction of postoperative pancreatic fistulas after pancreatectomy: assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse elastography. J Ultrasound Med. 2014; 33:781–786.78. Hocke M, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. Advanced endosonographic diagnostic tools for discrimination of focal chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma--elastography, contrast enhanced high mechanical index (CEHMI) and low mechanical index (CELMI) endosonography in direct comparison. Z Gastroenterol. 2012; 50:199–203.79. Wang W, Shpaner A, Krishna SG, et al. Use of EUS-FNA in diagnosing pancreatic neoplasm without a definitive mass on CT. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:73–80.
Article80. Krishna NB, Tummala P, Mehan CD, Reddy AV, Hartman JA, Agarwal B. Small and potentially resectable focal pancreatic lesions noted on CT/MRI scans in nonjaundiced patients: likelihood of neoplasia and utility of EUS. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:793–800.
Article81. Haba S, Yamao K, Bhatia V, et al. Diagnostic ability and factors affecting accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic solid lesions: Japanese large single center experience. J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:973–981.
Article82. Dawwas MF, Taha H, Leeds JS, Nayar MK, Oppong KW. Diagnostic accuracy of quantitative EUS elastography for discriminating malignant from benign solid pancreatic masses: a prospective, single-center study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:953–961.
Article83. Săftoiu A. State-of-the-art imaging techniques in endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:691–696.
Article84. Itokawa F, Itoi T, Sofuni A, et al. EUS elastography combined with the strain ratio of tissue elasticity for diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:843–853.
Article85. Hocke M, Topalidis T, Braden B, Dietrich CF. “Clinical” cytology for endoscopists: a practical guide. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6:83–89.
Article86. Onoyama T, Koda M, Fujise Y, et al. Utility of virtual touch quantification in the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Imaging. 2017; 42:64–67.
Article87. D’Onofrio M, De Robertis R, Crosara S, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse with shear wave speed quantification of pancreatic masses: a prospective study. Pancreatology. 2016; 16:106–109.
Article88. Park MK, Jo J, Kwon H, et al. Usefulness of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant solid pancreatic lesions. Ultrasonography. 2014; 33:26–33.
Article89. Hirooka Y, Kuwahara T, Irisawa A, et al. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: pancreas. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2015; 42:151–174.
Article90. Kawada N, Tanaka S. Elastography for the pancreas: current status and future perspective. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:3712–3724.
Article91. Chantarojanasiri T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound in diagnosis of solid pancreatic lesions: elastography or contrast-enhanced harmonic alone versus the combination. Endosc Int Open. 2017; 5:E1136–E1143.
Article92. Dyrla P, Gil J, Florek M, et al. Elastography in pancreatic solid tumours diagnoses. Prz Gastroenterol. 2015; 10:41–46.
Article93. Iglesias García JJ, Lariño Noia J, Alvarez Castro A, Cigarrán B, Domínguez Muñoz JE. Second-generation endoscopic ultrasound elastography in the differential diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses. Pancreatic cancer vs. inflammatory mass in chronic pancreatitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2009; 101:723–730.
Article94. Iglesias-Garcia J, Domínguez-Muñoz JE, Castiñeira-Alvariño M, Luaces-Regueira M, Lariño-Noia J. Quantitative elastography associated with endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:781–788.
Article95. Iglesias-Garcia J, Lindkvist B, Lariño-Noia J, Abdulkader-Nallib I, Dominguez-Muñoz JE. Differential diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses: contrast-enhanced harmonic (CEH-EUS), quantitative-elastography (QE-EUS), or both? United European Gastroenterol J. 2017; 5:236–246.96. Iordache S, Costache MI, Popescu CF, Streba CT, Cazacu S, Săftoiu A. Clinical impact of EUS elastography followed by contrast-enhanced EUS in patients with focal pancreatic masses and negative EUS-guided FNA. Med Ultrason. 2016; 18:18–24.
Article97. Kawada N, Tanaka S, Uehara H, et al. Alteration of strain ratio evaluated by transabdominal ultrasound elastography may predict the efficacy of preoperative chemoradiation performed for pancreatic ductal carcinoma: preliminary results. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014; 61:480–483.98. Kongkam P, Lakananurak N, Navicharern P, et al. Combination of EUS-FNA and elastography (strain ratio) to exclude malignant solid pancreatic lesions: a prospective single-blinded study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 30:1683–1689.
Article99. Opačić D, Rustemović N, Kalauz M, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography strain histograms in the evaluation of patients with pancreatic masses. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:4014–4019.
Article100. Rustemović N, Kalauz M, Grubelić Ravić K, et al. Differentiation of pancreatic masses via endoscopic ultrasound strain ratio elastography using adjacent pancreatic tissue as the reference. Pancreas. 2017; 46:347–351.
Article101. Dietrich CF. [Elastography, the new dimension in ultrasonography]. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2011; 100:1533–1542.102. Dietrich CF, Cantisani V. Current status and perspectives of elastography. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:403–404.
Article103. Azemoto N, Kumagi T, Koizumi M, et al. Diagnostic challenge in pancreatic sarcoidosis using endoscopic ultrasonography. Intern Med. 2018; 57:231–235.
Article104. Chantarojanasiri T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis of acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas: contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound elastography, and pathological correlation. Endosc Int Open. 2016; 4:E1223–E1226.
Article105. Jafri M, Sachdev AH, Khanna L, Gress FG. The role of real time endoscopic ultrasound guided elastography for targeting EUS-FNA of suspicious pancreatic masses: a review of the literature and a single center experience. JOP. 2016; 17:516–524.106. Lee TH, Cho YD, Cha SW, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography for the pancreas in Korea: a preliminary single center study. Clin Endosc. 2013; 46:172–177.
Article107. Pei Q, Zou X, Zhang X, Chen M, Guo Y, Luo H. Diagnostic value of EUS elastography in differentiation of benign and malignant solid pancreatic masses: a meta-analysis. Pancreatology. 2012; 12:402–408.
Article108. Popescu A, Ciocalteu AM, Gheonea DI, et al. Utility of endoscopic ultrasound multimodal examination with fine needle aspiration for the diagnosis of pancreatic insulinoma - a case report. Curr Health Sci J. 2012; 38:36–40.109. Rana SS, Sharma R, Guleria S, Gupta R. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) elastography and contrast enhanced EUS in groove pancreatitis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018; 37:70–71.
Article110. Schrader H, Wiese M, Ellrichmann M, et al. Diagnostic value of quantitative EUS elastography for malignant pancreatic tumors: relationship with pancreatic fibrosis. Ultraschall Med. 2012; 33:E196–E201.111. Soares JB, Iglesias-Garcia J, Goncalves B, et al. Interobserver agreement of EUS elastography in the evaluation of solid pancreatic lesions. Endosc Ultrasound. 2015; 4:244–249.
Article112. Rustemovic N, Opacic D, Ostojic Z, et al. Comparison of elastography methods in patients with pancreatic masses. Endosc Ultrasound. 2014; 3(Suppl 1):S4.113. He Y, Wang H, Li XP, Zheng JJ, Jin CX. Pancreatic elastography from acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for evaluation of diabetic microangiopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017; 209:775–780.
Article114. Sağlam D, Bilgici MC, Kara C, Yilmaz GC, Çamlıdağ I. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in determining the effects of type 1 diabetes on pancreas and kidney elasticity in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017; 209:1143–1149.
Article115. Zaro R, Lupsor-Platon M, Cheviet A, Badea R. The pursuit of normal reference values of pancreas stiffness by using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography. Med Ultrason. 2016; 18:425–430.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- EUS Elastography: Advances in Diagnostic EUS of the Pancreas
- Ultrasound elastography of the thyroid: principles and current status
- Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules by Elastography
- Elastographic measurement of the cervix during pregnancy: Current status and future challenges
- Ultrasound elastography for thyroid nodules: recent advances