J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2018 Aug;48(4):261-271. 10.5051/jpis.2018.48.4.261.
Real-time PCR quantification of 9 periodontal pathogens in saliva samples from periodontally healthy Korean young adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Institute of Translational Dental Sciences, Pusan National University School of Dentistry, Yangsan, Korea. joojy@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Gerotech Inc., Ulsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Periodontology and Dental Research Institute, Pusan National University Dental Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2465391
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2018.48.4.261
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Few studies have examined periodontal pathogens from saliva samples in periodontally healthy young adults. The purposes of this study were to determine the prevalence of periodontopathic bacteria and to quantify periodontal pathogens in saliva samples using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays in periodontally healthy Korean young adults under 35 years of age.
METHODS
Nine major periodontal pathogens were analyzed by real-time PCR in saliva from 94 periodontally healthy young adults. Quantification of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, Treponema denticola, Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Campylobacter rectus, Peptostreptococcus anaerobius, and Eikenella corrodens was performed by DNA copy number measurement.
RESULTS
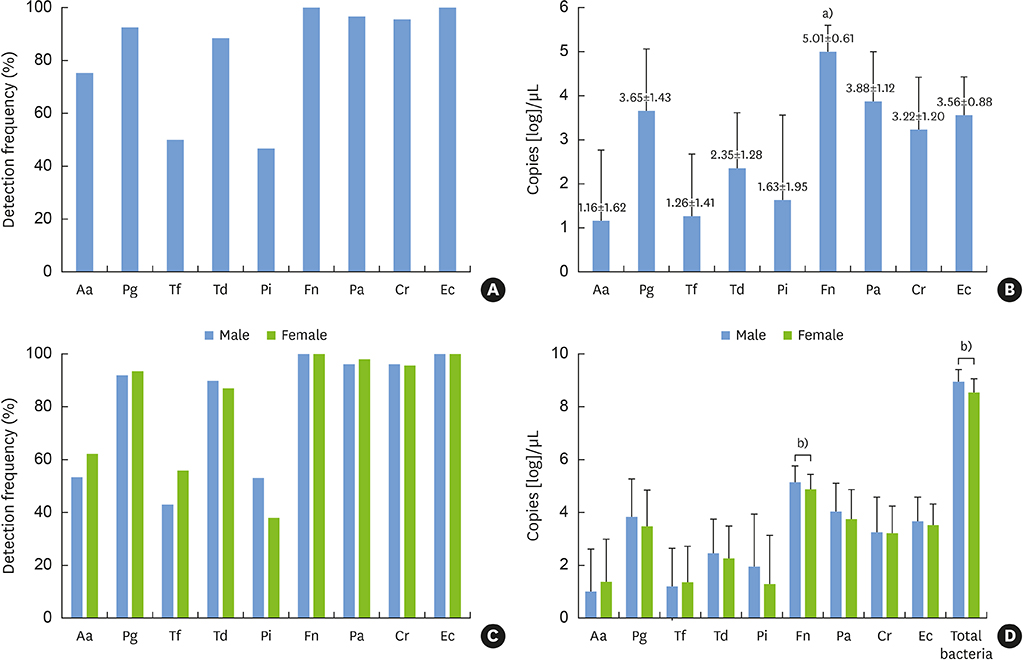
F. nucleatum and E. corrodens were detected in all subjects; the numbers of positive samples were 87 (92.6%), 91 (96.8%), and 90 (95.7%) for P. gingivalis, P. anaerobius, and C. rectus, respectively. Other pathogens were also detected in periodontally healthy subjects. Analysis of DNA copy numbers revealed that the most abundant periodontal pathogen was F. nucleatum, which was significantly more prevalent than all other bacteria (P < 0.001), followed by P. anaerobius, P. gingivalis, E. corrodens, C. rectus, and T. denticola. There was no significant difference in the prevalence of each bacterium between men and women. The DNA copy number of total bacteria was significantly higher in men than in women.
CONCLUSIONS
Major periodontal pathogens were prevalent in the saliva of periodontally healthy Korean young adults. Therefore, we suggest that the development of periodontal disease should not be overlooked in periodontally healthy young people, as it can arise due to periodontal pathogen imbalance and host susceptibility.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Bacteria
Bacterial Load
Campylobacter rectus
Chronic Periodontitis
DNA
Eikenella corrodens
Female
Forsythia
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Healthy Volunteers
Humans
Male
Peptostreptococcus
Periodontal Diseases
Porphyromonas gingivalis
Prevalence
Prevotella intermedia
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction*
Saliva*
Treponema denticola
Young Adult*
DNA
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mark Bartold P, Van Dyke TE. Host modulation: controlling the inflammation to control the infection. Periodontol 2000. 2017; 75:317–329.
Article2. Socransky SS, Haffajee AD, Cugini MA, Smith C, Kent RL Jr. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol. 1998; 25:134–144.
Article3. Cullinan MP, Hamlet SM, Westerman B, Palmer JE, Faddy MJ, Seymour GJ. Acquisition and loss of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Prevotella intermedia over a 5-year period: effect of a triclosan/copolymer dentifrice. J Clin Periodontol. 2003; 30:532–541.
Article4. Aas JA, Paster BJ, Stokes LN, Olsen I, Dewhirst FE. Defining the normal bacterial flora of the oral cavity. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:5721–5732.
Article5. Haffajee AD, Socransky SS. Microbial etiological agents of destructive periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 1994; 5:78–111.
Article6. Socransky SS, Haffajee AD. Dental biofilms: difficult therapeutic targets. Periodontol 2000. 2002; 28:12–55.
Article7. Yang EY, Tanner AC, Milgrom P, Mokeem SA, Riedy CA, Spadafora AT, et al. Periodontal pathogen detection in gingiva/tooth and tongue flora samples from 18- to 48-month-old children and periodontal status of their mothers. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002; 17:55–59.
Article8. Tanner AC, Milgrom PM, Kent R Jr, Mokeem SA, Page RC, Riedy CA, et al. The microbiota of young children from tooth and tongue samples. J Dent Res. 2002; 81:53–57.
Article9. Könönen E. Pigmented Prevotella species in the periodontally healthy oral cavity. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993; 6:201–205.10. McClellan DL, Griffen AL, Leys EJ. Age and prevalence of Porphyromonas gingivalis in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1996; 34:2017–2019.
Article11. Kamma JJ, Diamanti-Kipioti A, Nakou M, Mitsis FJ. Profile of subgingival microbiota in children with mixed dentition. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2000; 15:103–111.
Article12. Lamell CW, Griffen AL, McClellan DL, Leys EJ. Acquisition and colonization stability of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in children. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:1196–1199.
Article13. Loomer PM. Microbiological diagnostic testing in the treatment of periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 2004; 34:49–56.
Article14. Sanz M, Lau L, Herrera D, Morillo JM, Silva A. Methods of detection of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythensis in periodontal microbiology, with special emphasis on advanced molecular techniques: a review. J Clin Periodontol. 2004; 31:1034–1047.
Article15. Göhler A, Hetzer A, Holtfreter B, Geisel MH, Schmidt CO, Steinmetz I, et al. Quantitative molecular detection of putative periodontal pathogens in clinically healthy and periodontally diseased subjects. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e99244.
Article16. Jünemann S, Prior K, Szczepanowski R, Harks I, Ehmke B, Goesmann A, et al. Bacterial community shift in treated periodontitis patients revealed by ion torrent 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e41606.
Article17. Ammann TW, Bostanci N, Belibasakis GN, Thurnheer T. Validation of a quantitative real-time PCR assay and comparison with fluorescence microscopy and selective agar plate counting for species-specific quantification of an in vitro subgingival biofilm model. J Periodontal Res. 2013; 48:517–526.
Article18. Shet UK, Oh HK, Kim HJ, Chung HJ, Kim YJ, Kim OS, et al. Quantitative analysis of periodontal pathogens present in the saliva of geriatric subjects. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013; 43:183–190.
Article19. Umeda M, Contreras A, Chen C, Bakker I, Slots J. The utility of whole saliva to detect the oral presence of periodontopathic bacteria. J Periodontol. 1998; 69:828–833.
Article20. Kim JJ, Kim CJ, Camargo PM. Salivary biomarkers in the diagnosis of periodontal diseases. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2013; 41:119–124.21. Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H, Feres M, Lopez NJ, Socransky SS. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol. 2004; 31:996–1002.
Article22. Darveau RP, Hajishengallis G, Curtis MA. Porphyromonas gingivalis as a potential community activist for disease. J Dent Res. 2012; 91:816–820.
Article23. Feres M, Teles F, Teles R, Figueiredo LC, Faveri M. The subgingival periodontal microbiota of the aging mouth. Periodontol 2000. 2016; 72:30–53.
Article24. Zhuang LF, Watt RM, Mattheos N, Si MS, Lai HC, Lang NP. Periodontal and peri-implant microbiota in patients with healthy and inflamed periodontal and peri-implant tissues. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016; 27:13–21.
Article25. Testa M, Ruiz de Valladares R, Benito de Cárdenas IL. Correlation between bacterial counts in saliva and subgingival plaque. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 1999; 12:63–74.26. Sakamoto M, Takeuchi Y, Umeda M, Ishikawa I, Benno Y. Rapid detection and quantification of five periodontopathic bacteria by real-time PCR. Microbiol Immunol. 2001; 45:39–44.
Article27. Marsh PD, Moter A, Devine DA. Dental plaque biofilms: communities, conflict and control. Periodontol 2000. 2011; 55:16–35.
Article28. Arenas Rodrigues VA, de Avila ED, Nakano V, Avila-Campos MJ. Qualitative, quantitative and genotypic evaluation of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and Fusobacterium nucleatum isolated from individuals with different periodontal clinical conditions. Anaerobe. 2018; 52:50–58.
Article29. Zhou X, Liu X, Li J, Aprecio RM, Zhang W, Li Y. Real-time PCR quantification of six periodontal pathogens in saliva samples from healthy young adults. Clin Oral Investig. 2015; 19:937–946.
Article30. Papapanou PN, Neiderud AM, Papadimitriou A, Sandros J, Dahlén G. “Checkerboard” assessments of periodontal microbiota and serum antibody responses: a case-control study. J Periodontol. 2000; 71:885–897.
Article31. Griffen AL, Becker MR, Lyons SR, Moeschberger ML, Leys EJ. Prevalence of Porphyromonas gingivalis and periodontal health status. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:3239–3242.
Article32. Amano A, Kuboniwa M, Nakagawa I, Akiyama S, Morisaki I, Hamada S. Prevalence of specific genotypes of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimA and periodontal health status. J Dent Res. 2000; 79:1664–1668.
Article33. Hyvärinen K, Laitinen S, Paju S, Hakala A, Suominen-Taipale L, Skurnik M, et al. Detection and quantification of five major periodontal pathogens by single copy gene-based real-time PCR. Innate Immun. 2009; 15:195–204.
Article34. Haffajee AD, Japlit M, Bogren A, Kent RL Jr, Goodson JM, Socransky SS. Differences in the subgingival microbiota of Swedish and USA subjects who were periodontally healthy or exhibited minimal periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 2005; 32:33–39.
Article35. Lira-Junior R, Åkerman S, Klinge B, Boström EA, Gustafsson A. Salivary microbial profiles in relation to age, periodontal, and systemic diseases. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0189374.
Article36. Nonnenmacher C, Dalpke A, Rochon J, Flores-de-Jacoby L, Mutters R, Heeg K. Real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection and quantification of bacteria in periodontal patients. J Periodontol. 2005; 76:1542–1549.
Article37. Papaioannou W, Gizani S, Haffajee AD, Quirynen M, Mamai-Homata E, Papagiannoulis L. The microbiota on different oral surfaces in healthy children. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2009; 24:183–189.
Article38. Bartold PM, Van Dyke TE. Periodontitis: a host-mediated disruption of microbial homeostasis. Unlearning learned concepts. Periodontol 2000. 2013; 62:203–217.
Article39. Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ. How has research into cytokine interactions and their role in driving immune responses impacted our understanding of periodontitis? J Clin Periodontol. 2011; 38:Suppl 11. 60–84.
Article40. Ebersole JL, Dawson DR 3rd, Morford LA, Peyyala R, Miller CS, Gonzaléz OA. Periodontal disease immunology: ‘double indemnity’ in protecting the host. Periodontol 2000. 2013; 62:163–202.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and abundance of 9 periodontal pathogens in the saliva of periodontally healthy adults and patients undergoing supportive periodontal therapy
- Comparison between Real-Time PCR and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis for DNA Quantification
- Influence of Standard Curves on Relative Quantification using Real-time PCR
- Efficacy of salivary versus subgingival bacterial sampling for the detection and quantification of periodontal pathogens
- Quantitative analysis of periodontal pathogens present in the saliva of geriatric subjects