J Korean Soc Radiol.
2019 Nov;80(6):1229-1234. 10.3348/jksr.2019.80.6.1229.
Exercise-Induced Paraspinal Muscle Rhabdomyolysis with Seconary Compartment Syndrome: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hongage8@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2464919
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2019.80.6.1229
Abstract
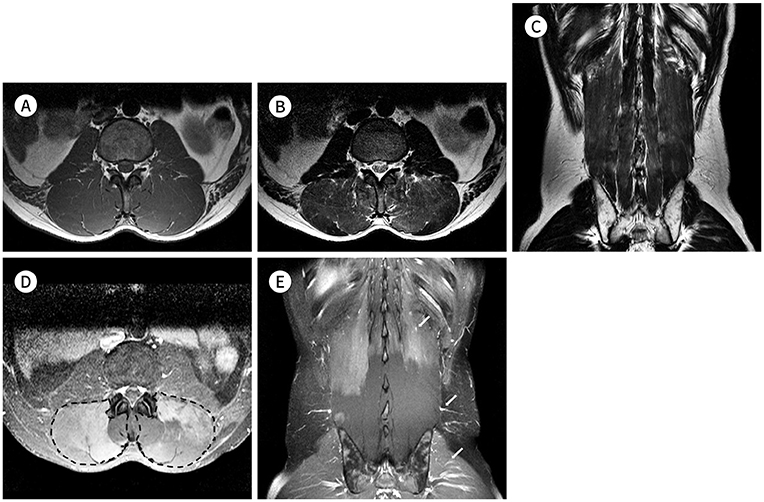
- Lumbar paraspinal compartment syndrome is an uncommon cause of acute lower back pain. It can result from intense physical activity or as a complication of surgery or medication. Lumbar paraspinal compartment syndrome without external trauma is rarely reported in literature. We report a case of compartment syndrome that followed back muscle exercise and caused rhabdomyolysis. MRI findings include bilateral bulging of the paraspinal muscle, hyperintensity on T2-weighted image, and heterogeneous enhancement. Moreover, loss of intramuscular vasculature on a contrast-enhanced CT scan attributed to diagnose compartment syndrome in this case.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alfaraj AM, Alfaraj ZM, Alsahwan AG. Acute lumbar paraspinal compartment syndrome: a case report and detailed literature review. Int Surg J. 2017; 4:775–779.2. Alexander W, Low N, Pratt G. Acute lumbar paraspinal compartment syndrome: a systematic review. ANZ J Surg. 2018; 88:854–859.3. Rogers ME, Lowe JA, Vanlandingham SC. Acute erector spinae compartment syndrome: case report and review of diagnostic criteria. Injury. 2014; 45:813–815.4. Rominger MB, Lukosch CJ, Bachmann GF. MR imaging of compartment syndrome of the lower leg: a case control study. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:1432–1439.5. Weng KH, Tzeng WS, Shu GH, Lo CW, Chen CK. Magnetic resonance imaging of compartment syndrome: report of three cases. J Radiol Sci. 2013; 38:65–70.6. Nathan ST, Roberts CS, Deliberato D. Lumbar paraspinal compartment syndrome. Int Orthop. 2012; 36:1221–1227.7. Ringler MD, Litwiller DV, Felmlee JP, Shahid KR, Finnoff JT, Carter RE, et al. MRI accurately detects chronic exertional compartment syndrome: a validation study. Skeletal Radiol. 2013; 42:385–392.8. Mattiassich G, Larcher L, Leitinger M, Trinka E, Wechselberger G, Schubert H. Paravertebral compartment syndrome after training causing severe back pain in an amateur rugby player: report of a rare case and review of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013; 14:259.9. Kanaya H, Enokida M, Tanishima S, Hayashi I, Tanida A, Nagashima H. Conservative treatment for lumbar compartment syndrome shows efficacy over 2-year follow-up: a case report and literature review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017; 137:1233–1238.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Dorsal Compartment Syndrome of the Forearm in a Patient with Rhabdomyolysis
- Acute Lumbar Paraspinal Compartment Syndrome after Weightlifting: A Case Report
- Acute Compartment Syndrome Which Causes Rhabdomyolysis by Carbon Monoxide Poisoning and Sciatic Nerve Injury Associated with It: A Case Report
- Sciatic Nerve Palsy Complicating Gluteal Compartment Syndrome due to Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report
- Lumbar Paraspinal Rhabdomyolysis after a Prostatectomy: A Case Report