J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Jun;62(6):571-573.
Lumbar Paraspinal Rhabdomyolysis after a Prostatectomy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul Veterans Hospital, Seoul, Korea. orabykim@lycos.co.kr
Abstract
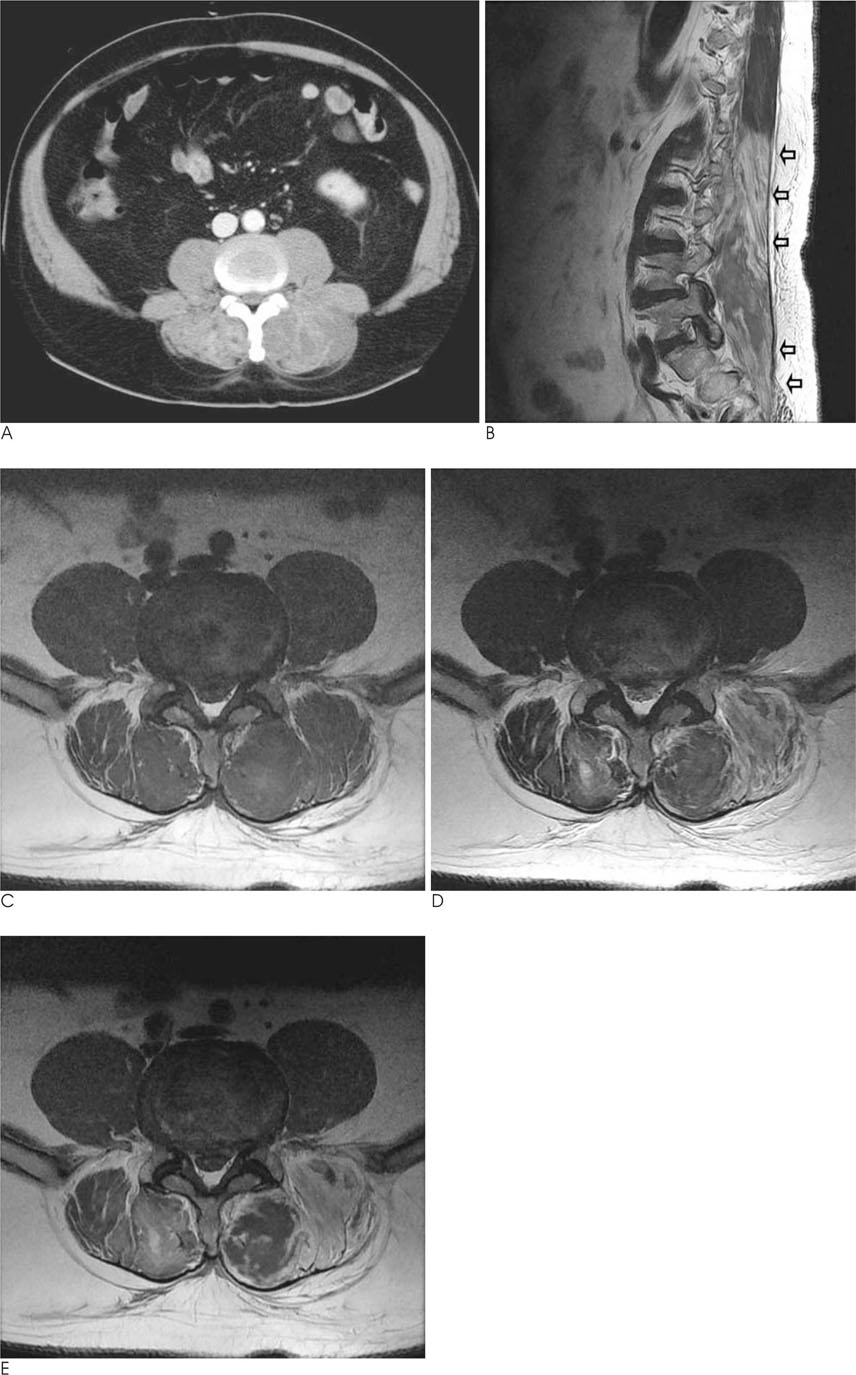
- Acute rhabdomyolysis corresponds to the destruction of striated muscles causing the release of their cellular contents into the plasma and circulation. It could be caused by alcohol abuse, drug abuse, infection, trauma, exertional exercise, and coma. Rhabdomyolysis associcated with surgery is rare, however, we present a case of bilateral paraspinal rhadomyolysis after a prostatectomy in the supine position.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vonholder R, Sever MS, Erek E, Lameire N. Rhabdomyolysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000; 11:1553–1561.2. Ferreira J, Galle C, Aminian A, Michel P, Guyot S, Wilde JP, et al. Lumbar paraspinal rhabdomyolysis and compartment syndrome after abdominal aortic aneurysmrepair. J Vasc Surg. 2003; 37:198–201.3. Jung KC, Kwon ST, Cho KH, Kang SK, Kim JM. MR Findings of Acute Rhabdomyolysis: Case Report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003; 49:119–123.4. Glassman DT, Merriam WG, Trabulsi EJ, Byrne D, Gomella L. Rhabdomyolysis after laparoscopic nephrectomy. JSLS. 2007; 11:432–437.5. Lee JH, Yoon YS, Park IC, Kim SH. Rhabdomyolysis due to Sunburn. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2003; 14:455–457.6. Lappalainen H, Tiula E, Uotila L. Elimination kinetics of myoglobin and creatine kinase in rhabdomyolysis: implications for followup. Crit Care Med. 2002; 30:2212–2215.7. Sava J, Moelleken A, Waxman K. Cardiac arrest caused by reperfusion injury after lumbar paraspinal compartment syndrome. J Trauma. 1999; 46:196–197.8. Osamura N, Takahashi K, Endo M, Kurumaya H, Shima I. Lumbar paraspinal myonecrosis after abdominal vascular surgery: a case report. Spine. 2000; 25:1852–1854.9. Stock KW, Helwig A. MRI of acute exertional rhabdomyolysis--in the paraspinal compartment. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996; 20:834–836.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Exercise-Induced Paraspinal Muscle Rhabdomyolysis with Seconary Compartment Syndrome: A Case Report
- Lumbar plexopathy after radical nephrectomy: A case report
- Acute Lumbar Paraspinal Compartment Syndrome after Weightlifting: A Case Report
- Rhabdomyolysis following posterior lumbar interbody fusion in prone position: report 2 cases: Two cases report
- Rhabdomyolysis in Aortic Surgery: case report