Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Nov;74(5):267-273. 10.4166/kjg.2019.74.5.267.
New Potential Therapies for Chronic Hepatitis B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea. doctorkwon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2464185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.74.5.267
Abstract
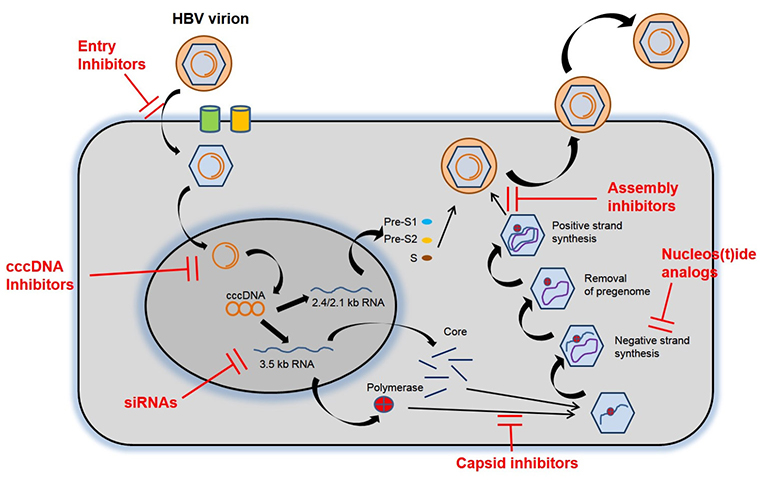
- A HBV infection is a dynamic disease and long-term liver inflammation contributes to the development of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Currently available nucleos(t)ide analogues and pegylated interferon are effective in inhibiting HBV replication but rarely achieve HBsAg clearance. The present article introduces a new definition of HBV cure and several emerging therapies for HBV cure, including direct acting antivirals and immune modulatory antivirals.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2019; 25:93–159.2. Global hepatitis report, 2017. [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2017. Apr. cited 2019 April 4. Available from: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/.3. Revill PA, Chisari FV, Block JM, et al. A global scientific strategy to cure hepatitis B. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 4:545–558.4. Lok AS, Zoulim F, Dusheiko G, Ghany MG. Hepatitis B cure: from discovery to regulatory approval. Hepatology. 2017; 66:1296–1313.5. Likhitsup A, Lok AS. Understanding the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection and the new definitions of cure and the endpoints of clinical trials. Clin Liver Dis. 2019; 23:401–416.6. Blank A, Markert C, Hohmann N, et al. First-in-human application of the novel hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus entry inhibitor myrcludex B. J Hepatol. 2016; 65:483–489.7. Bogomolov P, Alexandrov A, Voronkova N, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: first results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J Hepatol. 2016; 65:490–498.8. Liang TJ, Block TM, McMahon BJ, et al. Present and future therapies of hepatitis B: from discovery to cure. Hepatology. 2015; 62:1893–1908.9. Lee HM, Banini BA. Updates on chronic HBV: current challenges and future goals. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019; 17:271–291.10. Wang XJ, Hu W, Zhang TY, Mao YY, Liu NN, Wang SQ. Irbesartan, an FDA approved drug for hypertension and diabetic nephropathy, is a potent inhibitor for hepatitis B virus entry by disturbing Na(+)-dependent taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide activity. Antiviral Res. 2015; 120:140–146.11. Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F, et al. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:529–537.12. Cai D, Mills C, Yu W, et al. Identification of disubstituted sulfonamide compounds as specific inhibitors of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:4277–4288.13. Moyo B, Bloom K, Scott T, Ely A, Arbuthnot P. Advances with using CRISPR/Cas-mediated gene editing to treat infections with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. Virus Res. 2018; 244:311–320.14. Hynes RO, Coller BS, Porteus M. Toward responsible human genome editing. JAMA. 2017; 317:1829–1830.15. Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science. 2014; 343:1221–1228.16. Seeger C, Sohn JA. Complete spectrum of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutations on HBV cccDNA. Mol Ther. 2016; 24:1258–1266.17. Flisiak R, Jaroszewicz J, Łucejko M. siRNA drug development against hepatitis B virus infection. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018; 18:609–617.18. Streinu-Cercel A, Gane E, Cheng W, et al. A phase 2a study evaluating the multi-dose activity of ARB-1467 in HBeAg positive and negative virally suppressed subjects with hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:S688–S689.19. Javanbakht H, Mueller H, Walther J, et al. Liver-targeted anti-HBV single-stranded oligonucleotides with locked nucleic acid potently reduce HBV gene expression in vivo. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018; 11:441–454.20. Brezillon N, Brunelle MN, Massinet H, et al. Antiviral activity of Bay 41-4109 on hepatitis B virus in humanized Alb-uPA/SCID mice. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e25096.21. Ren Q, Liu X, Luo Z, et al. Discovery of hepatitis B virus capsid assembly inhibitors leading to a heteroaryldihydropyrimidine based clinical candidate (GLS4). Bioorg Med Chem. 2017; 25:1042–1056.22. Al-Mahtab M, Bazinet M, Vaillant A. Safety and efficacy of nucleic acid polymers in monotherapy and combined with immunotherapy in treatment-naive Bangladeshi patients with HBeAg+ chronic hepatitis B infection. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0156667.23. Bazinet M, Pantea V, Placinta G, et al. Update on safety and efficacy in the REP 401 protocol: REP 2139-Mgor REP 2165-Mg used in combination with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and pegylated interferon lpha-2a in treatment naïve caucasian patients with chronic HBeAg negative HBV infection. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:S688–S699.24. Lanford RE, Guerra B, Chavez D, et al. GS-9620, an oral agonist of toll-like receptor-7, induces prolonged suppression of hepatitis B virus in chronically infected chimpanzees. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:1508–1517.25. Gane EJ, Lim YS, Gordon SC, et al. The oral toll-like receptor-7 agonist GS-9620 in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2015; 63:320–328.26. Boni C, Vecchi A, Rossi M, et al. TLR7 agonist increases responses of hepatitis B virus-specific T cells and natural killer cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology. 2018; 154:1764–1777.27. Janssen HLA, Brunetto MR, Kim YJ, et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2018; 68:431–440.28. Koh S, Kah J, Tham CYL, et al. Nonlytic lymphocytes engineered to express virus-specific T-cell receptors limit HBV infection by activating APOBEC3. Gastroenterology. 2018; 155:180–193.29. Rao M, Valentini D, Dodoo E, Zumla A, Maeurer M. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for infectious diseases: learning from the cancer paradigm. Int J Infect Dis. 2017; 56:221–228.30. Pei Y, Wang C, Yan SF, Liu G. Past, current, and future developments of therapeutic agents for treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Med Chem. 2017; 60:6461–6479.31. Lok AS, Pan CQ, Han SH, et al. Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2016; 65:509–516.32. Boni C, Janssen HLA, Rossi M, et al. Combined GS-4774 and tenofovir therapy can improve HBV-specific T-cell responses in patients with chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2019; 157:227–241.e7.33. Höner Zu Siederdissen C, Hui AJ, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, et al. Contrasting timing of virological relapse after discontinuation of tenofovir or entecavir in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients. J Infect Dis. 2018; 218:1480–1484.34. Wedemeyer H, Hui AJ, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, et al. Therapeutic vaccination of chronic hepatitis B patients with ABX203 (NASVAC) to prevent relapse after stopping NUCs: contrasting timing rebound between tenofovir and entecavir. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:S101.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New and Experimental Therapies for Chronic Hepatitis B and C
- Immunotherapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- 2017 KASL clinical practice guidelines management of hepatitis C: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C
- A Study on Periphral T Cell Subsets in Asymptomatic HBsAg Carriers and Children with Chronic Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B vaccine Inoculated Infants
- Pre-S Defective Hepatitis B Virus in Patients with Acute and chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection