Nutr Res Pract.
2019 Dec;13(6):461-472. 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.6.461.
Research trends in obesity & obesogenic environments in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition & Research Institute of Obesity Sciences, Sungshin Women's University, 76ga-55, Dobong-ro, Gangbuk-gu, Soeul 01133, Republic of Korea. mlee@sungshin.ac.kr
- KMID: 2464125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2019.13.6.461
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
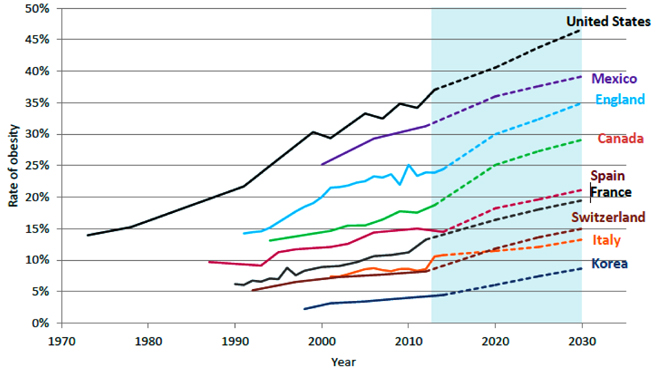
Globally, it has been projected that there will be 2 billion overweight and 1 billion obese individuals by 2030. In Korea, the prevalence of adult obesity (BMI>25) increased from 29.7% in 2009 to 32.4% in 2015. Moreover, childhood obesity, which leads to adulthood obesity, has increasingly become a social problem. The purpose of this review is to summarize the scientific basis for the development of effective models and policies aimed at preventing obesity over a lifetime based on research modeling obesogenic environments.
MATERIALS/METHODS
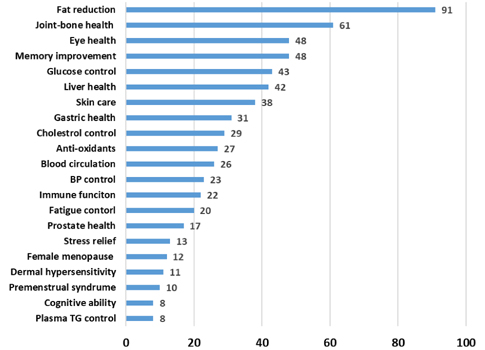
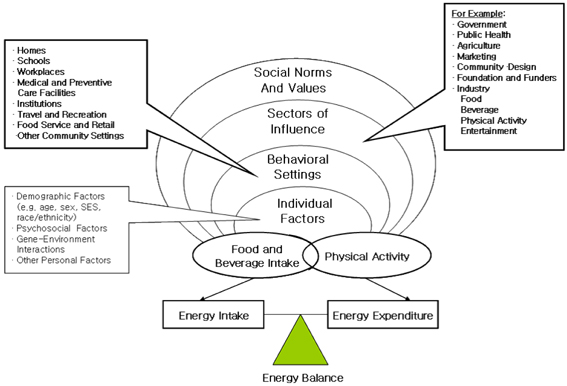
The review focuses on the characteristics of obesity prevalence and trends in 3P analysis (papers, patents, and products) as well as government-funded projects in Korean obesity obesogenic environments over the last 10 years.
RESULTS
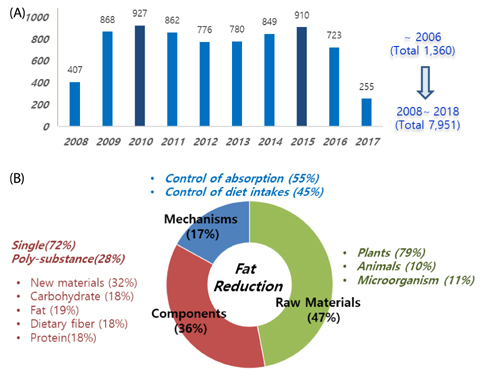
AND DISCUSSION: As a result of the 3P analysis, studies on obesity risk factors were frequently carried out, according to two data bases RISS (4.9%) and PubMed (24.7%). Since there were only 17% patents related to the mechanism of preventing obesity in 7,951 Korean patents related to obesity, new paradigms of technologies to dominate the global obesity markets are needed. After government-funded projects were analyzed, communication and cooperation in multi-governmental departments were suggested to elucidate the characteristics of Korean obesity. Government should also produce short- and long-term road maps to develop a practical, successful outcome. Although the rate of obesity in Korea is currently lower than in other developed countries according to WHO criteria, without adequate governmental intervention, obesity rates will approach those of the top countries with high incidence rates of obesity within the next 10 years.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Organization for Economic Co-operaion and Development (OECD). OECD obesity update 2017. Paris: OECD;2017. Cited 2017 May 18. Available from: http://www.oecd.org/health/obesity-update.htm.2. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2013–2014 National Health Nutrition Examination Survey Report [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2014. cited 2015 Dec 1. Available from: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.3. Seo MH, Kim YH, Han K, Jung JH, Park YG, Lee SS, Kwon HS, Lee WY, Yoo SJ. Prevalence of obesity and incidence of obesity-related comorbidities in Koreans based on National Health Insurance Service health checkup data 2006–2015. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2018; 27:46–52.4. Yoon YS, Oh SW. Recent shift of body mass index distribution in Korea: a population-based Korea national health insurance database, 2002–2013. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:434–438.
Article5. Ministry of Education (KR). 2015 Sample statistics reports for student's health examination in elementary, middle & high school, 2015. [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Education;2015. Cited 2015 December. Available from: http://www.gbe.kr/cmmn/download.do?idx=1408721.6. OECD. Health at a Glance 2017: OECD Indicators. Paris: OECD Publishing.7. Kim MK, Lee WY, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim BT, Kim SM, Kim EM, Suh SH, Shin HJ, Lee KR, Lee KY, Lee SY, Lee SY, Lee SK, Lee CB, Chung S, Jeong IK, Hur KY, Kim SS, Woo JT. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. 2014 clinical pratice guidelines for overweight and obesity in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014; 29:405–409.8. Kim YE, Lee YR, Yoon SJ, Kim YA, Oh IH. Years of life lost due to premature death in people with disabilities in Korea: the Korean national burden of disease study framework. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34:e22.
Article9. Cleveland Clinic (US). Obesity is top cause of preventable life-years lost, study shows [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Science Daily;2017. Cited 2017 April 22. Available from: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/04/170422101614.htm.10. Lee JE, Nam CM, Lee SG, Park S, Kim TH, Park CH. The economic burden of cancer attributable to obesity in Korea: a population-based cohort study. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2019; 28:e13084.
Article11. Lee SM, Paik JW, Kim SH, Kang HL. A Study on Construction of Obesity Management to Improve the Disability Adjusted Life Expectancy. Wonju: National Health Insurance Service;2017.12. National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation. Amendment for Product-Specific Health Functional Food Ingredients. Cheongju: National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation;2018.13. KIPRIS. Title [Internet]. Daejeon: KIPRIS;2019. Cited 2019 Sep 3. Available from: http://kportal.kipris.or.kr/kportal/search/total_search.do.14. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (KR). 2016 Ministry of food and drug safety white paper [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2016. Cited 2016 July. Available from: http://www.kobia.kr/skin/bbs/downloads_e2/download.php?tbl=policy_report&no=405.15. James WP, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal LF, Maggioni AP, Torp-Pedersen C, Sharma AM, Shepherd GM, Rode RA, Renz CL. SCOUT Investigators. Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:905–917.
Article16. Korea Health Promotion Institute. Health promotion research project of Ministry of Health & Welfare, evaluation framework for obesity prevention policy [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Health Promotion Institute;2016. Cited 2019 Sep 3. Available from: http://www.khealth.or.kr.17. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. A study on the development of policy and strategies for national overweight and obesity prevention programs in children and adolescents [Internet]. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2009. Cited 2009 January. Available from: https://www.kihasa.re.kr/common/filedown.do?seq=17203.18. Seo YJ, Jeon MS. Effects of an education program on sanitation status at centers for children's food service management: focusing on Jung-gu and Dong-gu regions of Daejeon Metropolitan City. Korean J Community Nutr. 2015; 20:447–459.
Article19. Ju SY, Hong WS. Assessment of the effectiveness and perception of education by center for child-care foodservice management: focus on parents of child-care and kindergarten in Seoul. Korean J Food Cookery Sci. 2018; 34:404–412.
Article20. Trust of America's Health. The state of obesity 2018: better policies for a healthier America [Internet]. Washington, D.C.: Trust of America's Health;2018. Cited 2018 September. Available from: https://www.tfah.org/report-details/the-state-of-obesity-2018.21. Interagency Committee on Human Nutrition Research (US). National nutrition research roadmap 2016-2021: advancing nutrition research to improve and sustain health [Internet]. Washington, D.C.: Interagency Committee on Human Nutrition Research;2016. Cited 2016 November 2. Available from: https://www.nal.usda.gov/sites/default/files/fnic_uploads/2016-03-30-%20ICHNR%20NNRR%20%282%29.pdf.22. Interagency Committee on Human Nutrition Research (US). National nutrition research roadmap 2016-2021: advancing nutrition research to improve and sustain health executive summary [Internet]. Washington, D.C.: Interagency Committee on Human Nutrition Research;2016. cited 2016 November 2. Available from: https://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/interagency-committee-human-nutrition-research.23. United States Department of Agriculture. National program 107 human nutrition [Internet]. Washington, D.C.: United States Department of Agriculture;2015. cited 2015 December 25. Available from: http://fliphtml5.com/kcka/ujth/basic.24. National Agricultural Research Organization (JP). The Food Research Institute, NARO (NFRI) conducts innovative R&D to ensure a safe and healthy dietary life and resolve food issues in Japan [Internet]. Tsukuba: National Agricultural Research Organization;2017. cited 2017 March. Available from: http://www.naro.affrc.go.jp/publicity_report/publication/files/nfri_pamphlet_en.pdf.25. The Australian Health Ministers Advisory Council. Healthy weight 2008 - Australia's future - the national action agenda for children and young people and their families [Internet]. Canberra: The Australian Health Ministers Advisory Council;2011. cited 2011 July 4. Available from: http://www.health.gov.au/internet/publications/publishing.nsf/Content/healthy-weight-2008.26. Government Office for Science (GB). Research and analysis reducing obesity: obesity system map [Internet]. London: Government Office for Science;2007. cited 2007 October 2007. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/reducing-obesity-obesity-system-map.27. World Health Organization. Health promoting schools [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2018. Cited 2019 Sep 3. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-promoting-schools/en/.28. European Commission. EU action plan on childhood obesity 2014-2020 [Internet]. Brussels: European Union;2014. cited 2014 July 28. Available from: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/nutrition_physical_activity/docs/childhoodobesity_actionplan_2014_2020_en.pdf.29. Royal Society for Public Health (GB). The child's obesity strategy: how our young people would solve the childhood obesity crisis [Internet]. London: Royal Society for Public Health;2016. cited 2016 June 23. Available from: https://www.rsph.org.uk/uploads/assets/uploaded/403f6527-dd7a-4b7e-8ad62dab7bef33fd.pdf.30. National Obesity Forum (GB). Childhood obesity: the scale of the problem [Internet]. Nottingham: National Obesity Forum;2015. Cited 2019 Sep 3. Available from: http://www.nationalobesityforum.org.uk/images/stories/PDF_training_resource/in-depth-childhood-obesity.pdf.31. Cross-Government Obesity Unit, Department of Health and Department of Children, Schools and Families (GB). Healthy weight, healthy lives: a cross-government strategy for England [Internet]. London: Cross-Government Obesity Unit;2008. cited 2008 January 23. Available from: http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20130401151715/http://www.education.gov.uk/publications/eOrderingDownload/DH-9087.pdf.32. Hamre R, Kuester S, Renaud J, Williams-Piehota P, Franco E, Roussel A, Hersey J. Improving nutrition, physical activity, and obesity prevention [Internet]. Atlanta (GA), Research Triangle Park (NC): Centers for Disease Control, RTI International;2006. cited 2006 July. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/downloads/NPAO_Performance_Report_2005.pdf.33. The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. CATCH - coordinated approach to child health: curriculum & training [Internet]. Houston (TX): The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston;2018. cited 2018 March 8. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/prc/resources/pdf/tools/CATCH_508tagged.pdf.34. Hoelscher DM, Springer AE, Ranjit N, Perry CL, Evans AE, Stigler M, Kelder SH. Reductions in child obesity among disadvantaged school children with community involvement: the Travis County CATCH Trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010; 18 Suppl 1:S36–S44.
Article35. Ministry of Education Singapore. Educating for health conference [Internet]. Singapore: Ministry of Education Singapore;2007. cited 2007 November 12. Available from: http://www.nas.gov.sg/archivesonline/data/pdfdoc/20071112983.pdf.36. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (KR). Safety assurance on food and eating/nutrition environment (SAFENET) for children [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2011. cited 2011 November 30. Available from: http://www.ndsl.kr/ndsl/search/detail/report/reportSearchResultDetail.do?cn=TRKO201600010653.37. MetaHit. MetaHit website [Internet]. [place unknown]: INRA - MICA Division;2008. cited 2011 June 1. Available from: http://www.metahit.eu/.38. NIH HMP Working Group. Peterson J, Garges S, Giovanni M, McInnes P, Wang L, Schloss JA, Bonazzi V, McEwen JE, Wetterstrand KA, Deal C, Baker CC, Di Francesco V, Howcroft TK, Karp RW, Lunsford RD, Wellington CR, Belachew T, Wright M, Giblin C, David H, Mills M, Salomon R, Mullins C, Akolkar B, Begg L, Davis C, Grandison L, Humble M, Khalsa J, Little AR, Peavy H, Pontzer C, Portnoy M, Sayre MH, Starke-Reed P, Zakhari S, Read J, Watson B, Guyer M. The NIH human microbiome project. Genome Res. 2009; 19:2317–2323.
Article39. Choi S, Cho SH, Yi H. Human microbiome studies in Korea. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016; 4:311–320.
Article40. Kyrpides NC, Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Ivanova NN. Microbiome data science: understanding our microbial plane. Trends Microbiol. 2016; 24:425–427.41. Gombojav B, Song YM, Lee K, Yang S, Kho M, Hwang YC, Ko G, Sung J. The healthy twin study, Korea updates: resources for omics and genome epidemiology studies. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2013; 16:241–245.
Article42. Lee M, Jang Y, Kim K, Cho H, Jee SH, Park Y, Kim MK. Relationship between HDL3 subclasses and waist circumferences on the prevalence of metabolic syndrome: KMSRI-Seoul study. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 213:288–293.
Article43. Hong S, Song Y, Lee KH, Lee HS, Lee M, Jee SH, Joung H. A fruit and dairy dietary pattern is associated with a reduced risk of metabolic syndrome. Metabolism. 2012; 61:883–890.
Article44. Kim Y, Lee M, Lim Y, Jang Y, Park HK, Lee Y. The gene-diet interaction, LPL PvuII and HindIII and carbohydrate, on the criteria of metabolic syndrome: KMSRI-Seoul study. Nutrition. 2013; 29:1115–1121.
Article45. Shin E, Park NY, Jang Y, Oh H, Jeong J, Lim Y, Lee M. The association of lipoprotein lipase PvuII polymorphism and niacin intake in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome: a KMSRI-Seoul study. Genes Nutr. 2012; 7:331–341.
Article46. Jung KJ, Jee YH, Jee SH. Metabolic risk score and vascular mortality among Korean adults. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2017; 29:122–131.
Article47. Oh HY, Kim MK, Lee M, Kim YO. Macronutrient composition and sodium intake of diet are associated with risk of metabolic syndrome and hypertension in Korean women. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e78088.
Article48. Lee MR, Lim CJ, Lee YH, Park JG, Sonn SK, Lee MN, Jung IH, Jeong SJ, Jeon S, Lee M, Oh KS, Yang Y, Kim JB, Choi HS, Jeong W, Jeong TS, Yoon WK, Kim HC, Choi JH, Oh GT. The adipokine Retnla modulates cholesterol homeostasis in hyperlipidemic mice. Nat Commun. 2014; 5:4410.
Article49. Choi M, Park H, Cho S, Lee M. Vitamin D3 supplementation modulates inflammatory responses from the muscle damage induced by high-intensity exercise in SD rats. Cytokine. 2013; 63:27–35.
Article50. Lim HH, Yang SJ, Kim Y, Lee M, Lim Y. Combined treatment of mulberry leaf and fruit extract ameliorates obesity-related inflammation and oxidative stress in high fat diet-induced obese mice. J Med Food. 2013; 16:673–680.
Article51. Kim SY, Wi HR, Choi S, Ha TJ, Lee BW, Lee M. Inhibitory effect of anthocyanin-rich black soybean testa (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) on the inflammation-induced adipogenesis in a DIO mouse model. J Funct Foods. 2015; 14:623–633.
Article52. Eo H, Jeon YJ, Lee M, Lim Y. Brown Alga Ecklonia cava polyphenol extract ameliorates hepatic lipogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation by activation of AMPK and SIRT1 in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2015; 63:349–359.
Article53. Lee M, Kwon DY, Park J. The impacts of the interaction of genetic variation, CYP11β2 and NEDD4L, with sodium intake on pediatric obesity with gender difference: a 3-year panel study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2017; 41:542–550.
Article54. Lee M, Kwon DY, Kim MS, Choi CR, Park MY, Kim AJ. Genome-wide association study for the interaction between BMR and BMI in obese Korean women including overweight. Nutr Res Pract. 2016; 10:115–124.
Article55. Choi JR, Kwon IS, Kwon DY, Kim MS, Lee M. TT mutant homozygote of Kruppel-like factor 5 is a key factor for increasing basal metabolic rate and resting metabolic rate in Korean elementary school children. Genomics Inform. 2013; 11:263–271.
Article56. Cho K, Moon JS, Kang JH, Jang HB, Lee HJ, Park SI, Yu KS, Cho JY. Combined untargeted and targeted metabolomic profiling reveals urinary biomarkers for discriminating obese from normal-weight adolescents. Pediatr Obes. 2017; 12:93–101.
Article57. Lee JE, Lee DE, Kim K, Shim JE, Sung E, Kang JH, Hwang JY. Development of tailored nutrition information messages based on the transtheoretical model for smartphone application of an obesity prevention and management program for elementary-school students. Nutr Res Pract. 2017; 11:247–256.
Article58. Kim H, Kang JH, Park HA, Cho SH, Jeon SH, Jung JH, Sung S. Development of a smartphone application prototype for child obesity prevention: rationale and study design of acceptability and feasibility tests. Korean J Health Promot. 2015; 15:194–201.
Article59. Song M, Kang K, An JY. Investigating drug-disease interactions in drug-symptom-disease triples via citation relations. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol. 2018; 69:1355–1368.
Article60. Gu MY, Chun YS, Yong RS, Yang HO. Licoflavonol reduces Aβ secretion by increasing BACE1 phosphorylation to facilitate BACE1 degradation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019; 63:e1800474.
Article61. Kim YJ, Kim S, Jung Y, Jung E, Kwon HJ, Kim J. Eupatilin rescues ciliary transition zone defects to ameliorate ciliopathy-related phenotypes. J Clin Invest. 2018; 128:3642–3648.
Article62. Hong CP, Park A, Yang BG, Yun CH, Kwak MJ, Lee GW, Kim JH, Jang MS, Lee EJ, Jeun EJ, You G, Kim KS, Choi Y, Park JH, Hwang D, Im SH, Kim JF, Kim YK, Seoh JY, Surh CD, Kim YM, Jang MH. Gut-specific delivery of t-helper 17 cells reduces obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152:1998–2010.
Article63. Nam YD, Jung MJ, Roh SW, Kim MS, Bae JW. Comparative analysis of Korean human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e22109.
Article64. Strategic Initiative for Microbiomes in Agriculture and Food (KR). Report for the research and the trend of microbiome [Internet]. Seoul: Strategic Initiative for Microbiomes in Agriculture and Food;2015. cited 2015 August 10. Available from: http://moog2015.cafe24.com/bizdemo21250/img/report001.pdf.65. OECD. OECD obesity update 2014 [Internet]. Paris: OECD;2014. cited 2014 June. Available from: http://www.oecd.org/health/Obesity-Update-2014.pdf.66. Mexico New Daily. Subway ticket worth 10 squats in DF [Internet]. Oaxaca: Mexico New Daily;2015. cited 2015 January 27. Available from: https://mexiconewsdaily.com/news/subway-ticket-worth-10-squats-df/.67. WHO Regional Office for Europe. Assessment of the impact of a public health product tax [Internet]. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe;2015. cited 2015 November 11. Available from: http://www.euro.who.int/_data/assets/pdf_file/0008/332882/assessment-impact-PH-tax-report.pdf.68. Kim YM. Current status of obesity and countermeasure [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Insurance Research Institute;2017. cited 2017 October 16. Available from: http://www.kiri.or.kr/pdf/%EC%A0%84%EB%AC%B8%EC%9E%90%EB%A3%8C/KIRI_20171012_174540.pdf.69. World Health Organization. 5 A day for better health program USA [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2003. cited 2003 August 26. Available from: https://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/media/en/gs_fv_ppt_lorelei.pdf?ua=1.70. In : Tan A, Deurenberg-Yap M, Ling A, Naidu RS, Ng SA, editors. Evaluating national nutrition promotion programs in Singapore. 135th APHA Annual Meeting and Exposition; 2007 Nov 3–7; Washington, D.C., USA. Washington, D.C.: American Public Health Association;2007. 11.71. Lee M, Kim MK, Kim SM, Park H, Park CG, Park HK. Gender-based differences on the association between salt-sensitive genes and obesity in Korean children aged between 8 and 9 years. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0120111.
Article72. Chung S, Kim YJ, Yang SJ, Lee Y, Lee M. Nutrigenomic functions of PPARs in obesogenic environments. PPAR Res. 2016; 2016:4794576.
Article73. Petrosino JF. The microbiome in precision medicine: the way forward. Genome Med. 2018; 10:12.
Article74. Lee Y, Cha YS, Park Y, Lee M. PPARγ2 C1431T polymorphism interacts with the antiobesogenic effects of Kochujang, a Korean fermented, soybean-based red pepper paste, in overweight/obese subjects: a 12-week, double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Med Food. 2017; 20:610–617.
Article75. International Union of Nutritional Sciences (AT). The global challenge of obesity and the international obesity task force [Internet]. Vienna: International Union of Nutritional Sciences;2015. cited 2015 July 23. Available from: http://www.iuns.org/resources/the-global-challenge-of-obesity-and-the-international-obesity-task-force/.76. Leeman J, Sommers J, Leung MM, Ammerman A. Disseminating evidence from research and practice: a model for selecting evidence to guide obesity prevention. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2011; 17:133–140.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Obesogenic Behavior and Binge Eating Disorder in an Elderly Female with Schizophrenia
- The COVID-19 pandemic: an unprecedented tragedy in the battle against childhood obesity
- Validation of G-protein beta-3 subunit gene C825T polymorphism as predictor of obesogenic epidemics in overweight/obese Korean children
- Research on obesity using the National Health Information Database: recent trends
- Endoscopic Treatment for Obesity: New Emerging Technology Trends