Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2020 Jan;12(1):99-109. 10.4168/aair.2020.12.1.99.
Efficacy of Allergen Immunotherapy for Allergic Asthma in Real World Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. yhnam@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2462575
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2020.12.1.99
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) induces immunological tolerance, and there is increasing evidence of the clinical efficacy of AIT in the treatment of allergic asthma. However, the optimal parameters for asthma control in clinical trials are still unclear. We investigated the efficacy of AIT with respect to changes in the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) dose in patients with allergic asthma.
METHODS
A total of 117 adults with allergic asthma who had used ICS for more than 1 year in a single tertiary hospital in Korea were included in this retrospective study. We compared the clinical parameters and outcomes between the AIT group (ICS with AIT, n = 48) and the non-AIT group (ICS without AIT, n = 69) by applying an inverse probability of treatment weighting method. The patients in the AIT group had received subcutaneous AIT monthly as a maintenance treatment for more than 1 year. The changes in the ICS dose from baseline were evaluated in the 2 groups for 3 years.
RESULTS
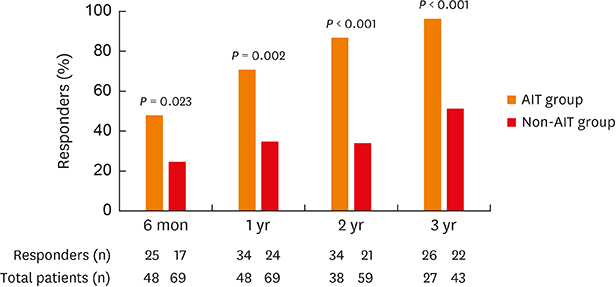
The proportion of responders who discontinued or decreased in the ICS dose with achieving control status of asthma was significantly higher in the AIT group than in the non-AIT group throughout the study period (at 6 months, 52.1% vs. 24.6%; at 1 year, 70.8% vs. 34.7%; at 2 years, 89.5% vs. 35.6%; at 3 years, 96.3% vs. 51.2%). Treatment responses did not differ significantly by type of allergen (single- or multi-allergens or 3 different products) used throughout the study period.
CONCLUSIONS
Irrespective of the type of allergen, long-term maintenance AIT helps to spare ICS dose and achieve better control in patients with allergic asthma in real-world clinical practice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Safety and Utility of Rush Immunotherapy with Aqueous Allergen Extracts for Treatment of Respiratory Allergies
Ji-Ho Lee, Jae-Hwa Choi, Keun-Bae Jeong, Seok Jeong Lee, Myoung Kyu Lee, Won-Yeon Lee, Suk Joong Yong, Sang-Ha Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;36(3):e18. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e18.
Reference
-
1. McCracken JL, Veeranki SP, Ameredes BT, Calhoun WJ. Diagnosis and management of asthma in adults: a review. JAMA. 2017; 318:279–290.2. Reddel HK, Busse WW, Pedersen S, Tan WC, Chen YZ, Jorup C, et al. Should recommendations about starting inhaled corticosteroid treatment for mild asthma be based on symptom frequency: a post-hoc efficacy analysis of the START study. Lancet. 2017; 389:157–166.3. Gerber AN. Measuring safety of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016; 117:577–581.
Article4. Heffler E, Madeira LN, Ferrando M, Puggioni F, Racca F, Malvezzi L, et al. Inhaled corticosteroids safety and adverse effects in patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018; 6:776–781.
Article5. Zielen S, Kardos P, Madonini E. Steroid-sparing effects with allergen-specific immunotherapy in children with asthma: a randomized controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:942–949.6. Heffler E, Bagnasco D, Canonica GW. Strategies to reduce corticosteroid-related adverse events in asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019; 19:61–67.
Article7. Yukselen A, Kendirli SG. Role of immunotherapy in the treatment of allergic asthma. World J Clin Cases. 2014; 2:859–865.
Article8. Tsabouri S, Mavroudi A, Feketea G, Guibas GV. Subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy in allergic asthma in children. Front Pediatr. 2017; 5:82.
Article9. Tamaoki J, Isono K, Taira M, Tagaya E, Nakata J, Kawatani K, et al. Role of regular treatment with inhaled corticosteroid or leukotriene receptor antagonist in mild intermittent asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008; 29:189–196.
Article10. Halken S, Larenas-Linnemann D, Roberts G, Calderón MA, Angier E, Pfaar O, et al. EAACI guidelines on allergen immunotherapy: prevention of allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017; 28:728–745.
Article11. Asamoah F, Kakourou A, Dhami S, Lau S, Agache I, Muraro A, et al. Allergen immunotherapy for allergic asthma: a systematic overview of systematic reviews. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017; 7:25.
Article12. Reddel HK, FitzGerald JM, Bateman ED, Bacharier LB, Becker A, Brusselle G, et al. GINA 2019: a fundamental change in asthma management: treatment of asthma with short-acting bronchodilators alone is no longer recommended for adults and adolescents. Eur Respir J. 2019; 53:1901046.13. Passalacqua G, Rogkakou A, Mincarini M, Canonica GW. Allergen immunotherapy in asthma; what is new? Asthma Res Pract. 2015; 1:6.
Article14. Horak F, Doberer D, Eber E, Horak E, Pohl W, Riedler J, et al. Diagnosis and management of asthma - Statement on the 2015 GINA Guidelines. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016; 128:541–554.
Article15. Cox L, Larenas-Linnemann D, Lockey RF, Passalacqua G. Speaking the same language: the world allergy organization subcutaneous immunotherapy systemic reaction grading system. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:569–574. 574.e1–567.
Article16. Mosbech H, Deckelmann R, de Blay F, Pastorello EA, Trebas-Pietras E, Andres LP, et al. Standardized quality (SQ) house dust mite sublingual immunotherapy tablet (ALK) reduces inhaled corticosteroid use while maintaining asthma control: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 134:568–575.e7.17. Virchow JC, Backer V, Kuna P, Prieto L, Nolte H, Villesen HH, et al. Efficacy of a house dust mite sublingual allergen immunotherapy tablet in adults with allergic asthma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016; 315:1715–1725.18. Lee JH, Kim SC, Choi H, Jung CG, Ban GY, Shin YS, et al. A retrospective study of clinical response predictors in subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy with house dust mites for allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:18–24.
Article19. Jutel M, Kosowska A, Smolinska S. Allergen immunotherapy: past, present, and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:191–197.
Article20. Blumberga G, Groes L, Haugaard L, Dahl R. Steroid-sparing effect of subcutaneous SQ-standardised specific immunotherapy in moderate and severe house dust mite allergic asthmatics. Allergy. 2006; 61:843–848.
Article21. Feng B, Xiang H, Jin H, Gao J, Huang S, Shi Y, et al. Efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy for house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:220–228.
Article22. Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 140:950–958.23. Sohn MH. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:1–3.
Article