J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2018 Dec;20(4):231-234. 10.7461/jcen.2018.20.4.231.
A Type 1 Persistent Proatlantal Artery Originating from the External Carotid Artery Detected by Computed Tomographic Angiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hanibalkms@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2461921
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2018.20.4.231
Abstract
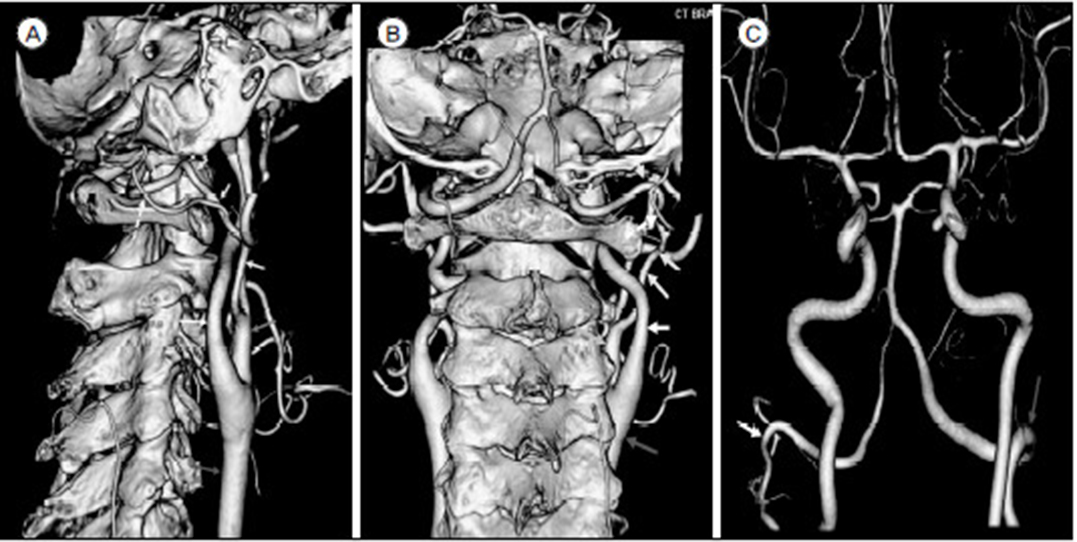
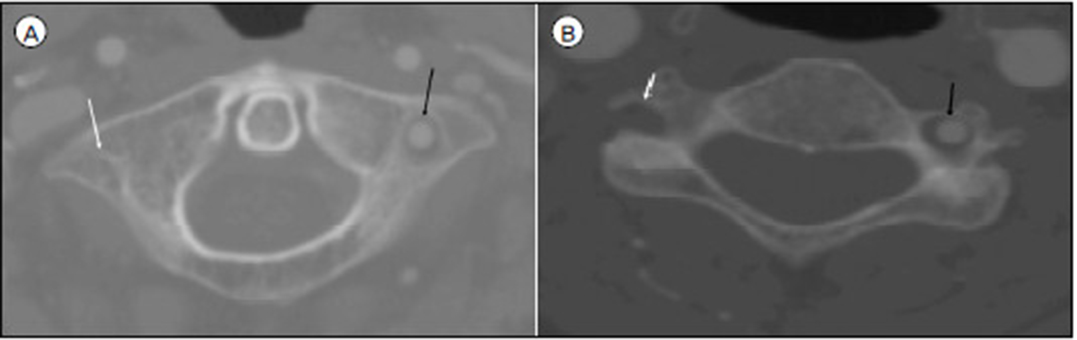
- A persistent proatlantal artery (PA) is rare. We report a type 1 persistent PA originating from the right external carotid artery (ECA). A 78-year-old woman presented with dizziness. Computed tomographic (CT) angiography showed a persistent PA originating from the right ECA. This persistent PA did not pass through the atlas transverse foramen. The extracranial segment of this artery in the atlas transverse process level had a more lateral position than a normal left vertebral artery. CT angiography well demonstrated the relationship with bony structures and the course of this persistent PA. This anomalous artery in our patient presented as an incidental finding. Surgeon should recognize a persistent PA when performing carotid endarterectomy or ligation of the ECA for avoidance of complication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bahşi YZ, Uysal H, Peker S, Yurdakul M. Persistent primitive proatlantal intersegmental artery (proatlantal artery I) results in ‘top of the basilar’ syndrome. Stroke. 1993; 12. 24(12):2114–2117.
Article2. Basekim CC, Silit E, Mutlu H, Pekkafali MZ, Ozturk E, Kizilkaya E. Type I proatlantal artery with bilateral absence of the external carotid arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 10. 25(9):1619–1621.3. Buljan K, Hegeduš I, Gilman Kuric T, Salha T, Tomić S, Butković Soldo S, et al. Type I persistent proatlantal artery associated with fusiform subclavian artery aneurysm: report of one case. Rev Med Chil. 2015; 08. 143(8):1081–1084.
Article4. Grego F, Stramanà R, Lepidi S, Antonello M, Bonvini S, Zaramella M, et al. Primitive proatlantal intersegmental artery and carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg. 2004; 03. 39(3):691.
Article5. Gumus T, Onal B, Ilgit ET. Bilateral persistence of type 1 proatlantal arteries: report of a case and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 10. 25(9):1622–1624.6. Kolbinger R. Heindel W, Pawlik G, Erasmi-Körber H. Right proatlantal artery type I, right internal carotid occlusion, and left internal carotid stenosis: case report and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 1993; 07. 117(1-2):232–239.7. Montechiari M, Iadanza A, Falini A, Politi LS. Monolateral type I proatlantal artery with bilateral absence of vertebral arteries: description of a case and review of the literature. Surg Radiol Anat. 2013; 11. 35(9):863–865.
Article8. Purkayastha S, Gupta AK, Varma R, Kapilamoorthy TR. Proatlantal intersegmental arteries of external carotid artery origin associated with Galen's vein malformation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 10. 26(9):2378–2383.9. Schoof J, Skalej M, Halloul Z, Wunderlich MT. Carotid endarterectomy in a patient with persistent proatlantal artery. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 23(5-6):458–459.
Article10. Zarghouni M, Marichal D. Persistent bilateral proatlantal type II artery. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 013; 01. 26(1):50–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Persistent Proatlantal Artery in Magnetic Resonance Angiography: A Case Report
- Persistent Proatlantal artery Type I Observed in a Patient with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Case Report
- A Pitfall in the Use of Three Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography for Early Surgery of Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Case Report
- Coexistence of the Absence of the Left Common Carotid Artery, a Common Origin of the Left External Carotid Artery and the Right Common Carotid Artery, and an Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery: A Case Report
- Anglographic Findings of Collateral Vessels in Cervicofacial Vascular Lesions with Previously Ligated Carotid Artery