Investig Clin Urol.
2019 Nov;60(6):463-471. 10.4111/icu.2019.60.6.463.
Oncological and functional outcomes of robot-assisted radical cystectomy in bladder cancer patients in a single tertiary center: Can these be preserved throughout the learning curve?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Korea University Medical Center, Korea University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdksh@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2461058
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.6.463
Abstract
- PURPOSE
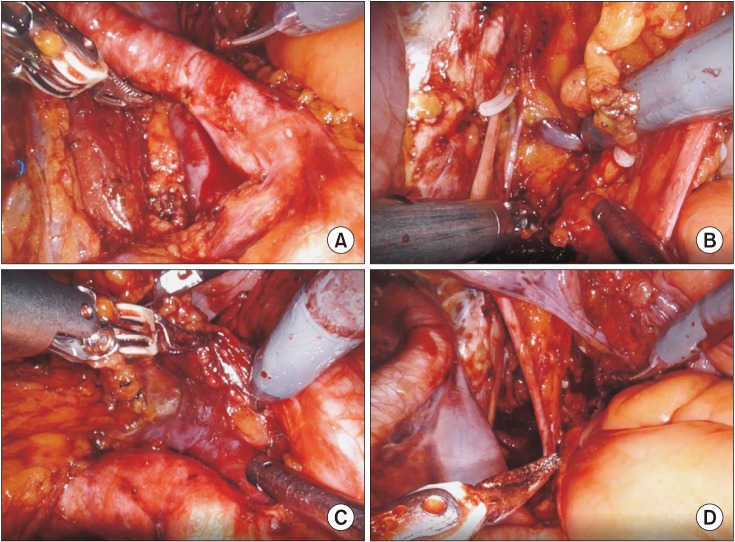
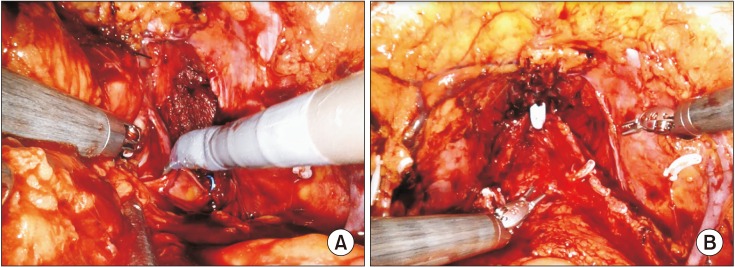
To evaluate the overall and segmental oncological and functional outcome of robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) during the learning curve.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From August 2007 to November 2017, a total of 120 bladder cancer patients were treated with RARC in a single-tertiary hospital. These were divided into three groups of 40 consecutive cases. Overall and subgroup analysis of each group was used to evaluate oncological and functional outcomes throughout the learning curve.
RESULTS
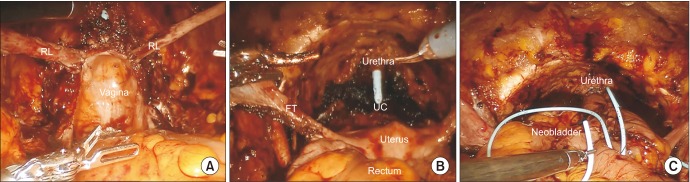
Among the 120 RARC cases, 42, 73, and 5 patients received extracorporeal urinary diversion (ECUD), intracorporeal urinary diversion (ICUD), and ureterocutaneostomy, respectively. There was a transition from ECUD to ICUD during the learning curve. The positive surgical margin rate was 0.8%. The mean lymph node yield for the standard and extended pelvic lymph node dissection was 12.5 and 30.1, respectively, and increased to 19.8 and 31.2 and further to 20.0 and 37.9, respectively, with each additional series of 40 cases. The 5-year overall survival and 3-year recurrence-free survival rates were 86.6% and 81.4%, respectively. The 1-year daytime continence rate was 75.7%, while the nighttime continence rate was 51.4%. The potency preservation rate was 66.7% (n=8) with or without phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5-I) at 1 year and 33.3% without PDE5-I (n=4).
CONCLUSIONS
RARC results in comparable oncological and functional outcomes to open radical cystectomy. In addition, the oncological and functional outcomes were well maintained throughout the learning curve. ECUD transition to ICUD was safe and did not compromise oncological or functional outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Palapattu GS, Lotan Y, Rogers CG, Amiel GE, et al. Outcomes of radical cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: a contemporary series from the Bladder Cancer Research Consortium. J Urol. 2006; 176:2414–2422. discussion 2422. PMID: 17085118.
Article2. Challacombe BJ, Bochner BH, Dasgupta P, Gill I, Guru K, Herr H, et al. The role of laparoscopic and robotic cystectomy in the management of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with special emphasis on cancer control and complications. Eur Urol. 2011; 60:767–775. PMID: 21620562.
Article3. Guiote I, Gaya JM, Gausa L, Rodríguez O, Palou J. Complications from robot-assisted radical cystectomy: where do we stand. Actas Urol Esp. 2016; 40:108–114. PMID: 25914065.
Article4. Parekh DJ, Reis IM, Castle EP, Gonzalgo ML, Woods ME, Svatek RS, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer (RAZOR): an open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018; 391:2525–2536. PMID: 29976469.5. Bochner BH, Dalbagni G, Sjoberg DD, Silberstein J, Keren Paz GE, Donat SM, et al. Comparing open radical cystectomy and robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:1042–1050. PMID: 25496767.
Article6. Menon M, Hemal AK, Tewari A, Shrivastava A, Shoma AM, El-Tabey NA, et al. Nerve-sparing robot-assisted radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion. BJU Int. 2003; 92:232–236. PMID: 12887473.
Article7. Nix J, Smith A, Kurpad R, Nielsen ME, Wallen EM, Pruthi RS. Prospective randomized controlled trial of robotic versus open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: perioperative and pathologic results. Eur Urol. 2010; 57:196–201. PMID: 19853987.
Article8. Bachman AG, Parker AA, Shaw MD, Cross BW, Stratton KL, Cookson MS, et al. Minimally invasive versus open approach for cystectomy: trends in the utilization and demographic or clinical predictors using the National Cancer Database. Urology. 2017; 103:99–105. PMID: 28214574.
Article9. Hanna N, Leow JJ, Sun M, Friedlander DF, Seisen T, Abdollah F, et al. Comparative effectiveness of robot-assisted vs. open radical cystectomy. Urol Oncol. 2018; 36:88.e1–88.e9.
Article10. Parekh DJ, Messer J, Fitzgerald J, Ercole B, Svatek R. Perioperative outcomes and oncologic efficacy from a pilot prospective randomized clinical trial of open versus robotic assisted radical cystectomy. J Urol. 2013; 189:474–479. PMID: 23017529.
Article11. Khan MS, Gan C, Ahmed K, Ismail AF, Watkins J, Summers JA, et al. A single-centre early phase randomised controlled three-arm trial of open, robotic, and laparoscopic radical cystectomy (CORAL). Eur Urol. 2016; 69:613–621. PMID: 26272237.
Article12. Parekh D. Pnflba-18: a prospective, multicenter, randomized trial of open versus robotic radical cystectomy (RAZOR). J Urol. 2017; 197:e918.
Article13. Augestad KM, Delaney CP. Postoperative ileus: impact of pharmacological treatment, laparoscopic surgery and enhanced recovery pathways. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2067–2074. PMID: 20440846.
Article14. Kang SG, Kang SH, Lee YG, Rha KH, Jeong BC, Ko YH, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: a multi-institutional study from Korea. J Endourol. 2010; 24:1435–1440. PMID: 20839973.
Article15. Kang SG, Ko YH, Jang HA, Kim J, Kim SH, Cheon J, et al. Initial experience of robot-assisted radical cystectomy with total intracorporeal urinary diversion: comparison with extracorporeal method. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2012; 22:456–462. PMID: 22462649.
Article16. Ali-El-Dein B, Gomha M, Ghoneim MA. Critical evaluation of the problem of chronic urinary retention after orthotopic bladder substitution in women. J Urol. 2002; 168:587–592. PMID: 12131315.
Article17. Niver BE, Daneshmand S, Satkunasivam R. Female reproductive organ-sparing radical cystectomy: contemporary indications, techniques and outcomes. Curr Opin Urol. 2015; 25:105–110. PMID: 25581538.18. Herr H, Lee C, Chang S, Lerner S. Bladder Cancer Collaborative Group. Standardization of radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection for bladder cancer: a collaborative group report. J Urol. 2004; 171:1823–1828. discussion 1827-8. PMID: 15076285.
Article19. Wilson TG, Guru K, Rosen RC, Wiklund P, Annerstedt M, Bochner BH, et al. Pasadena Consensus Panel. Best practices in robot-assisted radical cystectomy and urinary reconstruction: recommendations of the Pasadena Consensus Panel. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:363–375. PMID: 25582930.
Article20. Yuh B, Wilson T, Bochner B, Chan K, Palou J, Stenzl A, et al. Systematic review and cumulative analysis of oncologic and functional outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:402–422. PMID: 25560797.
Article21. Hautmann RE, de Petriconi RC, Volkmer BG. 25 years of experience with 1,000 neobladders: long-term complications. J Urol. 2011; 185:2207–2212. PMID: 21497841.
Article22. Lee RK, Abol-Enein H, Artibani W, Bochner B, Dalbagni G, Daneshmand S, et al. Urinary diversion after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: options, patient selection, and outcomes. BJU Int. 2014; 113:11–23. PMID: 24330062.
Article23. Hautmann RE, Abol-Enein H, Davidsson T, Gudjonsson S, Hautmann SH, Holm HV, et al. International Consultation on Urologic Disease-European Association of Urology Consultation on Bladder Cancer 2012. ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Bladder Cancer 2012: urinary diversion. Eur Urol. 2013; 63:67–80. PMID: 22995974.24. Novara G, Ficarra V, Minja A, De Marco V, Artibani W. Functional results following vescica ileale Padovana (VIP) neobladder: midterm follow-up analysis with validated questionnaires. Eur Urol. 2010; 57:1045–1051. PMID: 20096993.
Article25. Koie T, Hatakeyama S, Yoneyama T, Ishimura H, Yamato T, Ohyama C. Experience and functional outcome of modified ileal neobladder in 95 patients. Int J Urol. 2006; 13:1175–1179. PMID: 16984548.
Article26. Nayak AL, Cagiannos I, Lavallée LT, Morash C, Hickling D, Mallick R, et al. Urinary function following radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder urinary reconstruction. Can Urol Assoc J. 2018; 12:181–186. PMID: 29485037.
Article27. Schwentner C, Sim A, Balbay MD, Todenhöfer T, Aufderklamm S, Halalsheh O, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy and intracorporeal neobladder formation: on the way to a standardized procedure. World J Surg Oncol. 2015; 13:3. PMID: 25560783.
Article28. Simone G, Papalia R, Misuraca L, Tuderti G, Minisola F, Ferriero M, et al. Robotic intracorporeal padua ileal bladder: surgical technique, perioperative, oncologic and functional outcomes. Eur Urol. 2018; 73:934–940. PMID: 27780643.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy
- Learning Curve of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy for a Single Experienced Surgeon: Comparison with Simultaneous Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- Robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Where we are in 2023
- Comparison of functional and oncological outcomes between uterus-sparing radical cystectomy and standard radical cystectomy in females: A retrospective study
- Pure Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy with Ileal Conduit: A Single Surgeon's Mid-Term Outcomes