Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Oct;74(4):205-211. 10.4166/kjg.2019.74.4.205.
Serum Aminotransferase Level in Rhabdomyolysis according to Concurrent Liver Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. nyheo@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2460985
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.74.4.205
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The serum aminotransferase level is usually elevated in rhabdomyolysis, and these enzymes originate from the skeletal muscle. On the other hand, there is limited data showing whether the degree of elevation of these enzymes differs according to the concurrent liver disease.
METHODS
Patients with rhabdomyolysis were selected when their serum creatinine kinase level was >1,000 U/L. They were categorized as the group with and without concurrent liver disease. The AST and ALT levels in both groups were compared. In addition, the aminotransferase level was compared between those with rhabdomyolysis and those with alcoholic liver disease.
RESULTS
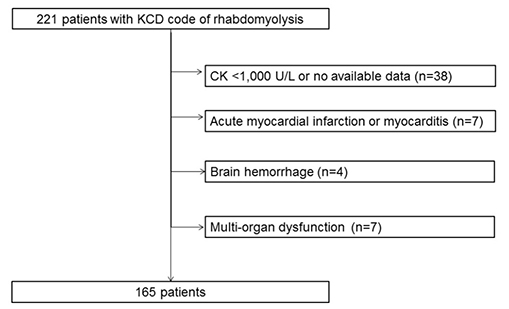
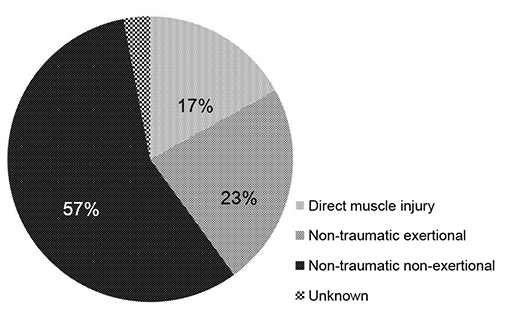
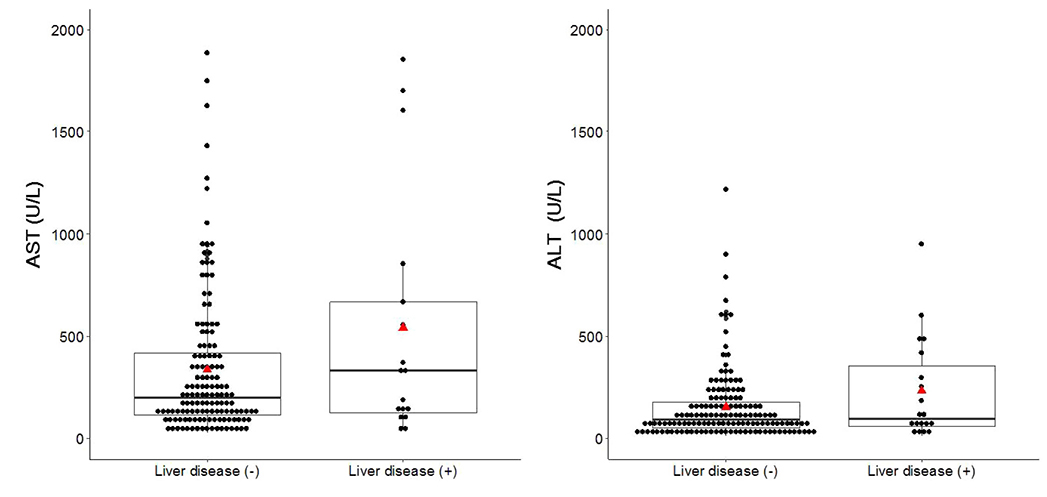
Among the 165 patients with rhabdomyolysis, 19 had concurrent liver disease. The median peak AST was higher in the group with concurrent liver disease (332 U/L [interquartile range (IQR), 127-1,604] vs. 219 U/L [IQR, 115-504]). In addition, the median peak ALT was higher in the group with concurrent liver disease (107 U/L [IQR, 74-418] vs. 101 U/L [IQR, 56-218]). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in both enzymes between the two groups. The median peak AST level was significantly higher in those with rhabdomyolysis than in those with alcoholic liver disease (221 U/L [IQR, 118-553] vs. 103 U/L [IQR, 59-206]), but the median peak ALT was not significantly different (102 U/L [IQR, 58-222] vs. 51 U/L [IQR, 26-117]).
CONCLUSIONS
Rhabdomyolysis showed an elevated AST-dominant aminotransferase level, which is not different according to concurrent liver disease. Therefore, it is recommended that rhabdomyolysis be considered first in cases of elevated aminotransferase levels in patients with a suspicious skeletal muscle injury.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The effect of adenosine triphosphate on propofol-induced myopathy in rats: a biochemical and histopathological evaluation
Kezban Tuna Ozkaloglu Erdem, Zehra Bedir, Irem Ates, Ufuk Kuyrukluyildiz, Taha Abdulkadir Coban, Gulce Naz Yazici, Yusuf Kemal Arslan, Zeynep Suleyman, Halis Suleyman
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;25(1):69-77. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.1.69.
Reference
-
1. Pratt DS. Liver chemistry and function tests. In : Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, editors. Sleisenger and fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease. 10th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elevier Saunders;2016. p. 1245–1246.2. Lee GY, Lee H, Kim YJ. Rhabdomyolysis recognized after elevation of liver enzymes following prolonged urologic surgery with lateral decubitus position: A case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2011; 61:341–343.
Article3. Nathwani RA, Pais S, Reynolds TB, Kaplowitz N. Serum alanine aminotransferase in skeletal muscle diseases. Hepatology. 2005; 41:380–382.
Article4. Weibrecht K, Dayno M, Darling C, Bird SB. Liver aminotransferases are elevated with rhabdomyolysis in the absence of significant liver injury. J Med Toxicol. 2010; 6:294–300.
Article5. Wroblewski F. The clinical significance of alterations in transaminase activities of serum and other body fluids. Adv Clin Chem. 1958; 1:313–351.6. Liangpunsakul S, Qi R, Crabb DW, Witzmann F. Relationship between alcohol drinking and aspartate aminotransferase:alanine aminotransferase (AST:ALT) ratio, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), and apolipoprotein A1 and B in the U.S. population. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2010; 71:249–252.
Article7. Nyblom H, Björnsson E, Simrén M, Aldenborg F, Almer S, Olsson R. The AST/ALT ratio as an indicator of cirrhosis in patients with PBC. Liver Int. 2006; 26:840–845.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rhabdomyolysis recognized after elevation of liver enzymes following prolonged urologic surgery with lateral decubitus position: A case report
- Bullae and Sweet Gland Necrosis Concurrent with Nontraumatic Rhabdomyolysis in a Non-comatose Patient after Alcohol and Drug Intoxication
- The Clinical Usefulness of Serum Aminotransferase Activities for Predicting Fatty Liver in Obese Children
- Clinical Characteristics of Nontraumatic Rhabdomyolysis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
- Liver function in Clonorchis sinensis-infected rabbits