Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2019 Sep;23(3):264-269. 10.13104/imri.2019.23.3.264.
Cavernous Hemangioma of the Gallbladder: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. shinshlee@naver.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2459881
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2019.23.3.264
Abstract
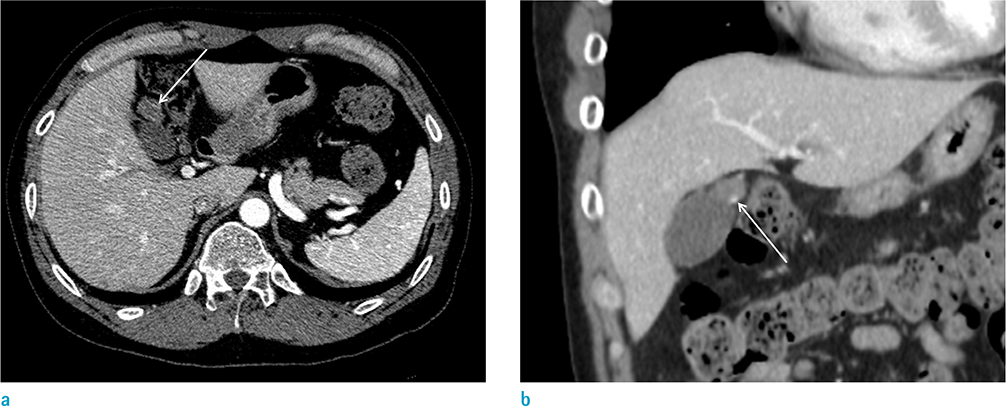
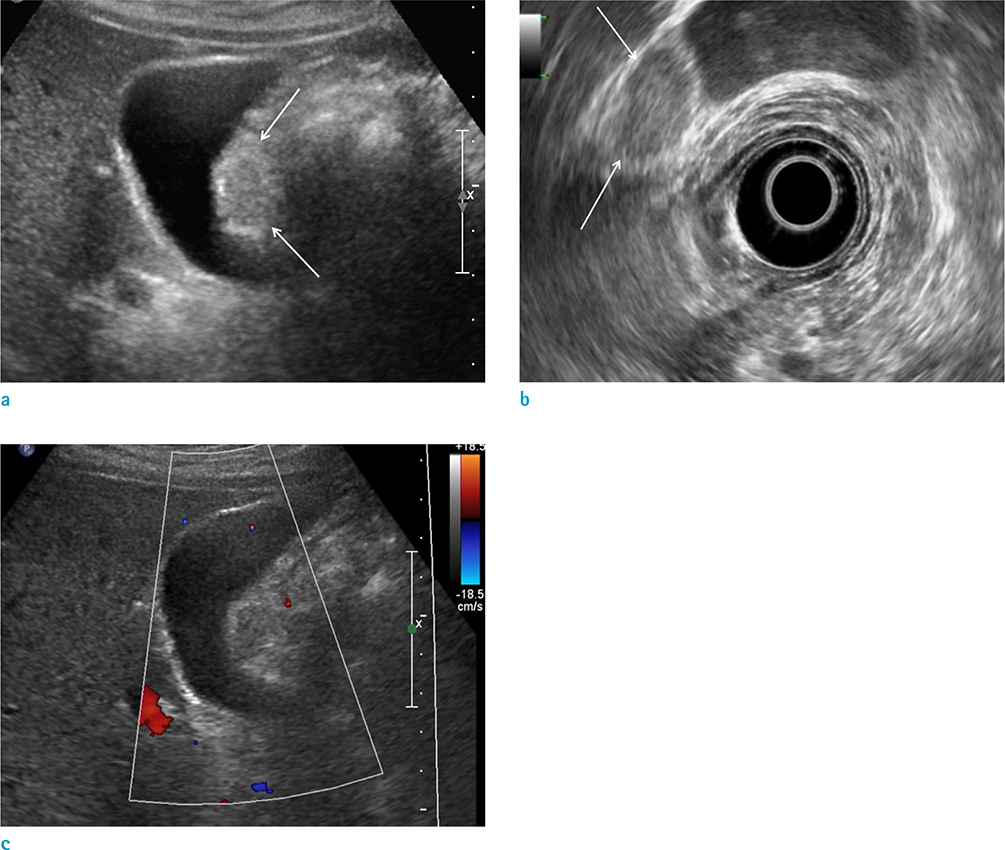
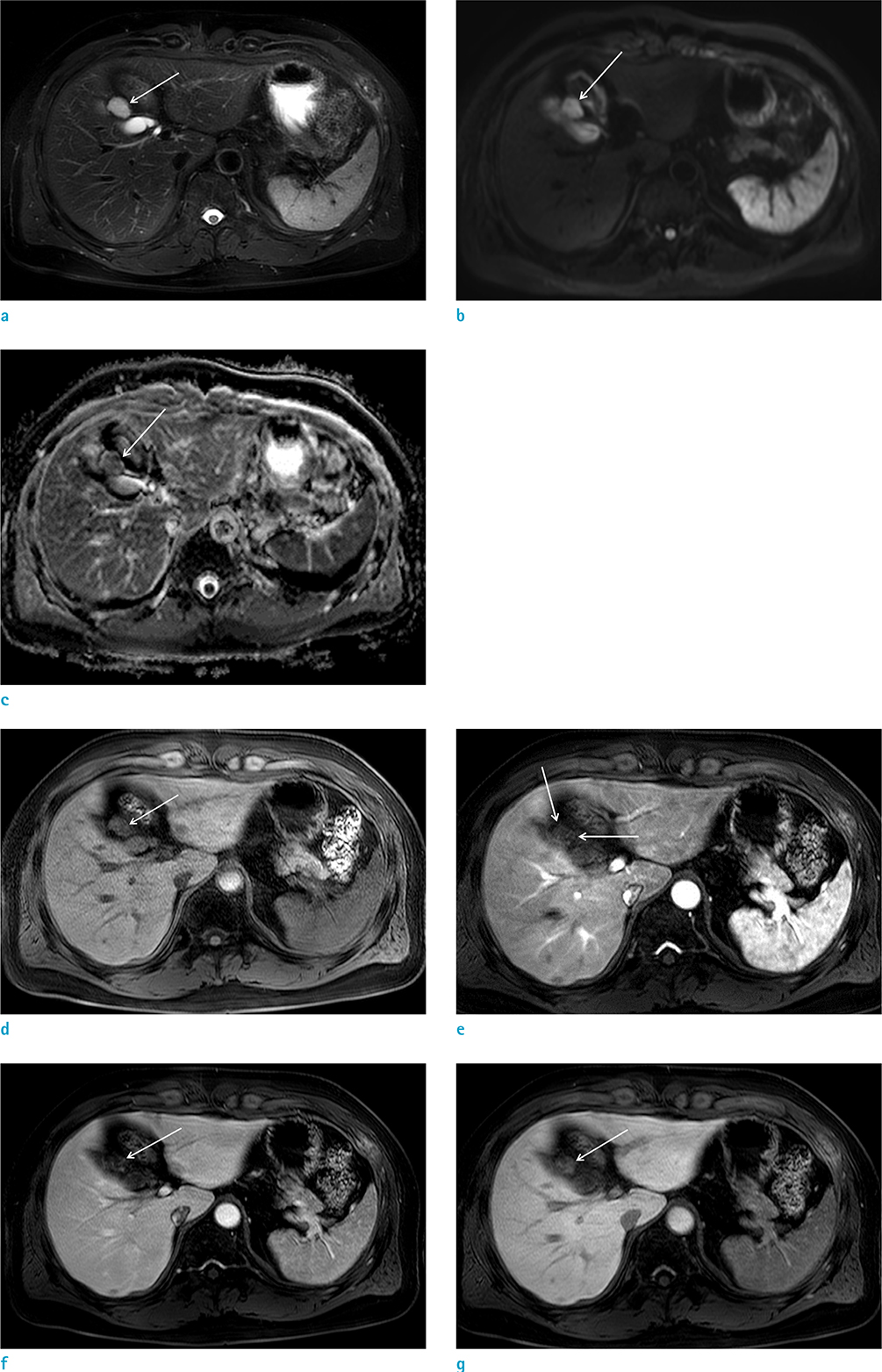
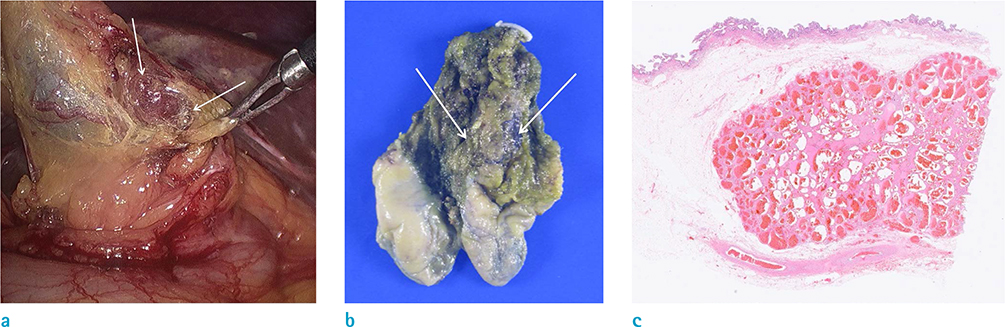
- Cavernous hemangioma of the gallbladder is an extremely rare benign tumor. The tumor has only a few cases being reported in literature. However, to the best of our knowledge, no reports focusing on the MRI findings of cavernous hemangioma of the gallbladder have been published. This study reports a case of gallbladder hemangioma with pathologic and radiologic reviews, including MRI findings.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Crucitti A, La Greca A, Antinori A, Antonacci V, Magistrelli P. Cavernous hemangioma of the gallbladder. Case report and review of the literature. Tumori. 2005; 91:432–443.
Article2. Akama Y, Mizuguchi Y, Mamada Y, et al. A case of cavernous hemangioma of the gallbladder treated with single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Int Surg. 2016; 101:431–436.
Article3. Anderson SW, Kruskal JB, Kane RA. Benign hepatic tumors and iatrogenic pseudotumors. Radiographics. 2009; 29:211–229.
Article4. Melson GL, Reiter F, Evens RG. Tumorous conditions of the gallbladder. Semin Roentgenol. 1976; 11:269–282.
Article5. Jones WP, Keller FS, Odrezin GT, Kelly DR. Venous hemangioma of the gallbladder. Gastrointest Radiol. 1987; 12:319–321.
Article6. Catalano OA, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, et al. MR imaging of the gallbladder: a pictorial essay. Radiographics. 2008; 28:135–155. quiz 324.
Article7. Levy AD, Murakata LA, Rohrmann CA Jr. Gallbladder carcinoma: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2001; 21:295–314. questionnaire, 549–255.
Article8. Choi WS, Kim SH, Lee ES, et al. CT findings of gallbladder metastases: emphasis on differences according to primary tumors. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:334–345.
Article9. Ishida M, Shiomi H, Naka S, Tani T, Okabe H. Leiomyoma of the gallbladder in a patient with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor in the liver: a case report with differential diagnostic considerations. Oncol Lett. 2012; 4:1171–1173.
Article10. Botsford A, McKay K, Hartery A, Hapgood C. MRCP imaging of duplicate gallbladder: a case report and review of the literature. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015; 37:425–429.
Article