Blood Res.
2019 Sep;54(3):210-217. 10.5045/br.2019.54.3.210.
Clinical features and treatment outcomes of Hodgkin lymphoma: A retrospective review in a Malaysian tertiary hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Haematology, Hospital Sultanah Aminah, Ministry of Health Malaysia, Johor Bahru, Malaysia. coolrontin@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Hospital Enche' Besar Hajjah Khalsom, Ministry of Health Malaysia, Kluang, Johor, Malaysia.
- KMID: 2459387
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2019.54.3.210
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is a clinicopathologically unique, aggressive lymphoma arising from germinal center B-cells and is one of the most curable hematological malignancies. This study aimed to determine the clinical course, treatment regimens, response rates, and survival data of patients diagnosed with cHL in a tertiary center.
METHODS
A retrospective review was conducted to include patients with a diagnosis of cHL from 2013 to 2017. Data of demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment regimens, and outcomes were collected and analyzed.
RESULTS
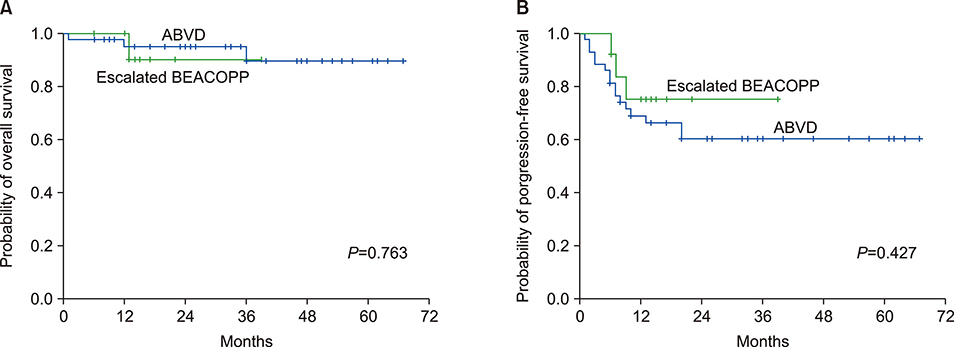
We recruited 94 patients with a median age of 27.0 [interquartile range (IQR), 12] years. Most of the patients were male (61.7%) and 73.4% were ethnic Malay. Nodular sclerosis was the most common histology (77.6%), followed by mixed cellularity (6.4%) and others (16%). The median follow-up time was 28.0 (IQR, 32) months. All patients received chemotherapy but only 13.8% received radiotherapy as consolidation. The doxorubicin-bleomycin-vinblastine-dacarbazine regimen was the most common (85.1%), followed by the escalated bleomycin-etoposide-doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide-vincristineprednisolone-procarbazine regimen (14.9%). Following treatment, 76.1% of patients achieved complete response. The 2-year overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) of the entire cohort were 96.5% and 71.1%, respectively. The 2-year OS and PFS for advanced-stage disease were 93.9% and 62.8%, compared to 100% and 82.7% for early-stage disease, respectively (P=0.252 and P=0.052, respectively).
CONCLUSION
This study provides insight into the clinical presentation and treatment outcomes among patients with cHL in Malaysia. A longer study duration is required to identify OS and PFS benefits and treatment-related complications for different chemotherapeutic regimens.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Cancer stat facts: Hodgkin lymphoma, 2018. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute;2018. Accessed March 20, 2019. at https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/hodg.html.2. Thomas RK, Re D, Zander T, Wolf J, Diehl V. Epidemiology and etiology of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2002; 13 Suppl 4:147–152.
Article3. Kuppers R. New insights in the biology of Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012; 2012:328–334.
Article4. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2017.5. Canellos GP, Niedzwiecki D, Johnson JL. Long-term follow-up of survival in Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2390–2391.
Article6. Spinner MA, Advani RH. Risk-adapted therapy for advancedstage Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2018; 2018:200–206.
Article7. Azizah AM, Nor Saleha IT, Noor Hasimah A, Asmah ZA, Mastulu W. Malaysian National cancer registry report 2007 – 2011. Putrajaya, Malaysia: National Cancer Institute, Ministry of Health Malaysia;2016. Accessed March 20, 2019. at https://www.crc.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/documents/report/MNCRRrepor2007-2011.pdf.8. Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff K, Smithers DW, Tubiana M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin's Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971; 31:1860–1861.9. Shamoon RP, Ali MD, Shabila NP. Overview and outcome of Hodgkin's Lymphoma: experience of a single developing country's oncology centre. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0195629.
Article10. Hasenclever D, Diehl V. A prognostic score for advanced Hodgkin's disease. International Prognostic Factors Project on Advanced Hodgkin's Disease. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:1506–1514.11. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:579–586.
Article12. Law MF, Ng TY, Chan HN, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of Hodgkin's lymphoma in Hong Kong Chinese. Arch Med Sci. 2014; 10:498–504.
Article13. Shanbhag S, Ambinder RF. Hodgkin lymphoma: a review and update on recent progress. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:116–132.
Article14. Bazzeh F, Rihani R, Howard S, Sultan I. Comparing adult and pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma in the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, 1988-2005: an analysis of 21 734 cases. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010; 51:2198–2207.
Article15. Avagyan A, Danielyan S, Voskanyan A, et al. Treating adults with Hodgkin lymphoma in the developing world: a hospital-based cohort study from Armenia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016; 17:101–104.
Article16. Shafi RG, Al-Mansour MM, Kanfar SS, et al. Hodgkin lymphoma outcome: a retrospective study from 3 tertiary centers in Saudi Arabia. Oncol Res Treat. 2017; 40:288–292.
Article17. Arya LS, Dinand V, Thavaraj V, et al. Hodgkin's disease in Indian children: outcome with chemotherapy alone. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2006; 46:26–34.
Article18. Jain S, Kapoor G, Bajpai R. ABVD-based therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma in children and adolescents: lessons learnt in a tertiary care oncology center in a developing country. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016; 63:1024–1030.
Article19. Meyer RM, Gospodarowicz MK, Connors JM, et al. ABVD alone versus radiation-based therapy in limited-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:399–408.
Article20. Brockelmann PJ, Sasse S, Engert A. Balancing risk and benefit in early-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2018; 131:1666–1678.
Article21. Johnson P, Federico M, Kirkwood A, et al. Adapted treatment guided by interim PET-CT scan in advanced Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:2419–2429.
Article22. Gallamini A, Tarella C, Viviani S, et al. Early chemotherapy intensification with escalated BEACOPP in patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma with a positive interim positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan after two ABVD cycles: long-term results of the GITIL/FIL HD 0607 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:454–462.
Article23. Merli F, Luminari S, Gobbi PG, et al. Long-term results of the HD2000 trial comparing ABVD versus BEACOPP versus COPP-EBV-CAD in untreated patients with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma: a study by Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:1175–1181.
Article24. Carde P, Karrasch M, Fortpied C, et al. Eight cycles of ABVD versus four cycles of BEACOPPescalated plus four cycles of BEACOPPbaseline in stage III to IV, international prognostic score ≥ 3, high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma: first results of the phase III EORTC 20012 intergroup trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:2028–2036.
Article25. Viviani S, Zinzani PL, Rambaldi A, et al. ABVD versus BEACOPP for Hodgkin's lymphoma when high-dose salvage is planned. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:203–212.
Article26. Cerci JJ, Pracchia LF, Linardi CC, et al. 18F-FDG PET after 2 cycles of ABVD predicts event-free survival in early and advanced Hodgkin lymphoma. J Nucl Med. 2010; 51:1337–1343.
Article27. Engert A, Goergen H, Markova J, et al. Reduced-intensity chemotherapy in patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma: updated results of the open-label, international, randomised phase 3 HD15 trial by the German Hodgkin Study Group. HemaSphere. 2017; 1:e5.