Endocrinol Metab.
2019 Sep;34(3):268-274. 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.268.
Changes in Thyroid Peroxidase and Thyroglobulin Antibodies Might Be Associated with Graves' Disease Relapse after Antithyroid Drug Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea. hegletter@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2458629
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.268
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Graves' disease (GD) is an autoimmune thyroid disorder caused by antibodies stimulating the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor. TSH receptor antibody (TRAb) measurement is useful for predicting GD relapse after antithyroid drug (ATD) treatment. However, the association of other thyroid autoantibodies with GD relapse remains obscure.
METHODS
This retrospective study enrolled patients with GD who were initially treated with ATD. TRAb, thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb), and thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb) were measured at the initial diagnosis and at the time of ATD discontinuation.
RESULTS
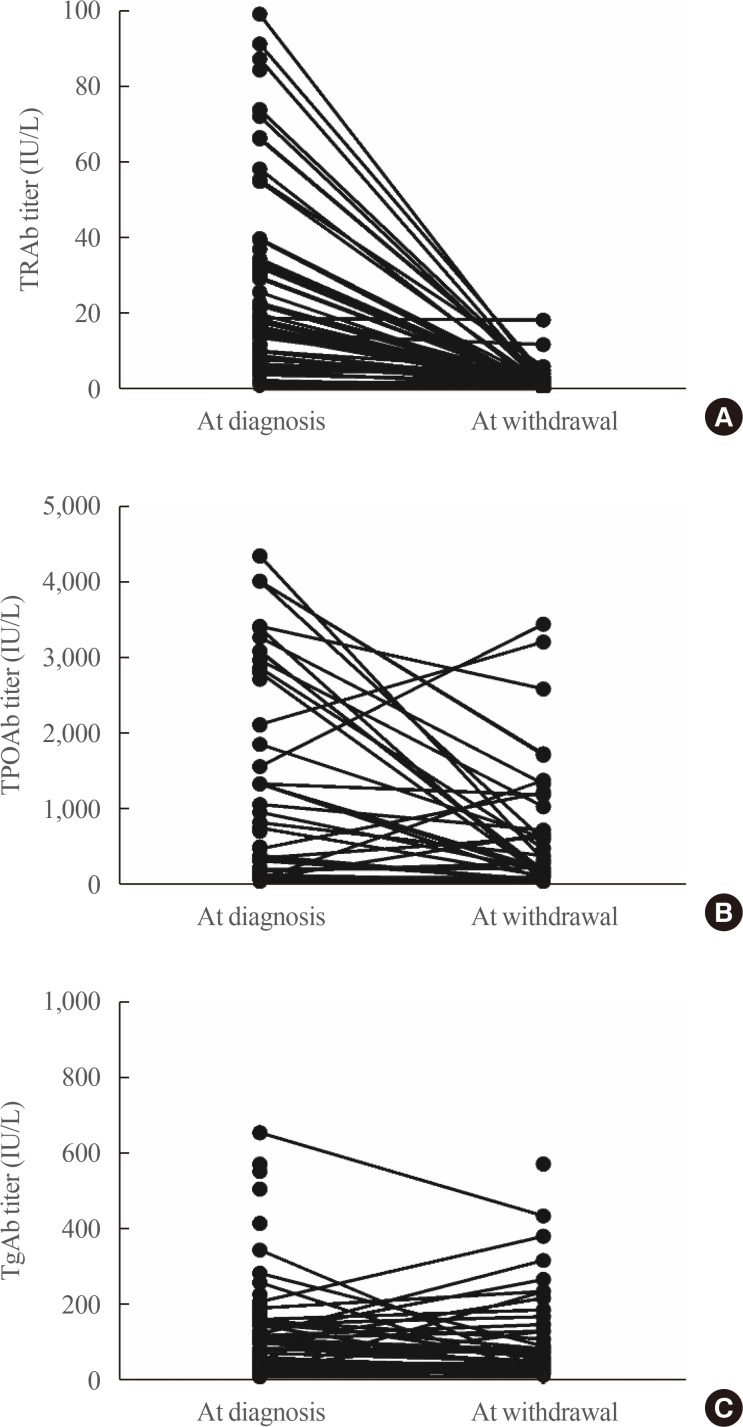
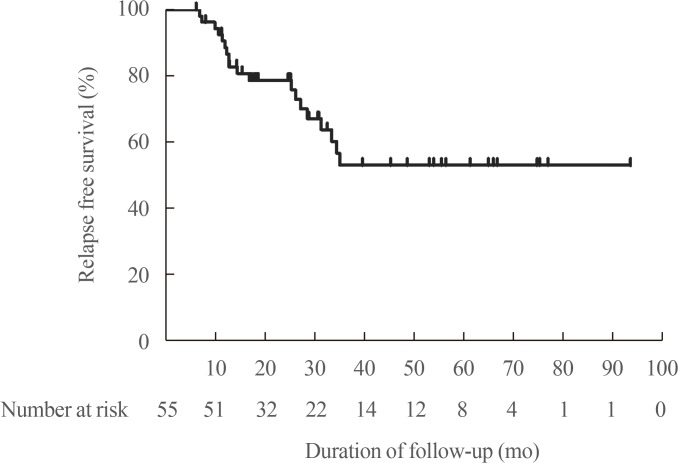
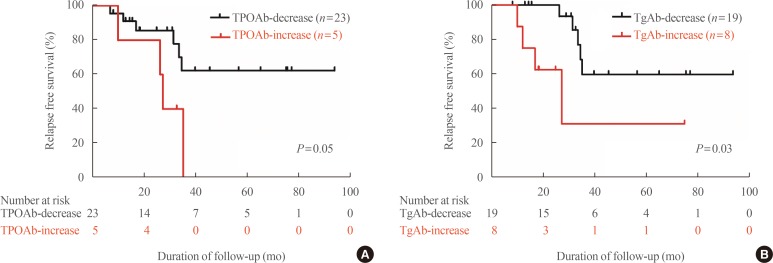
A total of 55 patients were enrolled. The mean age was 49.7 years, and 39 patients (70.9%) were female. Antibody positivity at diagnosis was 90.9%, 69.1%, and 61.9% for TRAb, TPOAb, TgAb, respectively. Median ATD treatment period was 15.1 months. At the time of ATD withdrawal, TRAb titers decreased uniformly overall. Conversely, TPOAb and TgAb showed various changes. After withdrawal of ATD, 19 patients (34.5%) experienced relapse. No clinical features or laboratory results were significantly related to relapse in the overall patient group. However, in the TPOAb positive group at diagnosis, increasing titer of TPOAb or TgAb after ATD treatment was significantly and independently related to relapse free survival (TPOAb: hazard ratio [HR], 17.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.66 to 195.43; P=0.02) (TgAb: HR, 5.73; 95% CI, 1.21 to 27.26; P=0.03).
CONCLUSION
Changes in TPOAb or TgAb titers during treatment might be useful for predicting relapse after ATD treatment in patients with positive TPOAb at diagnosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 (
PD-L1 ) gene Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Graves’ Disease and Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis in Korean Patients
Jee Hee Yoon, Min-ho Shin, Hee Nam Kim, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A Ram Hong, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):599-606. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.965.Usefulness of Real-Time Quantitative Microvascular Ultrasonography for Differentiation of Graves’ Disease from Destructive Thyroiditis in Thyrotoxic Patients
Han-Sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Chai-Ho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang, Dong-Jun Lim
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):323-332. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1413.
Reference
-
1. Burch HB, Cooper DS. Management of Graves disease: a review. JAMA. 2015; 314:2544–2554. PMID: 26670972.2. Struja T, Fehlberg H, Kutz A, Guebelin L, Degen C, Mueller B, et al. Can we predict relapse in Graves' disease? Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2017; 176:87–97. PMID: 27780830.
Article3. Laurberg P. Remission of Graves' disease during anti-thyroid drug therapy. Time to reconsider the mechanism? Eur J Endocrinol. 2006; 155:783–786. PMID: 17132745.
Article4. Guilhem I, Massart C, Poirier JY, Maugendre D. Differential evolution of thyroid peroxidase and thyrotropin receptor antibodies in Graves' disease: thyroid peroxidase antibody activity reverts to pretreatment level after carbimazole withdrawal. Thyroid. 2006; 16:1041–1045. PMID: 17042691.
Article5. Moon JH, Yi KH. The diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism in Korea: consensus report of the Korean Thyroid Association. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2013; 28:275–279. PMID: 24396691.
Article6. Laurberg P, Krejbjerg A, Andersen SL. Relapse following antithyroid drug therapy for Graves' hyperthyroidism. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014; 21:415–421. PMID: 25111942.
Article7. Wiersinga WM. Graves' disease: can it be cured? Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2019; 34:29–38. PMID: 30912336.
Article9. Liu J, Fu J, Xu Y, Wang G. Antithyroid drug therapy for Graves' disease and implications for recurrence. Int J Endocrinol. 2017; 2017:3813540. PMID: 28529524.
Article10. Kwon H, Kim WG, Jang EK, Kim M, Park S, Jeon MJ, et al. Usefulness of measuring thyroid stimulating antibody at the time of antithyroid drug withdrawal for predicting relapse of Graves disease. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016; 31:300–310. PMID: 27118279.
Article11. Carella C, Mazziotti G, Sorvillo F, Piscopo M, Cioffi M, Pilla P, et al. Serum thyrotropin receptor antibodies concentrations in patients with Graves' disease before, at the end of methimazole treatment, and after drug withdrawal: evidence that the activity of thyrotropin receptor antibody and/or thyroid response modify during the observation period. Thyroid. 2006; 16:295–302. PMID: 16571093.
Article12. Choi HS, Yoo WS. Free thyroxine, anti-thyroid stimulating hormone receptor antibody titers, and absence of goiter were associated with responsiveness to methimazole in patients with new onset Graves' disease. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017; 32:281–287. PMID: 28685517.
Article13. Huh JE, Suk JH, Kim MK, Choi IJ, Son SM, Kim IJ, et al. Clinical usefulness of the second generation TSH-binding inhibitory immunoglobulin assay using recombinant human TSH receptor in patients with Graves' disease. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008; 23:179–185.
Article14. Takaichi Y, Tamai H, Honda K, Nagai K, Kuma K, Nakagawa T. The significance of antithyroglobulin and antithyroidal microsomal antibodies in patients with hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease treated with antithyroidal drugs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989; 68:1097–1100. PMID: 2470772.
Article15. Smycznyska J, Cyniak-Magierska A, Stasiak M, Karbownik-Lewinska M, Lewinski A. Persistent remission of Graves' disease or evolution from Graves' disease to Hashimoto's thyroiditis in childhood: a report of 6 cases and clinical implications. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2014; 35:335–341. PMID: 25275265.16. Schott M, Eckstein A, Willenberg HS, Nguyen TB, Morgenthaler NG, Scherbaum WA. Improved prediction of relapse of Graves' thyrotoxicosis by combined determination of TSH receptor and thyroperoxidase antibodies. Horm Metab Res. 2007; 39:56–61. PMID: 17226115.
Article17. Hamada N, Ito K, Mimura T, Ishikawa N, Momotani N, Noh J, et al. Retrospective reevaluation of the significance of thyroid microsomal antibody in the treatment of Graves' disease. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1987; 114:328–335. PMID: 2436426.18. Romaldini JH, Bromberg N, Werner RS, Tanaka LM, Rodrigues HF, Werner MC, et al. Comparison of effects of high and low dosage regimens of antithyroid drugs in the management of Graves' hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983; 57:563–570. PMID: 6192139.
Article19. Weetman AP. The immunomodulatory effects of antithyroid drugs. Thyroid. 1994; 4:145–146. PMID: 7522682.
Article20. Marcocci C, Chiovato L, Mariotti S, Pinchera A. Changes of circulating thyroid autoantibody levels during and after the therapy with methimazole in patients with Graves' disease. J Endocrinol Invest. 1982; 5:13–19. PMID: 6896520.21. Chiovato L, Vitti P, Lombardi A, Kohn LD, Pinchera A. Expression of the microsomal antigen on the surface of continuously cultured rat thyroid cells is modulated by thyrotropin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985; 61:12–16. PMID: 3889033.
Article22. Stefanic M, Karner I. Thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies are associated with a lesser likelihood of late reversion to hyperthyroidism after successful non-ablative treatment of Graves' disease in Croatian patients. J Endocrinol Invest. 2014; 37:71–77. PMID: 24464453.
Article