J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2017 Sep;60(5):527-533. 10.3340/jkns.2016.1111.009.
The Role of Adjuvant Treatment in Patients with High-Grade Meningioma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. chaeyong@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2457959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.1111.009
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the efficacy of adjuvant treatment in patients with high-grade meningioma.
METHODS
A retrospective analysis was performed for patients with high-grade meningioma, World Health Organization grade 2 or 3, in a single center between 2003 and 2014. The patients were reviewed according to age at diagnosis, sex, the location of meningioma, degree of tumor resection, histological features, and type of adjuvant treatment. These factors were analyzed by Firth logistic regression analyses.
RESULTS
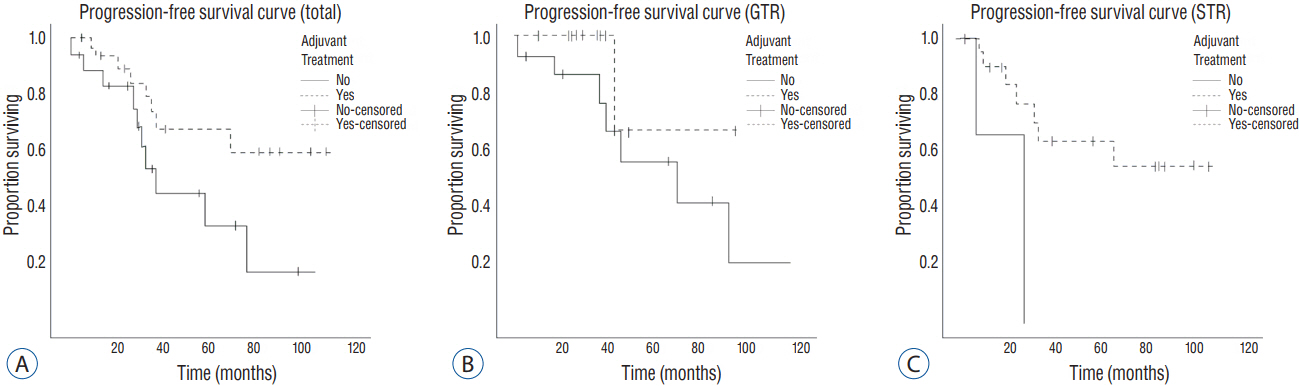
Fifty-three patients with high-grade meningioma were enrolled. Thirty-four patients received adjuvant treatment; conventional radiotherapy or radiosurgery. Clinical follow-up ranged from 13-113 months with a median follow-up of 35.5 months. Gross total removal (GTR), Simpson grade 1 or 2, was achieved in 29 patients and, among them, 13 patients received adjuvant treatment. In the other 24 patients with non-GTR, conventional adjuvant radiotherapy and radiosurgery were performed in 11 and 10 patients, respectively. The other 3 patients did not receive any adjuvant treatment. Radiation-related complications did not occur. Of the 53 patients, 19 patients had suffered from recurrence. The recurrence rate in the adjuvant treatment group was 23.5% (8 out of 34). On the other hand, the rate for the non-adjuvant treatment group was 57.9% (11 out of 19) (odds ratio [OR]=0.208, p=0.017). In the GTR group, the recurrence rate was 7.5% (1 out of 13) for patients with adjuvant treatment and 50% (8 out of 16) for patients without adjuvant treatment (OR=0.121, p=0.04).
CONCLUSION
Adjuvant treatment appears to be safe and effective, and could lead to a lower recurrence rate in high-grade meningioma, regardless of the extent of removal. Our results might be used as a reference for making decisions when planning adjuvant treatments for patients with high-grade meningioma after surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Aghi MK, Carter BS, Cosgrove GR, Ojemann RG, Amin-Hanjani S, Martuza RL, et al. Long-term recurrence rates of atypical meningiomas after gross total resection with or without postoperative adjuvant radiation. Neurosurgery. 64:56–60. discussion 60. 2009.
Article2. Dijkstra M, van Nieuwenhuizen D, Stalpers LJ, Wumkes M, Waagemans M, Vandertop WP, et al. Late neurocognitive sequelae in patients with WHO grade I meningioma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 80:910–915. 2009.
Article3. Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, Kruchko C. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009. Neuro Oncol. 14(Suppl 5):v1–v49. 2012.
Article4. Durand A, Labrousse F, Jouvet A, Bauchet L, Kalamaridès M, Menei P, et al. WHO grade II and III meningiomas: a study of prognostic factors. J Neurooncol. 95:367–375. 2009.
Article5. Dziuk TW, Woo S, Butler EB, Thornby J, Grossman R, Dennis WS, et al. Malignant meningioma: an indication for initial aggressive surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy. J Neurooncol. 37:177–188. 1998.6. Hardesty DA, Wolf AB, Brachman DG, McBride HL, Youssef E, Nakaji P, et al. The impact of adjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery on atypical meningioma recurrence following aggressive microsurgical resection. J Neurosurg. 119:475–481. 2013.
Article7. Hasan S, Young M, Albert T, Shah AH, Okoye C, Bregy A, et al. The role of adjuvant radiotherapy after gross total resection of atypical meningiomas. World Neurosurg. 83:808–815. 2015.
Article8. Kaur G, Sayegh ET, Larson A, Bloch O, Madden M, Sun MZ, et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy for atypical and malignant meningiomas: a systematic review. Neuro Oncol. 16:628–636. 2014.
Article9. Komotar RJ, Iorgulescu JB, Raper DMS, Holland EC, Beal K, Bilsky MH, et al. The role of radiotherapy following gross-total resection of atypical meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 117:679–686. 2012.
Article10. Lawrence YR, Li XA, el Naqa I, Hahn CA, Marks LB, Merchant TE, et al. Radiation dose-volume effects in the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76(3 Suppl):S20–S27. 2010.
Article11. Lee KD, DePowell JJ, Air EL, Dwivedi AK, Kendler A, McPherson CM. Atypical meningiomas: is postoperative radiotherapy indicated? Neurosurg Focus. 35:E15. 2013.
Article12. Mair R, Morris K, Scott I, Carroll TA. Radiotherapy for atypical meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 115:811–819. 2011.
Article13. Palma L, Celli P, Franco C, Cervoni L, Cantore G. Long-term prognosis for atypical and malignant meningiomas: a study of 71 surgical cases. J Neurosurg. 86:793–800. 1997.
Article14. Park HJ, Kang HC, Kim IH, Park SH, Kim DG, Park CK, et al. The role of adjuvant radiotherapy in atypical meningioma. J Neurooncol. 115:241–247. 2013.
Article15. Poon MT, Fung LH, Pu JK, Leung GK. Outcome comparison between younger and older patients undergoing intracranial meningioma resections. J Neurooncol. 114:219–227. 2013.
Article16. Provenzale JM, Ison C, DeLong D. Bidimensional measurements in brain tumors: assessment of interobserver variability. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 193:W515–W522. 2009.
Article17. Sanai N, Sughrue ME, Shangari G, Chung K, Berger MS, McDermott MW. Risk profile associated with convexity meningioma resection in the modern neurosurgical era. J Neurosurg. 112:913–919. 2010.
Article18. Saraf S, McCarthy BJ, Villano JL. Update on meningiomas. Oncologist. 16:1604–1613. 2011.
Article19. Simpson D. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 20:22–39. 1957.
Article20. Stessin AM, Schwartz A, Judanin G, Pannullo SC, Boockvar JA, Schwartz TH, et al. Does adjuvant external-beam radiotherapy improve outcomes for nonbenign meningiomas? A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–based analysis. J Neurosurg. 117:669–675. 2012.
Article21. van Nieuwenhuizen D, Klein M, Stalpers LJA, Leenstra S, Heimans JJ, Reijneveld JC. Differential effect of surgery and radiotherapy on neurocognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in WHO grade I meningioma patients. J Neurooncol. 84:271–278. 2007.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaplastic Meningioma: Clinical Characteristics, Prognostic Factors and Survival Outcome
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for meningioma
- Clinical Features and Treatment Outcome of Chordoid Meningiomas in a Single Institute
- Malignant Transformation of Meningioma With TERT Promoter Mutation: A Case Report
- Primary Extracranial Meningioma Mimicking Musculoskeletal Malignancy: A Case Report