Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Aug;43(4):530-534. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.4.530.
Subacute Combined Degeneration Caused by Nitrous Oxide Intoxication: A Report of Two Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. pmrdoc@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2457762
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.4.530
Abstract
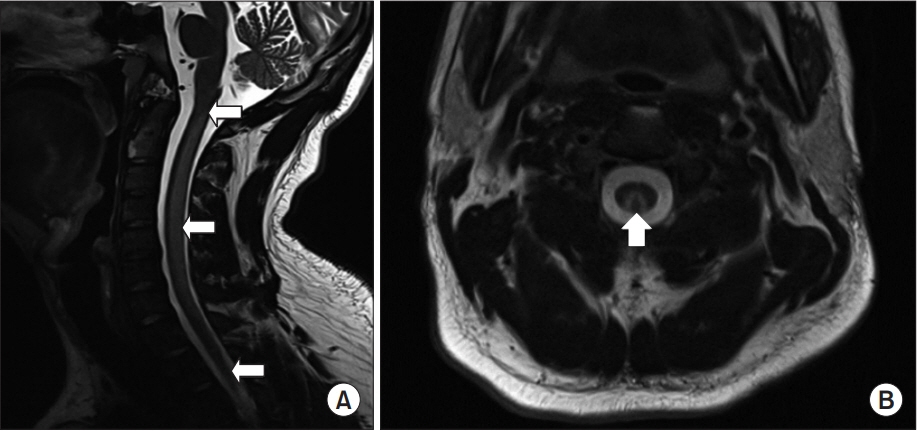
- We report two cases of subacute combined degeneration (SCD) caused by nitrous oxide (Nâ‚‚O) gas intoxication, which is rarely reported in Korea. Two patients recreationally inhaled Nâ‚‚O gas daily for several months. They presented with paresthesia of limbs, voiding difficulty, and gait disturbance. The initial vitamin Bâ‚â‚‚ levels were normal or decreased, but homocysteine levels of the two patients were increased. Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine showed T2-weighted hyperintensity in the bilateral dorsal columns of the cervical spinal cord. Electromyography and somatosensory evoked potential tests for both patients suggested posterior column lesion of the spinal cord combined with sensorimotor polyneuropathy. According to these findings, we concluded that the two patients had SCD. The patient's symptoms partially improved after cessation of Nâ‚‚O gas inhalation and the receiving of vitamin Bâ‚â‚‚ supplementation therapy. As the incidence of recreational Nâ‚‚O gas inhalation is increasing in Korea, physicians must be alert to the Nâ‚‚O induced SCD in patients presenting with progressive myelopathy.
MeSH Terms
-
Cervical Cord
Electromyography
Evoked Potentials, Somatosensory
Extremities
Gait
Homocysteine
Humans
Incidence
Inhalation
Korea
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Nitrous Oxide*
Paresthesia
Polyneuropathies
Recreation
Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord Diseases
Spine
Subacute Combined Degeneration*
Vitamin B 12
Vitamins
Homocysteine
Nitrous Oxide
Vitamin B 12
Vitamins
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Spectrum of nitrous oxide intoxication related neurological disorders in Korea: a case series and literature review
Jungsoo Lee, Yangmi Park, Hyunkee Kim, Nakhoon Kim, Wonjae Sung, Sanggon Lee, Jinseok Park
Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;23(2):108-116. doi: 10.14253/acn.2021.23.2.108.
Reference
-
1. Lin RJ, Chen HF, Chang YC, Su JJ. Subacute combined degeneration caused by nitrous oxide intoxication: case reports. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2011; 20:129–37.2. Hsu CK, Chen YQ, Lung VZ, His SC, Lo HC, Shyu HY. Myelopathy and polyneuropathy caused by nitrous oxide toxicity: a case report. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30:1016.3–6.
Article3. Katsaros VK, Glocker FX, Hemmer B, Schumacher M. MRI of spinal cord and brain lesions in subacute combined degeneration. Neuroradiology. 1998; 40:716–9.
Article4. Timms SR, Cure JK, Kurent JE. Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord: MR findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993; 14:1224–7.5. Shoults K. Case report: neurological complications of nitrous oxide abuse. B C Med J. 2016; 58:192–4.6. Pema PJ, Horak HA, Wyatt RH. Myelopathy caused by nitrous oxide toxicity. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:894–6.7. Ozkan FU, Kaysin MY, Boy FN, Ustun I, Aktas I. Progressive subacute combined degeneration: a severe relapse with dis-continuation of vitamin B12 treatment. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2016; 62:369–72.8. Vasconcelos OM, Poehm EH, McCarter RJ, Campbell WW, Quezado ZM. Potential outcome factors in subacute combined degeneration: review of observational studies. J Gen Intern Med. 2006; 21:1063–8.9. Singer MA, Lazaridis C, Nations SP, Wolfe GI. Reversible nitrous oxide-induced myeloneuropathy with pernicious anemia: case report and literature review. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37:125–9.
Article10. Kwoun YJ, Choi YJ, Oh JY, Park KD, Choi KG. Myeloneuropathy following chronic abuse of nitrous oxide. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2003; 21:432–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subacute Combined Degeneration and Pulmonary Thromboembolism due to Nitrous Oxide Inhalation for Recreational Use
- Unhappy End of ‘Happy Balloons’: Subacute Combined Degeneration Caused by Nitrous Oxide Gas
- Subacute Combined Degeneration with Involvement of Concurrent Anterior, Lateral, Posterior Column after Nitrous Oxide Exposure
- Subacute Combined Degeneration with Motor Neuropathy Following Nitrous Oxide Abuse
- Systematic Review of Vitamin B12 Regimen for Patient with Subacute Combined Degeneration of the Spinal Cord Following Nitrous Oxide Abuse