Ann Dermatol.
2018 Aug;30(4):462-464. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.4.462.
A Case of Moderate Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Psoriasis Treated with Secukinumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Section of Dermatology, Department of Biomedicine, Internal Medicine and Specialties (Di.Bi.MIS), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy. giuseppe.pistone@unipa.it
- KMID: 2457525
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.4.462
Abstract
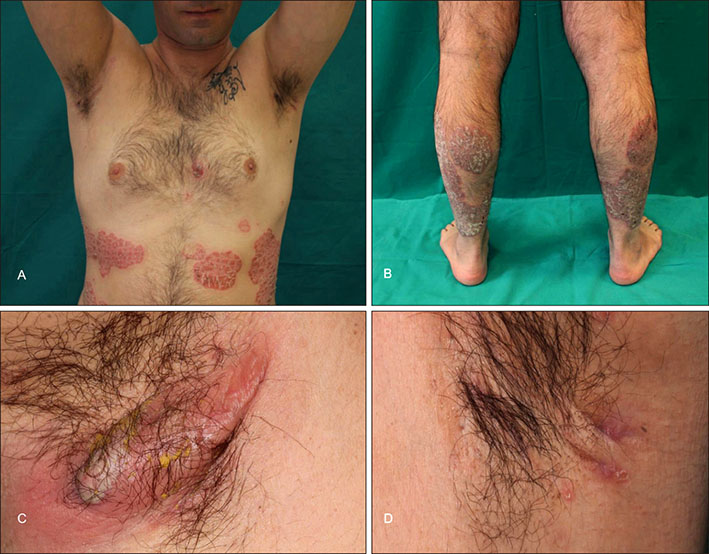
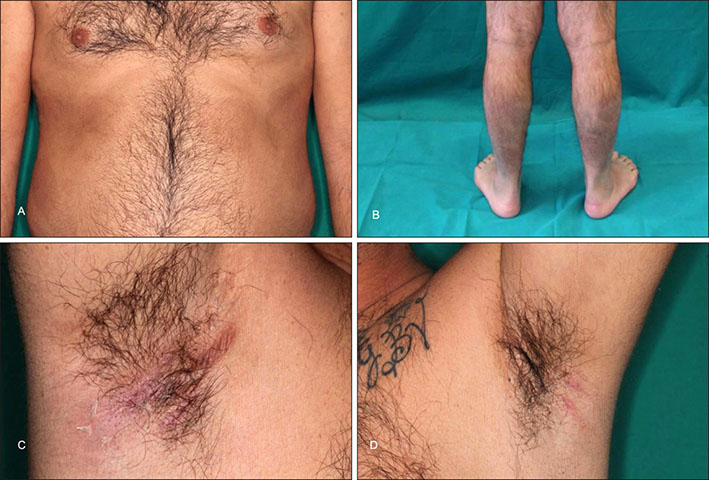
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a disorder of the apocrine gland causing a chronic, recurrent and painful inflammation. It is a disabilitating condition and, though many therapeutic options are available, the response is often ineffective in most cases and patients can present many recurrences with physical and psychological sequelae. Recent data had shown increased interleukin (IL)-17 serum levels in patients with HS. Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorder and new evidences have shown the role of Th17 cells in its pathogenesis and the therapeutic efficacy of anti-IL-17 antibodies. We present a case of a patient suffering from psoriasis and HS successfully treated with anti-IL-17 antibodies for both conditions. This is the first case report of HS treated with secukinumab.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Matusiak Ł, Szczęch J, Bieniek A, Nowicka-Suszko D, Szepietowski JC. Increased interleukin (IL)-17 serum levels in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: Implications for treatment with anti-IL-17 agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76:670–675.
Article2. Patel M, Cohen JM, Wright NA, Merola JF, Qureshi AA, Vleugels RA. Epidemiology of concomitant psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS): experience of a tertiary medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015; 73:701–702.
Article3. Lima AL, Karl I, Giner T, Poppe H, Schmidt M, Presser D, et al. Keratinocytes and neutrophils are important sources of proinflammatory molecules in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 174:514–521.
Article4. Lynde CW, Poulin Y, Vender R, Bourcier M, Khalil S. Interleukin 17A: toward a new understanding of psoriasis pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 71:141–150.
Article5. Bongiorno MR, Pistone G, Doukaki S, Aricò M. Adalimumab for treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Dermatol Ther. 2008; 21:Suppl 2. S15–S20.
Article6. Pistone G, La Vecchia M, Pistone A, Bongiorno MR. Achilles tendon ultrasonography may detect early features of psoriatic arthropathy in patients with cutaneous psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2014; 171:1220–1222.
Article7. Garnock-Jones KP. Secukinumab: a review in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015; 16:323–330.
Article8. Miller IM, Ellervik C, Vinding GR, Zarchi K, Ibler KS, Knudsen KM, et al. Association of metabolic syndrome and hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2014; 150:1273–1280.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Patients with Metabolic Comorbidities
- Skin Infection Caused by Serratia marcescens in an Immunocompetent Patient with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Sqamous Cell Carcinoma Arising from Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- A Case of Nummular Eczema-Like Eruption after Secukinumab Treatment