Ann Lab Med.
2020 Jan;40(1):76-79. 10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.76.
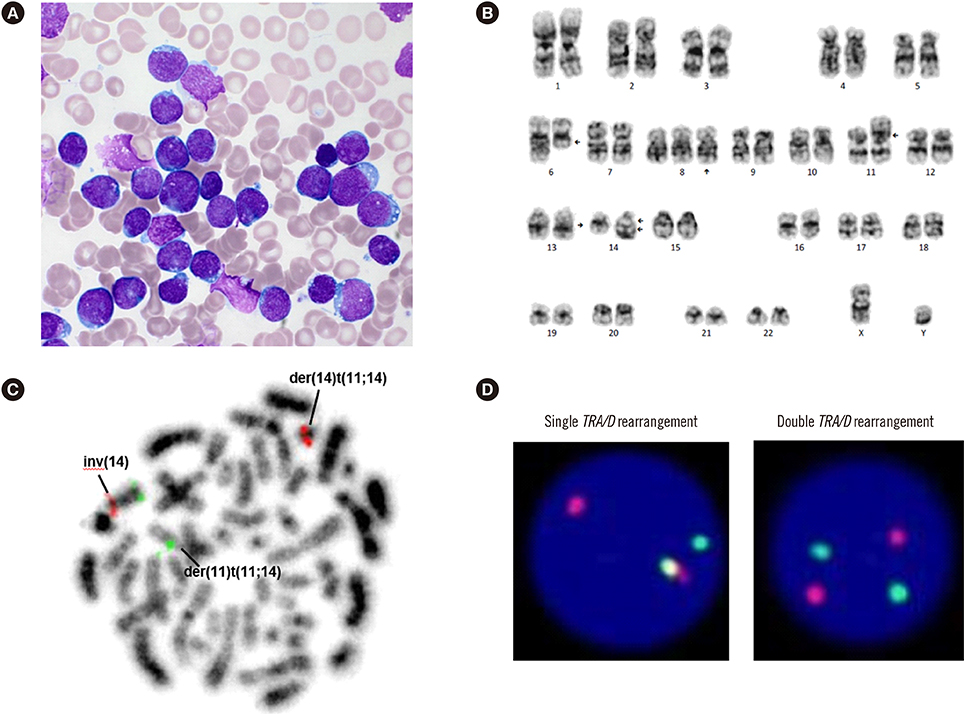
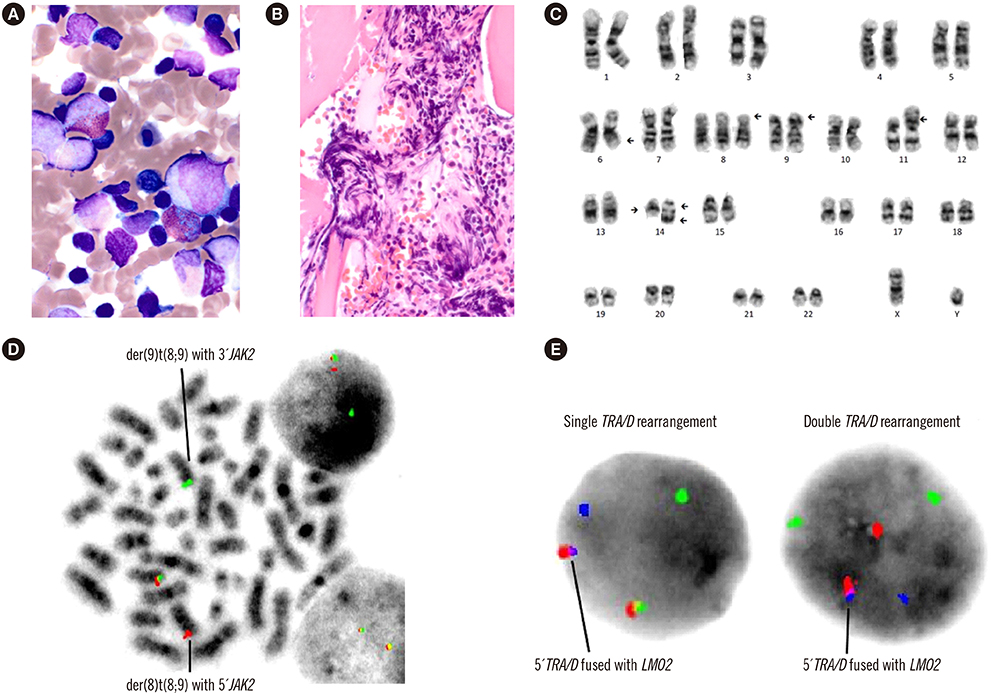
First Case of Double T-Cell Receptor Alpha/Delta Rearrangements of t(11;14) and inv(14) and Subsequent JAK2 Rearrangement in a Patient With T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ejseo@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2457498
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.76
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Belver L, Ferrando A. The genetics and mechanisms of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016; 16:494–507.
Article2. Chen B, Jiang L, Zhong ML, Li JF, Li BS, Peng LJ, et al. Identification of fusion genes and characterization of transcriptome features in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115:373–378.
Article3. Reiter A, Walz C, Watmore A, Schoch C, Blau I, Schlegelberger B, et al. The t(8;9)(p22;p24) is a recurrent abnormality in chronic and acute leukemia that fuses PCM1 to JAK2. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:2662–2667.4. Murati A, Gelsi-Boyer V, Adélaïde J, Perot C, Talmant P, Giraudier S, et al. PCM1-JAK2 fusion in myeloproliferative disorders and acute erythroid leukemia with t(8;9) translocation. Leukemia. 2005; 19:1692–1696.5. Liu Y, Easton J, Shao Y, Maciaszek J, Wang Z, Wilkinson MR, et al. The genomic landscape of pediatric and young adult T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2017; 49:1211–1218.
Article6. Wilkinson A, Walker DA, Smith NM, Calvert A, Monk AJ, Parkin CA. Inversion (14)(q11q32) in a patient with childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1996; 88:76–79.
Article7. Przybylski GK, Dik WA, Wanzeck J, Grabarczyk P, Majunke S, Martin-Subero JI, et al. Disruption of the BCL11B gene through inv(14)(q11.2q32.31) results in the expression of BCL11B-TRDC fusion transcripts and is associated with the absence of wild-type BCL11B transcripts in T-ALL. Leukemia. 2005; 19:201–208.
Article8. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2017. p. 78–79.9. Tang G, Sydney Sir, Weinberg O, Tam W, Sadigh S, Lake JI, et al. Hematopoietic neoplasms with 9p24/JAK2 rearrangement: a multicenter study. Mod Pathol. 2019; 32:490–498.
Article10. Girardi T, Vicente C, Cools J, De Keersmaecker K. The genetics and molecular biology of T-ALL. Blood. 2017; 129:1113–1123.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of CD7+, CD4-, CD8-, CD3-acute T cell lymphoblastic leukemia
- A Case of B-cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with the t(14;22)(q32;q11) Presenting Hyperleukocytosis
- Simultaneous Translocation of Both TCR Loci (14q11) with Rare Partner Loci (Xq22 and 12p13) in a Case of T-lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Simultaneous Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection of 7 Gene Rearrangements in Acute Leukemia
- Submicroscopic Deletions of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene (IGH) in Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia with IGH Rearrangements