Healthc Inform Res.
2019 Jul;25(3):201-211. 10.4258/hir.2019.25.3.201.
Deep Learning-Based Electrocardiogram Signal Noise Detection and Screening Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Informatics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. d.yoon.ajou@gmail.com
- 2Department of Biomedical Sciences, Graduate School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Cardiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 4Division of Trauma Surgery, Department of Surgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Software Convergence Engineering, College of Convergence Engineering, Kunsan National University, Gunsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2457472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2019.25.3.201
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Biosignal data captured by patient monitoring systems could provide key evidence for detecting or predicting critical clinical events; however, noise in these data hinders their use. Because deep learning algorithms can extract features without human annotation, this study hypothesized that they could be used to screen unacceptable electrocardiograms (ECGs) that include noise. To test that, a deep learning-based model for unacceptable ECG screening was developed, and its screening results were compared with the interpretations of a medical expert.
METHODS
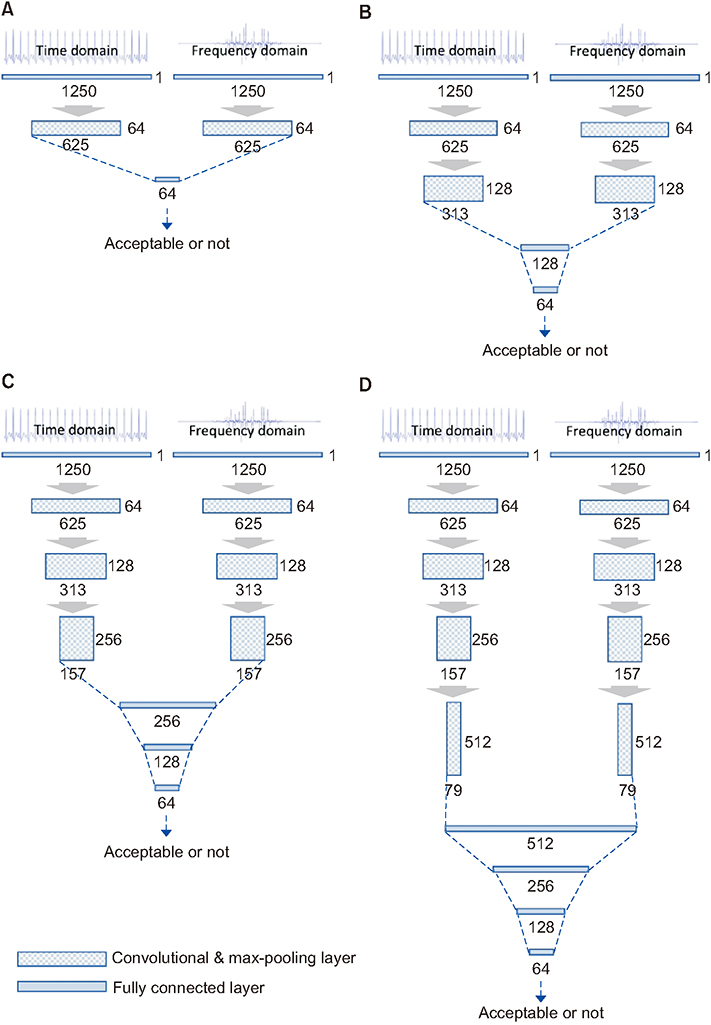
To develop and apply the screening model, we used a biosignal database comprising 165,142,920 ECG II (10-second lead II electrocardiogram) data gathered between August 31, 2016 and September 30, 2018 from a trauma intensive-care unit. Then, 2,700 and 300 ECGs (ratio of 9:1) were reviewed by a medical expert and used for 9-fold cross-validation (training and validation) and test datasets. A convolutional neural network-based model for unacceptable ECG screening was developed based on the training and validation datasets. The model exhibiting the lowest cross-validation loss was subsequently selected as the final model. Its performance was evaluated through comparison with a test dataset.
RESULTS
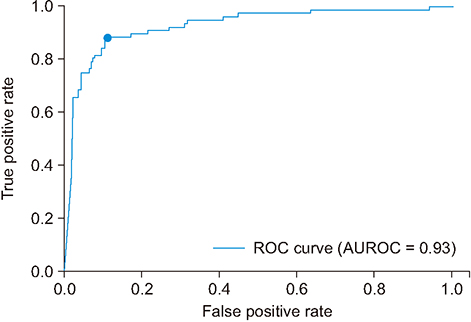
When the screening results of the proposed model were compared to the test dataset, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and the F1-score of the model were 0.93 and 0.80 (sensitivity = 0.88, specificity = 0.89, positive predictive value = 0.74, and negative predictive value = 0.96).
CONCLUSIONS
The deep learning-based model developed in this study is capable of detecting and screening unacceptable ECGs efficiently.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kumar A. ECG-simplified. [place unknown]: LifeHugger;2010.2. Kaplan NM. Systemic hypertension therapy. In : Braunwald E, editor. Braunwald's heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders;1997.3. Van Mieghem C, Sabbe M, Knockaert D. The clinical value of the ECG in noncardiac conditions. Chest. 2004; 125(4):1561–1576.
Article4. American Health Association. Part 8: Stabilization of the patient with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2005; 112:24_Suppl. IV.89–IV.110.5. Li H, Yuan D, Wang Y, Cui D, Cao L. Arrhythmia classification based on multi-domain feature extraction for an ECG recognition system. Sensors (Basel). 2016; 16(10):E1744.
Article6. Rodrigues J, Belo D, Gamboa H. Noise detection on ECG based on agglomerative clustering of morphological features. Comput Biol Med. 2017; 87:322–334.
Article7. Sivaraks H, Ratanamahatana CA. Robust and accurate anomaly detection in ECG artifacts using time series motif discovery. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015; 2015:453214.
Article8. Satija U, Ramkumar B, Manikandan MS. Automated ECG noise detection and classification system for unsupervised healthcare monitoring. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2018; 22(3):722–732.
Article9. Ercelebi E. Electrocardiogram signals de-noising using lifting-based discrete wavelet transform. Comput Biol Med. 2004; 34(6):479–493.
Article10. Ho CY, Ling BW, Wong TP, Chan AY, Tam PK. Fuzzy multiwavelet denoising on ECG signal. Electron Lett. 2003; 39(16):1163–1164.
Article11. Tikkanen PE. Nonlinear wavelet and wavelet packet denoising of electrocardiogram signal. Biol Cybern. 1999; 80(4):259–267.
Article12. Iravanian S, Tung L. A novel algorithm for cardiac biosignal filtering based on filtered residue method. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2002; 49(11):1310–1317.
Article13. Leski JM. Robust weighted averaging. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2002; 49(8):796–804.14. Almenar V, Albiol A. A new adaptive scheme for ECG enhancement. Signal Process. 1999; 75(3):253–263.
Article15. Barros AK, Mansour A, Ohnishi N. Removing artifacts from electrocardiographic signals using independent components analysis. Neurocomputing. 1998; 22(1-3):173–186.
Article16. Blanco-Velasco M, Weng B, Barner KE. ECG signal denoising and baseline wander correction based on the empirical mode decomposition. Comput Biol Med. 2008; 38(1):1–13.
Article17. Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MC, Shih HH, Zheng Q, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis. Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 1998; 454(1971):903–995.
Article18. Kabir MA, Shahnaz C. Denoising of ECG signals based on noise reduction algorithms in EMD and wavelet domains. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2012; 7(5):481–489.
Article19. Karagiannis A, Constantinou P. Noise-assisted data processing with empirical mode decomposition in biomedical signals. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2011; 15(1):11–18.
Article20. Xiong P, Wang H, Liu M, Zhou S, Hou Z, Liu X. ECG signal enhancement based on improved denoising autoencoder. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2016; 52:194–202.
Article21. Rahman MZ, Shaik RA, Reddy DR. Efficient and simplified adaptive noise cancelers for ECG sensor based remote health monitoring. IEEE Sens J. 2012; 12(3):566–573.
Article22. Kim YG, Shin D, Park MY, Lee S, Jeon MS, Yoon D, et al. ECG-ViEW II, a freely accessible electrocardiogram database. PLoS One. 2017; 12(4):e0176222.
Article23. Chung D, Choi J, Jang JH, Kim TY, Byun J, Park H, et al. Construction of an electrocardiogram database including 12 lead waveforms. Healthc Inform Res. 2018; 24(3):242–246.
Article24. Johnson AE, Pollard TJ, Shen L, Lehman LW, Feng M, Ghassemi M, et al. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci Data. 2016; 3:160035.
Article25. Yoon D, Lee S, Kim TY, Ko J, Chung WY, Park RW. System for collecting biosignal data from multiple patient monitoring systems. Healthc Inform Res. 2017; 23(4):333–337.
Article26. Reddy CK, Aggarwal CC. Healthcare data analytics. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press;2015.27. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org;2014. cited at 2019 Jul 10. Available from: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf.28. Huynh LN, Lee Y, Balan RK. Deepmon: mobile GPUbased deep learning framework for continuous vision applications. In : Proceedings of the 15th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services; 2007 Jun 19-23; Niagara Falls, NY. p. 82–95.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Obstructive sleep apnoea detection using convolutional neural network based deep learning framework
- Developing and Evaluating Deep Learning Algorithms for Object Detection: Key Points for Achieving Superior Model Performance
- Unsupervised speckle noise reduction technique for clinical ultrasound imaging
- Deep Learning in Dental Radiographic Imaging
- Development of an Optimized Deep Learning Model for Medical Imaging